Abstract
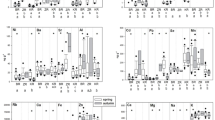
The binding of mercury (Hg) to metallothioneins (MTs) and the relation between Hg and selenium in supernatants of hepatopancreas and gill tissues of the common mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis (Lamarck, 1819) was investigated. The mussels were exposed to different Hg concentrations in laboratory conditions: 2.5 μgHg/L, 4 d exposure (short term) and 60 μgHg/L, 33 d exposure (long term). In addition, the results were compared to those found for mussels from nature (polluted and unpolluted region). In control and short-term-exposed mussles, the level of Hg extraction (cytosol) from hepatopancreas and gill cells was very low with respect to the total Hg concentrations in the corresponding tissues, around 10% in control and around 20% after exposure. As expected, Hg exposure was followed by Se increase. For Se, the levels of extraction were higher, around 20% in control and up to 50% (heaptopacrease) of 70% (gills) after exposure. In order to study the distribution of Hg and Se in the cells of these organs, the total Hg and Secconcentrations were analyzed in the subcellular fractions obtained after differential centrifugation. Although after exposure the concentrations of both element increased in all subcellular fractions, their percentages in particular fractions were lower or higher. In this study, the convincing binding of Hg to metallothionein-like proteins was perceived after long-term laboratory exposure (gills, heapatopancreas) and in wild mussels collected near industrial port (hepatopancreas). In latter case, we also detected the traces of Se bound to the MT fractions after size-exclusion chromatography.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
P. S. Rainbow, The significance of trace emtal concentrations in marine invertebrates, in Ecotoxicology of Metals in Invertebrates, R. Dallinger and P. S. Rainbow, eds., Lewis, Boca Raton, FL, pp. 3–23 (1993).
D. J. H. Phillips, The use of biologicla indicator organisms to monitor trace metal pollution in marine and estuarine environments: a review, Environ. Pollut. 13, 281–317 (1997).
F. Geret, F. Rainglet, and R. P. Cosson, Comparison between isolation protocols commonly used for the purification of mollusc metallothioneins, Marine Environ. Res. 46, 545–550 (1998).
D. Biršite, K. N. White, and D. A. Lovejey, Cloning and characterization of metallothionein cDNAs in the mussel Mytilus edulis L. digestive gland, Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C 122, 287–296 (1999).
N. Bodin, T. Burgeot, J. Y. Stanisiere, et al., Seasonal variations of a battery of biomarkers and physiological indices fort he mussels Mytilus galloprovincialis transplated into the northwest Mediterranean Sea, Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C 138, 411–427 (2004).
F. Geret, A. Jouan, V. Turpin, M. J. Bebianno, and R. P. Cosson, Influence of metal exposure on metallothionein synthesis and lipid peroxidation in two bivalve molluscs: the oyster (Crassostrea gigas) and the mussel (Mytilus edulis), Aquat. Living Resource 15, 61–66 (2002).
A. Viarengo, Heavy metals in marine invertebrates: mechanisms of regulation and toxicity at the cellular level, Aquat. Sci. 1, 295–317 (1989).
M. J. Bebianno and W. J. Langston, Cadmium and metallothionein turnover in different tissues of the gastropod Littorina litorrea. Talanta 46, 301–313 (1998).
J. H. R. Kagi, Overview of metallothionein, Methods Enzymol. 205, 613–626 (1991).
J. Pavičić, M. Škreblin, I. Kregar, M. Tušek-Žnidarič, and P. Stegnar, Embrio-larval tolerance of Mytilus galloprovincialis, exposed to the elevated sea water metal concentrations. I. Toxic effects of Cd, Zn and Hg in relation to the metallothionein level, Comp. Biochem. Physiol 107C(2) 249–257 (1994).
M. A. Serafim, R. M. Company, M. J. Bebianno, and W. J. Langston, Effect of temperature and size on metallothionein synthesis in the gill of Mytilus galloprovincialis exposed to cadmium, Marine Environ. Res. 54, 361–365 (2002).
G. Roesijadi, Metallothioneins in metal regulation and toxicity in aquatic animals. Aquat. Toxicol. 22, 81–114 (1992).
N. Romero-Isart and M. Vasak, Advances in the structure and chemistry of metallothioneins. Focused review, J. Inorg. Biochem. 88, 388–396 (2002).
F. Haq, M. Mahony and J. Koropatnick Signaling events for metallothionein induction, Rev. Mutal. Res. 533, 211–226 (2003).
G. Blackmore and W. Wang, The transfer of cadmium, mercury, methylmercury, and zinc in an intertidal rocky shore food chain, J. Exp. Marine Biol. Ecol. 307, 91–110 (2004).
