Abstract
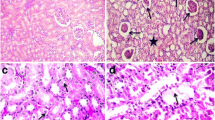
An experiment was carried out on Sprague-Dawley rats (adult males) that for 50 days were administered, in the drinking water, NaF and NaF with caffeine (doses, respectively: 4.9 mg of NaF/kg body mass/24 h and 3 mg of caffeine/kg body mass/24 h). Disturbances were noted in the functioning of kidneys, which were, particularly noticeable after the administration of NaF with caffeine. Changes in the functioning of kidneys were also confirmed by such parameters as the level of creatinine, urea, protein, and calcium. Modifications of the enzymatic antioxidative system (superoxide dismutase, catalase, and glutathione peroxidase) and lipid peroxidation (malondialdehyde) were also observed. Changes in the contents of the above parameters as well as pathomorphological examinations suggest increased diuresis, resulting in dehydration of the rats examined.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Gumińska, Fluorine in natural environment, Aura 4, 6–8 (1984).
M. Gumińska, The fluorine compounds in environment and their influence upon health, in Chemical Toxic Substances in Environment and Their Influence upon Human Health, Editorial PAN, Warsaw, pp. 59–81 (1990).
X. Chen and G. M. Whitford, Lack of significant effect of coffee and caffeine on fluoride metabolism in rats, J. Dent. Res. 73, 1173–1179 (1994).
D. Chlubek, J. Zawierta, A. Kazimierczyk, et al., Effect of different fluoride ion concentrations on malondialdehyde (MDA) formation in the mitochondrial fraction of human placental cells, Bromat. Chem. Toksykol. 2, 119–122 (1999).
S. Cuzzocrea, D. P. Riley, A. P. Caputi, et al., Antioxidant therapy: a new pharmacological approach in shock, inflammation, and ischemia/reperfusion injury, Pharmacol. Rev. 53, 135–159 (2001).
W. Droge, Free radicals in the physiological control of cell function, Physiol. Rev. 82, 47–95 (2002).
B. Halliwell and J. M. C. Gutteridge, Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine, Clarendon, Oxford (2001).
C. Bognan, M. Rollinghoff, and A. Diefenbach, Reactive oxygen and reactive nitrogen intermediates in innate and specific immunity, Curr. Opin. Immunol. 12, 64–76 (2000).
M. B. Hampton, A. J. Kettle, and C. C. Winterbourn, Inside the neutrophil phagosome: oxidants, myeloperoxidase, and bacterial killing, Blood 92, 3007–3017 (1998).
F. Gurkan, Y. Atamer, A. Ece, et al., Relationship among serum selenium levels, lipid peroxidation, and acute bronchiolitis in infancy, Biol. Trace Element Res. 100, 97–104 (2004).
V. J. Thannickal and B. L. Fanburg, Reactive oxygen species in cell signaling, Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 279, 1005–1028 (2000).
D. Zwolińska, Lipid peroxidation and antioxidant enzymes in patients with chronic renal failure (CRF), Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. 7, 87–92 (1998).
Y. Oyanagui Reevaluation of assay methods and establishment of kit for superoxide dismutase activity, Anal. Biochem. 142, 290–296 (1984).
H. Aebi, Catalase in vitro, Methods Enzymol. 105, 121–126 (1984).
D. E. Paglia and W. N. Valentine, Studies on the qualitative characterization of erythrocyte glutathione peroxidase, J. Lab. Clin. Med. 70, 158–169 (1967).
H. Okhawa, N. Ohishi, and K. Yagi, Assay for lipid peroxides in animal tissues by thiobarbituric acid reaction, Anal. Biochem. 95, 351–358 (1979).
J. Jankauskas, Effect of fluoride on kidney (a review), Fluoride 7, 93–105 (1974).
Editorial: Nonskeletal fluorosis Fluoride 11, 111–114 (1978).
P. A. Monsour and B. J. Kruger, Effect of fluoride on soft tissues in vertebrates (a review), Fluoride 18, 53–61 (1985).
T. Date, H. Nishiura, K. Usuda, et al., Dose response relationship between intravenous administration of sodium fluoride and acute renal damage in rats, Fluoride 31, 9 (1998) (abstract).
A. Sashi, J. P. Aihgh, and S. P. Thapar, Toxic effect of fluoride on rabbit kidney, Fluoride 35, 38–50 (2002).
J. A. Indulski, Sanitary Criteria of Environmental Fluorine and Fluorides, PZWL, Vol. 36 (1989).
E. Grucka-Mamczar, E. Birkner, R. Polaniak, et al., Disturbances of kidney function in young rats after chronic exposure to NaF contained in drinking water, Ann. Acad. Med. Siles 54–55, 9–14 (2003).
J. Kwiatkowski, Superoxide dismutase—structure, function, phylogenesis, Post. Biochem. 34, 311–333 (1988).
I. Mader-Wolyńska and D. Zwolińska, Peroxidation of lipids and activity of antioxidant enzymes in children with nephritic syndrome, Pol. Merk. Lek. 58, 233–236 (2001).
B. A. Zachara, D. Koterska, J. Manitius, et al., Selenium supplementation on plasma glutathione peroxidase activity in patients with end-stage chronic renal failure, Biol. Trace Element Res. 97, 15–30 (2004).
M. G. Soni, M. S. Kachole, and S. S. Pawar, Alterations in drug metabolising enzymes and lipid peroxidation an different rat tissues by fluoride, Toxicol. Lett. 21, 167–172 (1984).
D. S. Ikumari and P. R. Rao, Red cell membrane alterations in human chronic fluoride toxicity, Biochem. Int. 23, 639–648 (1991).
I. I. Silenko, O. I. Tsebrzhinski, and V. P. Mishchenko, The mechanism of the action of fluoride on periodontal tissues, Fiziol. Zh. 38, 85–90 (1992).
J. R. Diamond, J. V. Bonventre, and M. J. Karnovsky, A role for oxygen free radicals in aminonucleoside nephrosis, Kidney Int. 29, 478–483 (1986).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Birkner, E., Grucka-Mamczar, E., Żwirska-Korczala, K. et al. Influence of sodium fluoride and caffeine on the kidney function and free-radical processes in that organ in adult rats. Biol Trace Elem Res 109, 35–47 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1385/BTER:109:1:035
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/BTER:109:1:035