Abstract
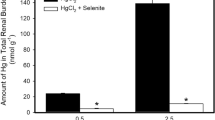
Selenium and methylmercuric chloride (MMC) interactions regarding cellular uptake and selenium protection on MMC toxicity have been studied. Human K-562 cells were pretreated or simultaneously treated with either selenite (5 or 50 µM) or selenomethionine (10 or 50 µM) together with (3.5 or 5 µM) MMC. Cells simultaneously treated with selenite or selenomethionine and 3.5 µM MMC showed a decreased mercury concentration with increased selenium dose especially seen in the selenite combinations. The simultaneous selenite and MMC 3.5 µM combinations showed growth curves with an increasing number of viable cells with increased selenite dose. All combinations with 5 µM MMC were toxic to the cells. Interactions between selenite or selenomethionine and MMC regarding cellular uptake of mercury and selenium were observed and indications of selenite protection against MMC toxicity in human K-562 cells were noticed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. E. Ganther, C. Goudie, M. L. Sunde, M.J. Kopecky, and P. Wagner, Selenium: relation to decreased toxicity of methylmercury added to diets containing tuna, Science 175(26), 1122–1124 (1972)
H. Iwata, H. Okamoto, and Y. Ohsawa, Effect of selenium on methylmercury poisoning, Res. Commun. Chem. Pathol. Pharmacol. 5(3), 673–680 (1973).
L. W. Chang, Protective effects of selenium against methylmercury neurotoxicity: a morphological and biochemical study, Exp. Pathol. 23(3), 143–156 (1983).
S. Potter and G. Matrone, Effect of selenite on the toxicity of dietary methyl mercury and mercuric chloride in the rat, J. Nutr. 104(5), 638–647 (1974).
J. L. Sell and F. G. Horani, Influence of selenium on toxicity and metabolism of methylmercury in chicks and quail, Nutr. Rep. Int. 14(4), 439–447 (1976).
S. Skerfving, Interaction between selenium and methylmercury, Environ. Health Perspect. 25, 57–65 (1978).
A. Naganuma and N. Imura, Bis(methylmercuric) selenide as a reaction product from methylmercury and selenite in rabbit blood, Res. Commun. Chem. Pathol. Pharmacol. 27(1), 163–173 (1980).
A. Naganuma, Y. Kojima, and N. Imura, Interaction of methylmercury and selenium in mouse: formation and decomposition of bis(methylmercuric) selenide, Res. Commun. Chem. Pathol. Pharmacol. 30(2), 301–316 (1980).
T. Masukawa, H. Kito, M. Hayashi, and H. Iwata, Formation and possible role of bis(methylmercuric) selenide in rats treated with methylmercury and selenite, Biochem. Pharmacol. 31(1), 75–78 (1982).
B. R. Stillings, H. Lagally, P. Bauersfeld, and J. Soares, Effect of cystine, selenium, and fish protein on the toxicity and metabolism of methylmercury in rats, Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol., 30,243–254 (1974).
H. E. Ganther, Modification of methylmercury toxicity and metabolism by selenium and vitamin E: possible mechanisms, Environ. Health Perspect. 25, 71–76 (1978).
L. W. Chang and R. Suber, Protective effect of selenium on methylmercury toxicity: a possible mechanism, Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 29(3), 285–289 (1982).
K. Sumino, R. Yamamoto, and S. Kitamura, A role of selenium against methylmercury toxicity, Nature 268(5615), 73–74 (1977).
E. Komsta-Szumska, K. R. Reuhl, and D. R. Miller, Effect of selenium on distribution, demethylation, and excretion of methylmercury by the guinea pig, J. Toxicol. Environ. Health 12(4–6), 775–785 (1983).
P. Frisk, A. Yaqob, K. Nilsson, J. Carlsson, and U. Lindh, Differences in the growth inhibition of cultured K-562 cells by selenium, mercury or cadmium in two tissue culture media (RPMI-1640, Ham’s F-10)., Biometals 13(2), 101–111 (2000).
U. Heintze, S. Edwardsson, T. Derand, and D. Birkhed, Methylation of mercury from dental amalgam and mercuric chloride by oral streptococci in vitro. Scand J Dent Res 91(2), 150–152 (1983).
