Abstract
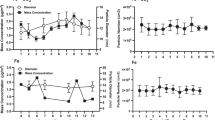
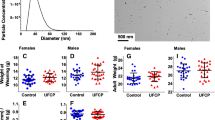
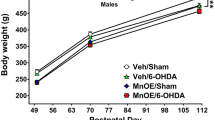
Neonatal rats were exposed to airborne manganese sulfate (MnSO4) (0, 0.05, 0.5, or 1.0 mg Mn/m3) during gestation (d 0–19) and postnatal days (PNDs) 1–18. On PND19, rats were killed, and we assessed biochemical end points indicative of oxidative stress in five brain regions: cerebellum, hippocampus, hypothalamus, olfactory bulb, and striatum. Glutamine synthetase (GS) and tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) protein levels, metallothionein (MT), TH and GS mRNA levels, and reduced and oxidized glutathione (GSH and GSSG, respectively) levels were determined for all five regions. Mn exposure (all three doses) significantly (p=0.0021) decreased GS protein levels in the cerebellum, and GS mRNA levels were significantly (p=0.0008) decreased in the striatum. Both the median and high dose of Mn significantly (p=0.0114) decreased MT mRNA in the striatum. Mn exposure had no effect on TH protein levels, but it significantly lowered TH mRNA levels in the olfactory bulb (p=0.0402) and in the striatum (p=0.0493). Mn eposure significantly lowered GSH levels at the median dose in the olfactory bulb (p=0.032) and at the median and high dose in the striatum (p=0.0346). Significantly elevated (p=0.0247) GSSG, which can be indicative of oxidative stress, was observed in the cerebellum of pups exposed to the high dose of Mn. These data reveal that alterations of oxidative stress biomarkers resulting from in utero and neonatal exposures of airborne Mn exist. Coupled with our previous study in which similarly exposed rats were allowed to recover from Mn exposure for 3 wk, it appears that many of these changes are reversible. It is important to note that the doses of Mn utilized represent levels that are a hundred- to a thousand-fold higher than the inhalation reference concentration set by the United States Environmental Protection Agency.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. W. Dobson, S. Weber, D. C. Dorman, L. K. Lash, K. M. Erikson, and M. Aschner, Inhaled manganes sulfate and measures of oxidative stress in rat brain, Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 93, 113–126 (2003).
S. Weber, D. C. Dorman, L. H. Lash, K. Erikson, K. E. Vrana, and M. Aschner, Effects of manganese (Mn) on the developing rat brain: oxidative-stress related endpoints, Neurotoxicology 23, 169–175 (2002).
K. M. Erikson, D. C. Dorman, L. H. Lash, A. W. Dobson, and M. Aschner, Airborne manganese exposure differentially affects endpoints of oxidative stress in an age and sex-dependent manner, Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 100, 49–62 (2004).
K. M. Erikson, D. C. Dorman, L. H. Lash, and M. Aschner. Persistent alterations in biomarkers of, oxidative stress resulting from combined in utero and neonatal manganese inhalation, Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 104, 151–164 (2005).
L. S. Hurley and C. L. Keen, Manganese in Trace Elements in Human Health and Animal Nutrition, E. Underwood and W. Mertz, eds., Academic, New York, pp. 185–223 (1987).
M. Aschner, K. M. Erikson, and D. C. Dorman, Manganese dosimetry: species differences and implications for neurotoxicity, Criti. Rev. Toxicol. 35, 1–32 (2005).
ATSDR (Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry). Toxiocological Profile for Manganese, US Department of Health And Human Services Public Health Service. available at http://www.atsdr.cdc.gov/toxprofiles/tp151.html (accessed September 2000).
D. Mergler, G. Huel, R. Bowler, et al., Nervous system dysfunction among workers with long-term exposure to manganese, Environ. Res. 64, 151–180 (1994).
P. K. Pal, A. Samii, and D. B. Calne, Manganese neurotoxicity: a review of clinical features, imaging and pathology, Neurotoxicology 20, 227–238 (1999).
E. D. Pellizzari, C. A. Clayton, C. E. Rodes, et al. Particulate matter and manganese exposures in Indianapolis, Indiana, J. Exp. Anal. Environ. Epidemiol. 11, 423–440. (2001).
M. Aschner, Manganese neurotoxicity and oxidative damage, in Metals and Oxidative Damage in Neurological Disorders, J. R. Connor, ed., Plenum, New York, pp. 77–93 (1997).
W. N. Sloot, J. Korf, J. F. Koster, L. E. A. DeWit, and J. B. P. Gramsbergen, Manganese-induced hydroxyl radical formation in rat striatum is not attenuated by dopamine depletion or iron chelation in vivo, Exp. Neurol. 138, 236–245 (1996).
P. Galvani, P. Fumagalli, and A. Santagostino, Vulnerability of mitochondrial complex I in PC12 cells exposed to manganese, Eur. J. Pharmacol. 293, 377–383 (1995).
E. P. Brouillet, L. Shinobu, U. McGarvey, F. Hochberg, and M. F. Beal. Manganese injection into the rat striatum produces excitotoxic lesionsby impairing energy metabolism, Exp. Neurol. 120, 89–94 (1993).
C. E. Gavin, K. K. Gunter, and T. E. Gunter, Manganese and calcium transport in mitochondria: implications for manganese toxicity, Neurotoxicology 20, 445–453 (1999).
F. S. Archibald and C. Tyree, Manganese poisoning and the attack of trivalent manganese upon catecholamines, Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 256, 638–650 (1987).
