Abstract
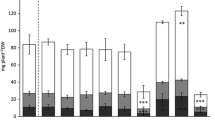
We investigated the uptake of inorganic elements (Be, Na, Mg, K, Ca, Sc, Mn, Co, Zn, Se, Rb, Sr, Y, Zr, Ce, Pm, Gd, and Hf) and the effect of Ca on their uptake in carrots (Daucus carota cv. U.S. harumakigosun) by the radioactive multitracer technique. The experimental results suggested that Na, Mg, K, and Rb competed for the functional groups outside the cells in roots with Ca but not for the transporter-binding sites on the plasma membrrane of the root cortex cells. In contrast, Y, Ce, Pm, and Gd competed with Ca for the transporters on the plasma membrane. The selectivity, which was defined as the value obtained by dividing the concentration ratio of an elemental pair, K/Na, Rb/Na, Be/Sr, and Mg/Sr, in the presence of 0.2 and 2 ppm Ca by that of the corresponding elemental pair in the absence of Ca in the solution was estimated. The selectivity of K and Rb in roots was increased in the presence of Ca. The selectivity of Be in roots was not affected, whereas the selectivity of Mg was increased by Ca. These observations suggest that the presence of Ca in the uptake solution enhances the selectivity in the uptake of metabolically important elements against unwanted elements.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
K. Koyama, M. Shirakawa, J. Takada, Y. Katayama, and T. Mastubara, Trace elements in land plants: concentration range and accumulators of rare earths, barium, radium, manganese, iron, cobalt, and heavy halogens, J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 112, 489–506, (1987).
T. Ozaki, S. Enomoto, Y. Minai, S. Ambe, and Y. Makide, A survey of trace elements in pteridophytes, Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 74, 259–273 (2000).
S. K. Hefler, and B. A. Averill, The ‘manganse (III)-containing’ purple acid phosphatase from sweet potates in an iron enzyme, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 146, 1173–1177 (1987).
B. L. Vallee, and D. S. Auld, Zinc coordination, function, and structure of zinc enzymes and other proteins, Biochemistry, 29, 5647–5659 (1990).
M. C. Edwards, G. N. Smith, and D. J. F. Bowling, Guard cells extrude protons prior to stomatal opening—a study using fluorescence microscopy and pH microelectrodes, J. Exp. Bot. 39, 1541–1547 (1988).
W. Busseler, Die Entwicklung von Calcium-Mangelsymptomen, Z. Pflanzener-naehr. Dueng. Bodenkd. 100, 53–58 (1963).
C. R. Caldwell, and A. Haug, Temperature dependence of the barley root plasma membrane-bound Ca2+ and Mg2+-dependent ATPase, Physiol. Plant 53, 117–124 (1981).
R. L. Legge, E. Thompson, J. E. Baker, and M. Lieberman, The effect of calcium on the fluidity and phase properties of microsomal membranes isolated from postclimacteric Golden Delicious Apples, Plant Cell Physiol. 23, 161–169 (1982).
H. Matsumoto, Repression of proton extrusion from intact cucumber roots and the proton transport rate of microsomal membrane vesicles of the roots due to Ca2+ starvation, Plant Cell Physiol. 29, 79–84 (1988).
S. Muhammed, M. Akbar, and H. U. Neue, Effect of Na/Ca and Na/K ratios in saline culture solution on the growth and mineral nutrition of rice (Oryza sativa L.), Plant Soil 104, 57–62 (1987).
C. Schimansky, Der Einfluss einiger Versuchsparameter auf das Fluxverhalten von 28Mg bei Gerstenkeimpflanzen in Hydrokulturversuchen, Landwirtsch. Forsch. 34, 154–165 (1981).
V. C. Baligar, J. H. Elgin, Jr., and C. D. Foy, Variability in alfalfa for growth and mineral uptake and efficiency ratios under aluminum stress, Agron. J. 81, 223–229 (1989).
H. Stienen, and J. Bauch, Element content in tissues of spruce seedlings from hydroponic cultures simulating acidification and deacidification, Plant Soil 106, 231–238 (1988).
C. A. Peterson, Exodermal Casparian bands: their significance for ion uptake by roots, Physiol. Plant 72, 204–208 (1988).
D. E. Enston, and C. A. Peterson, The apoplastic permeability of root apices, Can. J. Bot. 70, 1502–1512 (1992).
S. Ambe, S. Y. Chen, Y. Ohkubo, et al., Preparation of a radioactive multitracer soltuionf rom gold foil irradiated by 135 MeV/nucleon 14N ions, Chem. Lett. 1991, 149 (1991).
S. Ambe, T. Shinonaga, T. Ozaki, S. Enomoto, H. Yasuda, and S. Uchida, Ion competition effects on the selective absorption of radionuclides by komatsuna (Brassica rapa var. perviridis), Environ. Exp. Bot. 41, 185–194 (1999).
S. Gouthu, R. G. Weginwar, T. Arie, et al., Subcellular distribution and translocation of radionuclides in plants, Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 18, 2023–2027 (1999).
T. Ozaki, S. Enomoto, Y. Minai, S. Ambe, F. Ambe, and Y. Makide, Beneficial effect of rare earth elements on the growth of Dryopteris Erythrosora J. Plant Physiol. 156, 330–334 (2000).
H. F. Wang, N. Takematsu, and S. Ambe, Effects of soil acidity on the uptake of trace elements in soybean and tomato plants, Appl. Radiat. Isot. 52, 803–811 (2000).
