Abstract
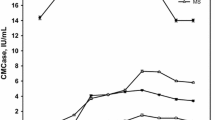
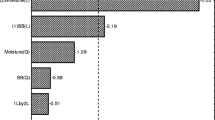
Economical production of cellulase enzyme is key for feasible bioethanol production from ligh ocellulosics using an enzyme-based process. On-site cellulase production can be more feasible with the process of separate hydrolysis and fermentation (SHF) than with simultaneous saccharification and fermentation, since the cost of enzyme is more important and a variety of substrates are available for the SHF process. Cellulase production using various biomass substrates available for SHF, including paper sludge, pretreated wood (steam exploded), and their hydrolysis residues, was investigated in shake flasks and a fermenter for their productivities and titers. Among the newspaper sludge, office paper sludge, and steam-exploded woods treated in various ways, the steam-exploded wood showed the best properties for substrate in cellulase production. The besttiter of 4.29 IU/mL was obtained using exploded wood of 2% (w/v) slurry in the shake flask, and the titer with the same substrate was duplicated to about 4.30 IU/mL in a 3.7-L fermenter. Also, the yield of enzyme reached 215 1U/g of substrate or 363 IU/g of cellulose. Despite various pretreatment attempts, newspaper and office paper substrate was inferior to the exploded-wood substrate for cellulase production. However, hydrolysis residues of papers showed quite promising results. The hydrolysis residue of office paper produced 2.48 IU/mL of cellulase in 7 d. Hence, the utilization of hydrolysis residues for cellulase production will be further investigated in the future.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vallander, L. (1999), Newsletter for IEA Task 26, Biotechnology for the Conversion of Lignocellulosics to Ethanol, no. 4, March.
Desmarquest, J. P. and Requillart, V. (1989), Proceedings of the 5th E.C. Conference on Biomass for Energy and Industry, 9–13 Oct., Lisbonne, Portugal.
Nguyen, Q. A. and Saddler, J. N. (1991), Bioresour. Technol. 35, 275–282.
Hayward, T. K., Hamilton, J., Templeton, D., Jennings, E., Ruth, M., Tholudur, A., Mcmillan, J. D., Tucker, M., and Mohagheghi, A. (1999), Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 77/79, 293–309.
Chahal, P. S., Chahal, D. S., and Le, G. B. B. (1996), Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 57/58, 433–442.
Kawamori, M., Morikawa, Y., Ado, Y., and Takasawa, S. (1986), Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 24, 454–458.
Kan, A. W. and Lamb, K. A. (1984), Biotechnol. Lett. 6, 663–666.
Szengyel, Z., Zacchi, G., and Reczey, K. (1997), Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 63/65, 351–362.
Chen, S. and Wayman, M. (1991), Process Biochem. 26, 93–100.
Doppelbauer, R., Esterbauer, H., Steiner, W., Lafferty, R. M., and Steinmuler, H. (1987), Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 26, 485–494.
Viesturs, U., Leite, M., Treimanis, A., Eremeeva, T., Apsite, A., Eismonte, M., and Jansens, P. (1996), Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 57/58, 349–360.
Qu, Y., Zhao, X., Gao, P., and Wang, Z. (1991), Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 28/29, 363–368.
Farid, M. A. and El-Shahed, K. Y. (1993), ZEntralbl. Mikrobiol. 148, 277–283.
Ghose, T. K. (1987), Pure Appl. Chem. 59, 257–268.
Bradford, M. M. (1976), Anal. Biochem. 72, 248–254.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shin, C.S., Lee, J.P., Lee, J.S. et al. Enzyme production of Trichoderma reesei rut C-30 on various lignocellulosic substrates. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 84, 237–245 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1385/ABAB:84-86:1-9:237
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/ABAB:84-86:1-9:237