S. F. Ali, H. M. Duhart, G. D. Newport, G. W. Lipe, and W. Slikke, Manganese-induced reactive oxygen species: comparison between Mn+2 and Mn+3, Neurodegeneration 4, 329–334 (1995).
J. Y. Chen, G. C. Tsao, Q. Zhao, and W. Zheng, Differential cytotoxicity of Mn(II) and Mn(III): special reference to mitochondrial [Fe−S] containing enzymes, Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 175, 160–168 (2001).
K. K. Gunter, L. M. Miller, M. Aschner, et al., XANES spectroscopy: a promising tool for toxicology: a tutorial, Neurotoxicology 23, 127–146 (2002).
D. HaMai, A. Campbell, and S. C. Bondy, Modulation of oxidative events by multivalent manganese complexes in brain tissue, Free Radical Biol. Med. 31, 763–768 (2001).
A. Meister and M. E. Anderson, Gltathione, Annu. Rev. Biochem. 52, 711–760 (1983).
M. E. Gegg, B. Beltran, S. Salas-Pino, et al., Differential effect of nitric oxide on GSH metabolism and mitochondrial function in astrocytes and neurons: implications for neuroprotection/neurodegeneration? J. Neurochem. 86, 228–237 (2003).
J. Sian, D. T. Dexter, A. J. Lees, et al., Alterations in glutathione levels in Parkinson's disease and other neurodegenerative disorders affecting basal ganglia, Ann. Neurol. 36, 356–361 (1994).
M. S. Desole, G. Esposito, R. Mighelli, et al., Cellular defence mechanisms in the striatum of young and aged rats subchronically exposed to manganese, Neuropharmacology 34, 289–295 (1995).
G. K. Andrews, Regulation of metallothioneins gene expression, Prog. Food Nutr. Sci. 14, 193–258 (1990).
M. T. Dunn, T. L. Blalock, and R. J. Cousins, Metallothionein, Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 185, 107–119 (1987).
D. H. Hamer, Metallothioneins, Annu. Rev. Biochem. 55, 913–951 (1986).
Y. Itano, S. Noji, E. Koyama, et al., Bacterial edotoxin-induced expression of metallothionein genes in rat brain, as revealed by in sit hybridization, Neurosci. Lett. 124, 13–16 (1991).
H. Shiraga, R. F. Pfeiffer, and M. Ebadi, The effects of 6-hydroxydopamine and oxidative stress on the level of brain metallothionein, Neurochem. Int. 23, 561–566 (1993).
J. W. Bauman, J. Liu, Y. P. Liu, and C. D. Klaassen, Increase in metallothionein produced by chemicals that induce oxidative stess, Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 110, 347–354 (1991).
A. Martinez-Hernandez, K. P. Bell, and M. D. Norenberg, Glutamine synthetase: glial localization in the brain, Science 195, 1356–1358 (1977).
C. J. Van den Berg and D. A. Garfinkel, A simulation study of brain compartments metabolism of glutamate and related substances in mouse brain, Biochem. J. 123, 211–218 (1971).
N. Westergaard, U. Sonneald, and A. Schousboe, Metabolic trafficking between neurons and astrocytes: the glutamate glutamine cycle revisited, Dev. Neurosci. 17, 203–211 (1995).
O. P. Ottersen, N. Zhang, and F. Walberg, Metabolic compartmentation of glutamate and glutamine: morphological evidence obtained by quantitative immunocytochemistry in rat cerebellum, Neuroscience 46, 519–534 (1992).
E. R. Stadtman, Protein oxidation and aging, Science 257, 1220–1224 (1992).
D. C. Dorman, A. M. McElveen, M. W. Marshall, et al., Tissue manganese concentrations in lactating rats and their offspring following combined in utero and lactation exposure to inhaled manganese sulfate, Toxicol. Sci. 84, 12–21 (2005).
V. Barbu and F. Dautry, Northern blot normalization with a 28S rRNA oligonucleotide probe, Nucleic Acids Res. 17, 7115 (1989).
M. W. Fariss and D. J. Reed, High-performance liquid chromatography of thiols and disulfides: dinitrophenol derivatives, Methods Enzymol. 143, 101–109 (1987).
L. H. Lash and J. J. Tokarz, Oxidative stress in isolated rat renal proximal and distal tubular cells, Am. J. Physiol., 259, F338-F347 (1990).
L. H. Lash and E. B. Woods, Cytotoxicity of alkylating agents in isolated rat kidney proxima and distal tubular cells, Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 286, 46–56 (1991).
US EPA, Integrated Risk Information System (IRIS), Health ris assessment for manganese, Envirionmental Criteria and Assessment Office, Cincinnati, OH (1993).
C. L. Keen, J. G. Bell, and B. Lonnerdal, The, effect of age on manganese uptake and retention from milk and infant formulas in rats, J. Nutr. 116, 395–402, 1986.
U. Sonnewald, N. Westergaard, and A. Schousboe, Glutamate transport and metabolism in astrocytes, Glia 21, 56–63 (1997).
S. Hussain, W. Slikker, Jr., and S. F. Ali, Role of metallothionein and other antoxidants in scavenging superoxide radicals and their possible role in neuroprotection, Neurochem. Int. 29, 145–152 (1996).
M. Kondoh, Y. Inoue, S. Atagi, N. Futakawa, M. Higashimoto, and M. Sato. Specific induction of metallothionein synthesis by mitochondrial oxidative stress, Life Sci. 69, 2137–2146 (2001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Erikson, K.M., Dorman, D.C., Fitsanakis, V. et al. Alterations of oxidative stress biomarkers due to in utero and neonatal exposures of airborne manganese. Biol Trace Elem Res 111, 199–215 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1385/BTER:111:1:199
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/BTER:111:1:199