S. Ambe, S. Sekido, T. Ozaki, and I. Yamaguchi, Uptake of trace elements by rice plants inoculated with Pyricularia oryzae, Appl. Radiat. Isot. 56, 473–476 (2002).
T. Ozaki, S. Ambe, S. Enomoto, Y. Minai, S. Yoshida, and Y. Makide, Multitracer study on the uptake mechanism of yttrium and rare-earth-elements by autumn fern, Radiochim. Acta 90, 303–307 (2002).
T. Ozaki, S. Ambe, T. Abe, and A. J. Francis, Effect of humic acid on the bioavailability of radionuclides to rice plants, Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 375, 505–510 (2003).
T. Ozaki, S. Ambe, T. Abe, and A. J. Francis, Uptake of short-half-life radionuclides, 28Mg, 43K and 47Ca, in carrot studied by the multitracer technique: feasibility of utilization of the radionuclides in environmental research, J. Radional. Nucl. Chem. 258, 89–92 (2003).
T. Ozaki, S. Enomoto, Y. Minai, S. Ambe, F. Ambe, and Y. Makide, Influence of aluminum on the uptake of various cations from a solution into carrots, J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 235, 285–289 (1998).
T. Ozaki, S. Enomoto, Y. Minai, S. Ambe, F. Ambe, and Y. Makide, Effect of zinc on the uptake of various elements into carrot, J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 242, 703–707 (1999).
T. Ozaki, S. Ambe, Y. Minai, et al., Effects of ionic valency of interacting metal elements in ion uptake by carrot (Daucus carota cv. U.S. harumakigosun), Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 84, 197–211 (2001).
S. Ambe, S. Y. Chen, Y. Ohkubo, et al., “Multitracer” a new tracer technique—its principle, features, and application, J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 195, 297–303 (1995).
S. Ambe, T. Ozaki, R. G. Weginwar, S. Enomoto, and F. Ambe, Simultaneous production of 28Mg and 47Ca by high-energy heavy ion irradiation for applications in biology, Radiochim. Acta 89, 63–66 (2001).
L. Erdei, and S. Trivedi, Caesium/potassium selectivity in wheat and lettuce of different K+ status, J. Plant. Physiol. 138, 696–699 (1991).
F. G. Viets, Jr., Calcium and other polyvalent cations as accelerators of ion accumulation by excised barley roots, Plant Physiol. 19, 466–480 (1944).
H. Marschner, General introduction to the mineral nutrition of plants, in Encyclopedia of Plant Physiology. New Series, A. Läuchli and R. L. Bieleski, eds., Springer-Verlag, Berlin, Vol. 15A, pp. 5–60 (1983).
D. P. Heenan, and L. C. Campbell, Influence of temperature on the expression of manganese toxicity by two soybean varieties, Plant Soil 47, 219–227 (1981).
C. H. Evans, Interesting and useful biochemical properties of lanthanides, Trends Biol. Sci. 8, 445–449 (1983).
C. T. Bernal, F. T. Bingham, and J. Oertli, Salt tolerance of Mexican wheat. II. Relation to variable sodium chloride and length of growing season, Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc. 38, 777–780 (1974).
N. S. Pasricha, V. K. Nayyar, N. S. Randhawa, and M. K. Sinha, Influence of sulphur fertilization on suppression of molybdenum uptake by berseem (Trifolium alexandriunum) and oats (Avena sativa) grown on a molybdenum-toxic soil, Plant Soil 46, 245–250 (1977).
C. Chatterjee, N. Nautiyal, and S. C. Agarwala, Excess sulphur partially alleviates copper deficiency effects in mustard, Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 38, 57–64 (1992).
W. D. Jeschke, and W. Jambor, Determination of unidirectional sodium fluxes in roots of intact sunflower seedlings, J. Exp. Bot. 32, 1257–1272 (1981).
H. Mennen, B. Jacoby, and H. Marschner, Is sodium proton antiport ubiquitous in plant cells?, J. Plant Physiol. 137, 180–183 (1990).
J. J. Lehr, Sodium as a plant nutrient, J. Sci. Food Agric. 4, 460–468 (1953).
C. Hecht-Buchholz, R. Pflüger, and H. Marschner, Einfluss von Natrium-chlorid auf Mitochondrienzahl und Atmung von Maiswurzelspitzen, Z. Planzenphysiol. 65, 410–417 (1971).
H. Kuppelwieser, and U. Feller, Transport of rubidium and strontium to the ear in mature, excised shoots of wheat: effects of temperature and stem length on rubidium removal from the xylem, Plant Soil 132, 281–288 (1991).
J. A. Laszlo, Changes in soybean fruit Ca2+(Sr2+) and K+ (Rb+) transport ability during development, Plant Physiol. 104, 937–944 (1994).
P. Cammarano, A. Felsani, M. Gentile, C. Gualerzi, C. Romeo, and G. Wolf, Formation of active hybrid 80-S particles from subunits of pea seedlings and mammalian liver ribosomes, Biochem. Biophys. Acta 281, 625–642 (1972).
D. T. Clarkson, and J. B. Hanson, The mineral nutrition of higher plants, Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. 31, 239–298 (1980).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ozaki, T., Ambe, S., Abe, T. et al. Competitive inhibition and selectivity enhancement by Ca in the uptake of inorganic elements (Be, Na, Mg, K, Ca, Sc, Mn, Co, Zn, Se, Rb, Sr, Y, Zr, Ce, Pm, Gd, Hf) by carrot (Daucus carota cv. U.S. harumakigosun). Biol Trace Elem Res 103, 69–82 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1385/BTER:103:1:069
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/BTER:103:1:069