Abstract
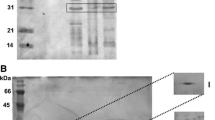
Changes in the composition of bacterial outer membrane proteins may result in antibiotic resistance and in altered invasive ability. A rapid method (microfluid chip technology) was used in this study to analyze the outer membrane protein profile changes of Erwinia strains under antibiotic effect and to compare it with the effect of essential oil and its constituents. Streptomycin, gentamicin and thyme essential oil were capable of significantly changing the protein profile. Neither of the main constituents of the essential oil (thymol and carvacrol) can be exclusively responsible for the changes induced. Quantitative changes in the protein profile may contribute to the explanation of antibacterial effect of thyme oil on pathogenic Erwinia. strains.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
McManus PS, Jones AL (1994) Phytopathology 84:627–633
McManus PS, Stockwell VO, Sundin GW, Jones AL (2002) Annu Rev Phytopathol 40:443–465. doi:10.1146/annurev.phyto.40.120301.093927
Hevesi M, Hudák I, Dorgai L, Szentkirályi A, Bubán T (2006) Phytopathol Pol 39:79–85
Gonçalves FA, Neto AM, Bezerra JN, Macrae A, Sousa OV, Fonteles-Filho AA, Vieira RH (2008) Rev Inst Med Trop Sao Paulo 50:11–15
Dorman HJD, Deans SG (2000) J Appl Microbiol 88:308–316. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2672.2000.00969.x
Tabanca N, Demirci B, Baser KH, Aytac Z, Ekici M, Khan SI, Jacob MR, Wedge DE (2006) J Agric Food Chem 54:6593–6597. doi:10.1021/jf0608773
Lee SB, Cha KH, Kim SN, Altantsetseg S, Shatar S, Sarangerel O, Nho CW (2007) J Microbiol 45:53–57
Ultee A, Gorris LG, Smid EJ (1998) J Appl Microbiol 85:211–218. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2672.1998.00467.x
Marino M, Bersani C, Comi G (1999) J Food Prot 62:1017–1023
Horváth G, Szabó LG, Lemberkovics É, Botz L, Kocsis B (2004) J Planar Chromatogr 17:300–304. doi:10.1556/JPC.17.2004.4.11
Longbottom CJ, Carson CF, Hammer KA, Mee BJ, Riley TV (2004) J Antimicrob Chemother 54:386–392. doi:10.1093/jac/dkh359
Denyer SP, Maillard JY (2002) J Appl Microbiol Symp Suppl 92:35S–45S. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2672.92.5s1.19.x
Kustos I, Andrásfalvy M, Kustos T, Kocsis B, Kilár F (2005) Electrophoresis 26:3789–3795. doi:10.1002/elps.200500291
Babujee L, Venkatesh B, Yamazaki A, Tsuyumu S (2007) J Proteome Res 6:62–69. doi:10.1021/pr060423l
Poole K (2002) J Appl Microbiol Symp Suppl 92:55S–64S. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2672.92.5s1.8.x
Jorgensen JH, Turnidge JD (2003) Susceptibility test methods: dilution and disk diffusion methods. In: Murray PR (ed) Manual of clinical microbiology. ASM Press, Washington, pp 1108–1127
Kustos I, Kocsis B, Kerepesi I, Kilár F (1998) Electrophoresis 19:2324–2330
Barabote RD, Johnson OL, Zetina E, San Francisco SK, Fralick JA, San Francisco MJ (2003) J Bacteriol 185:5772–5778. doi:10.1128/JB.185.19.5772-5778.2003
Toth IK, Thorpe CJ, Bentley SD, Mulholland V, Hyman LJ, Perombelon MC, Salmond GP (1999) Mol Plant Microbe Interact 12:499–507. doi:10.1094/MPMI.1999.12.6.499
Collins AC, Ashenafi M, Saunders AA, Byrnes WM (2007) Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand) 53:74–79
Vukovic N, Milosevic T, Sukdolak S, Solujic S (2007) Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 4:17–20. doi:10.1093/ecam/nem108
Firouzi R, Shekarforoush SS, Nazer AH, Borumand Z, Jooyandeh AR (2007) J Food Prot 70:2626–2630
Cox SD, Markham JL (2007) J Appl Microbiol 103:930–936. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2672.2007.03353.x
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Ferenc Kilár, Head of the Institute of Bioanalysis, University of Pécs, for the technical background.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Horváth, G., Kovács, K., Kocsis, B. et al. Effect of Thyme (Thymus vulgaris L.) Essential Oil and Its Main Constituents on the Outer Membrane Protein Composition of Erwinia Strains Studied with Microfluid Chip Technology. Chroma 70, 1645–1650 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1365/s10337-009-1374-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1365/s10337-009-1374-7