R. Lobinski and J. Szpunar, Biochemical speciation analysis by hyphenated techniques, Anal. Chim. Acta 400, 321–332 (1999).
M. Soto, M. P. Cajaraville, and I. Marigomez, Tissue and cell distribution of copper, zinc and cadmium in the mussel, Mytilus galloprovincialis, determined by autometallography, Tissue Cell 28, 557–568 (1996).
A. Viarengo, M. Pertica, L. Canesi, A. Mazzucotelli, M. Orunesu, and J. M. Bouquegneau, Purification and biochemical characterisation of a lysosomal copper-rich thionein-like protein involved in metal detoxification in the digestive gland of mussels, Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C: Comp. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 93, 389–395 (1989).
W. G. Wallace, G. R. Lopez, and J. S. Levinton, Cadmium resistance in an oligochaete and its effect on cadmium trophic transfer to an omnivorous shrimp., Marine Ecol. Prog. 172, 225–237 (1998).
M. M. Storelli and G. O. Marcotrigiano, Subcellular distribution of heavy metals in liver and kidneys of Stenella coeruleoalba and Tursiops truncates from the Mediterranean Sea, Marine Pollut. Bull. 44, 71–81 (2002).
T. Endo, K. Haraguchi, and M. Sakata, Mercury and selenium concentrations in the internal organs of toothed whales and dolphins marketed for human consumptions in Japan, Sci. Total Environ. 300, 15–22 (2002).
L. Bucio, C. Garcia, V. Souza, et al., Uptake, cellular distribution and DNA damage produced by mercuric chloride in a human fetal hepatic cell line. Mutat. Res. 423, 65–72 (1999).
L. Kosta, A. R. Byrne, and V. Zelenko, Correlation between selenium and mercury in man following exposure to inorganic mercury, Nature 254, 238 (1975).
I. Falnoga, M. Tušek-Žnidarič, M. Horvat, and P. Stegnar, Mercury, selenium and cadmium in human autopsy samples from Idrija residents and mercury mine workers, Environ. Res. 84, 211–218 (2000).
M. I. A. Cuvin-Alaral and R. W. Furness, Mercury and selenium interaction: a review. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Safety 21, 348–364 (1991).
C. N. Ferrarello, M. Rosario F. de la Campa, J. F. Carrasco, and A. Sanz-Medel, Speciation of metallothionein-like proteins of the mussel Mytilus edulis by orthogonal separation mechanisms with inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry detection: effect of selenium administration, Spectrochim. Acta B 57, 439–449 (2002).
V. Turk, United Nations Environmental Program, Mediterranean Action Plan-Phase III, National Monitoring Program of Slovenia, Report 2002.
C. K. Julshman and K. J. Andersen, Subcellular distribution of major and minor elements in unexposed molluscs in western norway. II. The distribution and binding of cadmium, zinc, copper, magnesium, managanese and iron in the kidney and digestive system of the common mussel Mytilus edulis, Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 75A, 1–13, (1983).
R. A. Byrne and L. Kosta, Sintultaneoous neutron activation determination of selenium and mercury in biological samples by volatilisation, Talanta 21, 1083–1090 (1974).
V. Stibilj, D. Mazej, and I. Falnoga, A study of low level selenium determination by hydride generation atomic fluorescence spectrometry in water soluble protein and peptide fractions, Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 377, 1175–1183 (2003).
A. Viarengo, E. Ponzano, F. Dondero, and R. Fabbri, A simple spectrophotometric method for metallothionein evaluation in marine organisms: an applicatoion to mediterranean and antarctic molluscs, Marine Environ. Res. 44, 69–84 (1997).
S. J. Duquesne and J. C. Coll, Metal accumulation in the clam Tridacna crocea under natural and experimental conditions. Aquat. Toxicol. 32, 239–253 (1995).
L. Soazig and L. Marc, Potential use of the levels of the mRNA of a specific metalloth-ionein isoform (MT-20) in mussel (Mytilus edulis) as a biomarker of cadmium contamination, Marine Pollut. Bull. 46, 1450–1455 (2003).
A. Giguere, Y. Couillard, P. G. C. Campbell, et al., Steady-state distribution of metals along metallothionein and other cytosolic ligands and links to cytotoxicity in bivalves living along a polymetalic gradient. Aquat. Toxicol. 64, 185–200 (2003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Znidaric, M.T., Falnoga, I., Skreblin, M. et al. Induction of metallothionein-like proteins by mercury and distribution of mercury and selenium in the cells of hepatopancreas and gill tissues in mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis . Biol Trace Elem Res 111, 121–135 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1385/BTER:111:1:121
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/BTER:111:1:121