Abstract
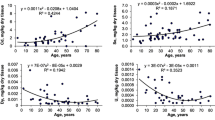
The contents of elements K, Ca, Fe, Cu, Zn, Se, and Rb in erythrocytes of 78 cases with different thyroid hormone status have been measured by proton-induced X-ray emission and neutron activation analysis. According to the status of thyroid hormones T3, T4, TSH, FT3, and FT4 detected by radioimmunoassay, the experiment subjects were divided into four groups (i.e., hyperthyroid, hypothyroid, critical [one of thyroid hormones was abnormal], and normal). Elements contents and hormones levels of four groups were analyzed by one-way analysis of variance and correlation using an SPSS/PC statistical package. The results showed that the Se contents of four groups were not significantly different (p<0.05). Zn content of hypothyroid group was significantly higher than those of hyperthyroid and critical groups. The Zn content of the normal group was higher than that of the hypothyroid group and lower than that of the hyperthyroid and critical groups. In the hyperthyroid group, there were significant correlations between elements contents and thyroid hormones levels (except TSH), but not between elements contents and levels of thyroid hormones. However, in the hypothyroid group, relatively strong correlations have been found between elements contents and thyroid hormones levels, especially between Zn and the T3/T4 ratio, and between Zn and TSH.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. Behne, A. Kyriakopoulos, H. Merinholg, and J. Kohrle, Identification of type I iodothyronine 5′-deiodinase as a selenoenzyme, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 173(3), 1143–1149 (1990).
M. J. Berry, L. Banu, and P. R. Larsen, Type I iodothyronine deiodinase is a selenocysteine-containing enzyme, Nature 349, 438–440 (1991).
J. R. Arthur, F. Nicol, and G. J. Becktt. Hepatic iodothyronine 5′-deiodinase. The role of selenium, Biochem. J. 272, 537–540 (1990).
J. P. Chanoine, M. Safran, A. P. Farwell, et al. Selenium deficiency and type II 5′-deiodinase regulation in the euthyroid and hypothyroid rat: evidence of a direct effect of thyroxin, Endocrinology 131 (1), 479–484 (1992).
D. Salvatore, T. Bartha, J. W. Harney, and P. R. Larsen, Molecular biological and biochemical characterization of the human type 2 selenodeiodinase. Endocrinology 137, 3308–3315 (1996)
M. Ramauge, S. Pallud, A. Esfandiari, J. M. Gavaret, A. M. Lennon, M. Pierre, et al., Evidence that type III iodothyronine deiodinase in rat astrocyte is a selenoprotein. Endocrinology 137, 3021–3025 (1996).
T. Miyamoto, A. Sakurai, and L. J. DeGroot, Effects of zinc and other divalent metals on deoxyribonucleic acid binding and hormone-binding activity of human alpha 1 thyroid hormone receptor expressed in Escherichia coli. Endocrinology 129, 3027–3033 (1991).
G. Simsek, G. Andican, Y. Karakoc, G. Yigit, H. Hatem, and G. Candan, Calcium, magnesium, and zinc status in experimental hypothyroidism. Biol. Trace Element Res. 60, 205–213 (1997).
N. Q. Liu, X. F. Zhang, L. N. Yan, S. L. Feng, M. Zhong, Y. J. Ji, et al., Variations of concentration of titanium and other elements in Wistar rats after titanium-ascorbate administration. Nucl. Techn. 15(4), 251–256 (1992).
K. Yoshida, Effects of thyroid hormone on erythrocyte carbonic anhydrase-I and zinc concentrations in vivo and in vitro: clinical usefulness of carbonic anhydrase-I and zinc concentrations in erythrocytes. Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 178, 345–356 (1996).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, N., Liu, P., Xu, Q. et al. Elements in erythrocytes of population with different thyroid hormone status. Biol Trace Elem Res 84, 37–43 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1385/BTER:84:1-3:037
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/BTER:84:1-3:037