Abstract
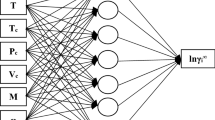
The quantitative structure–mobility relationship study has been done to develop the correlation between the electrophoretic mobility of a number of common organic acids in capillary electrophoresis and their molecular structures. Molecular descriptors calculated from structure, were used to represent molecular structures. A subset of the calculated descriptors was used in model development. Multiple linear regression and artificial neural networks are utilized to construct the linear and non-linear prediction models. This paper focuses on investigating the role of weight update function in artificial neural networks. Therefore, artificial neural networks with three different weight update functions including Levenberg–Marquardt algorithm, gradient descent with variable learning rate back propagation and resilient back propagation were trained. Finally, obtained results using three different artificial neural networks have been compared.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yao X, Zhang X, Zhang R, Liu M, Hu Z, Fan B (2002) J Comput Chem 26:159–169. doi:10.1016/s0097-8485(01)00093-6
Jouyban A, Bathish A, Rumbelow SJ, Clark BJ (2001) Analyst 126:101
Wronski M (1993) J Chromatogr A 657:165–173
Liang HR, Vuorela H, Vuorela P, Riekkola ML, Hiltunen R (1998) J Chromatogr A 798:233–242
Fu S, Lucy CA (1998) Anal Chem 70:173
Fu S, Li D, Lucy CA (1998) Analyst 123:1487–1492
Jalali-Heravi M, Garkani-Nejad Z (2001) J Chromatogr A 927:211–218. doi:10.1016/s0021-9673(01)01099-8
Jalali-Heravi M, Garkani-Nejad Z (2002) J Chromatogr A 945:173–184. doi:10.1016/s0021-9673(01)01513-8
Jalali-Heravi M, Shahbazikhah P (2008) Electrophoresis 29:363–374
Jalali-Heravi M, Asadollahi-Baboli M, Shahbazikhah P (2008) Euro J Med Chem 43:548–556. doi:10.1016/j.ejmech.2007.04.014
MATLAB, Mathworks Inc (2005) Version 7.1. http://www.mathworks.com/
Noblitt S, Mazzoleni LR, Hering SV, Collett JL Jr, Henry CS (2007) J Chromatogr A 1154:400–406. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2007.03.069
Hyperchem, Molecular Modeling System (1993) Hyper Cube Inc.
Stewart JJP, MOPAC (1990) Semi empirical Molecular Orbital Program, QCPE
Leonard JT, Roy K (2006) Bioorg Med Chem 14:1039–1046. doi:10.1016/j.bmcl.2006.031
Garkani-Nejad Z, Jalili-Jahani N, J Chromatogr Sci, Accepted
SPSS/PC Statistical Package, Version 16 (2004). http://www.spss.com/
Osten DW (1998) J Chemom 2:39–48. doi:10.1002/cem.1180020106
Evants DF, Tominanga T, Hubbard JB, Wolynes PG (1979) J Phys Chem 83:2669–2680
Hubbard JB, Onsager L (1977) J Chem Phys 67:4850–4857
Kay RL (1991) Pure Appl Chem 63:1393–1399
Acknowledgment
The support of this work by Vali-e-Asr University (Grant no. 2745) is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Garkani-Nejad, Z., Seyedbagheri, S.A. Prediction of Electrophoretic Mobilities of Organic Acids Using Artificial Neural Networks with Three Different Training Functions. Chroma 71, 431–437 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1365/s10337-009-1466-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1365/s10337-009-1466-4