J. T. Trevors, Mercury methylation by bacteria, J. Basic Microbiol. 26(8), 499–504 (1986).
L. Liang and R. J. Brooks, Mercury reactions in the human mouth with dental amalgams, Water, Air and Soil Pollution 80, 103–107 (1995).
C. B. Lozzio and B. B. Lozzio, Human chronic myelogenous leukemia cell-line with positive Philadelphia chromosome, Blood 45(3), 321–334 (1975).
L. C. Andersson, K. Nilsson, and C. G. Gahmberg, K562—a human erythroleukemic cell line, Int. J. Cancer 23(2), 143–147 (1979).
J. R. Tennant, Evaluation of the trypan blue technique for determination of cell viability, Transplantation 2(6), 685–694 (1964).
R. Houk, Elemental and isotopic analysis by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry, Acc. Chem. Res. 27, 333–339 (1994).
Y. Yamane, H. Fukino, Y. Aida, and M. Imagawa, Studies on the mechanism of protective effects of selenium against the toxicity of methylmercury, Chem. Pharm. Bull. (Tokyo) 25(11), 2831–2837 (1977).
P. Frisk, A. Yaqob, K. Nilsson, J. Carlsson and U. Lindh, Uptake and retention of selenite and selenomethionine in cultured K-562 cells, Biometals, 13(3), 204–215 (2000).
P. R. Sager, Selectivity of methyl mercury effects on cytoskeleton and mitotic progression in cultured cells, Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 94(3), 473–486 (1988).
R.M. Zucker, K.H. Elstein, R.E. Easterling, and E.J. Massaro. Flow cytometric analysis of the mechanism of methylmercury cytotoxicity, Am. J. Pathol. 137(5), 1187–1198 (1990).
A. Naganuma, K. Miura, T. Tanaka-Kagawa, J. Kitahara, Y. Seko, H. Toyoda, and N. Imura, Overexpression of manganese-superoxide dismutase prevents methylmercury toxicity in HeLa cells, Life Sci. 62(12), 157–161 (1998).
B. J. Shenker, T. L. Guo, I. O. Guo, and I. M. Shapiro, Induction of apoptosis in human T-cells by methyl mercury: temporal relationship between mitochondrial dysfunction and loss of reductive reserve, Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 157(1), 23–35 (1999).
L. Yan, J. A. Yee, L. M. Boylan, and J. E. Spallholz, Effect of selenium compounds and thiols on human mammary tumor cells, Biol. Trace Element Res. 30(2), 145–162 (1991).
M. S. Stewart, J. E. Spallholz, K. H. Neldner, and B. C. Pence, Selenium compounds have disparate abilities to impose oxidative stress and induce apoptosis, Free Radical Biol. Med. 26(1–2), 42–48 (1999).
J. Alexander, A. Hostmark, O. Forre, and M. Bryn, The influence of selenium on methyl mercury toxicity in rat hepatoma cells, human embryonic fibroblasts and human lymphocytes in culture, Acta Pharmacol. Toxicol. (Copenh.) 45(5), 379–386 (1979).
P. D. Whanger, Selenium in the treatment of heavy metal poisoning and chemical carcinogenesis, J. Trace Elements Electrolytes Health Dis. 6(4), 209–221 (1992).
J. Alexander and T. Norseth The effect of selenium on the biliary excretion and organ distribution of mercury in the rat after exposure to methyl mercuric chloride, Acta Pharmacol. Toxicol. 44(3), 168–176 (1979).
S. J. Kleinschuster, M. Yoneyama, and R. P. Sharma, A cell aggregation model for the protective effect of selenium and vitamin E on methylmercury toxicity, Toxicology 26(1), 1–9 (1983).
P. Frisk, A. Yaqob, K. Nilsson, J. Carlsson, and U. Lindh, Influence of selenium on mercuric chloride cellular uptake and toxicity indicating protection. Studies on cultured K-562 cells, Biol. Trace Elem. Res., to be published.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Frisk, P., Yaqob, A., Nilsson, K. et al. Selenite or selenomethionine interaction with methylmercury on uptake and toxicity showing a weak selenite protection. Biol Trace Elem Res 80, 251–268 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1385/BTER:80:3:251
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/BTER:80:3:251