Abstract
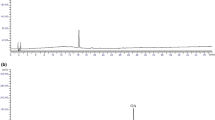
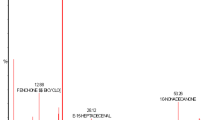
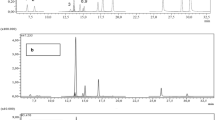
Erxian Decoction (EXD), a traditional Chinese medicine formula mainly composed of six Chinese herbs, was originally developed for menopausal syndromes and had been practiced since the 1950s in China. Previous studies only focused on the water-soluble compounds involved in EXD by LC or TLC. This study analyzed the whole profile of the volatile constituents contained in EXD to supplement its quality evaluation method. Several EXD samples were extracted with chloroform and ethyl acetate, respectively, to get the lipid-soluble chloroform and ethyl acetate fractions and compared their gas chromatographic profiles by GC–MS. The EXD samples were hydrolyzed with hydrochloric acid in a water-bath at 100 °C, neutralized with 40% NaOH, and finally extracted with ethyl acetate and chloroform for the quantification of the total sarsasapogenins contained in EXD. A total of 56 compounds belonging to a variety of natural product categories such as aromatic phenols, terpenes, fatty acids, ketones, esters, and aldehydes, etc. were identified from the chloroform and ethyl acetate extracts by using the online EI–MS characterization. The GC–MS method showed a linear response for sarsasapogenin quantification with r = 0.994. The intra-day and inter-day variations of precision and accuracy of the assay were less than 5%. This developed GC–MS method could thus be successfully applied for the identification of lipid-soluble constituents derived from EXD, and also for the accurate quantification of the total sarsasapogenins contained in the acid hydrolyzed EXD samples.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liu Q, Shi JR, Yang Y, Fang ZQ, Liang SH, Guo RX (2005) Chin J Chin Mater Med 30:1023–1026
Nian H, Qin LP, Zhang QY, Zheng HC, Yu Y, Huang BK (2006) J Ethnopharmacol 108:96–102
Qian LP, Ting H, Zhang QY, Cao DP, Nian H, Rahman K, Zhen HC (2008) J Ethnopharmacol 118:271–279
Chen KM, Ge BF, Ma HP, Liu XY, Bai MH, Wang Y (2005) Pharmazie 60:939–942
Meng FH, Li YB, Xiong ZL, Jiang ZM, Li FM (2005) Phytomedicine 12:189–193
Naeyer AD, Pocock V, Milligan S, Keukeleire DD (2005) Fitoterapia 76:35–40
Shen P, Guo BL, Gong Y, Hong D-YQ, Hong Y, Yong EL (2007) Phytochemistry 68:1448–1458
Wang ZQ, Lou YJ (2004) Eur J Pharmacol 504:147–153
Vijiayanarayana K, Rashmi SR, Chandrashekhar KS, Subrahmanyam EVS (2007) J Ethnopharmacol 114:241–245
Wei SY, Xu CJ, Mok DK-W, Cao H, Lau TY, Chau FT (2008) J Chromatogr A 1187:232–238
Zhao Y, Guo SH (2007) Strait Pharm J 19:59–60
Chen XJ, Guo BL, Li SP, Zhang QW, Tu PF, Wang YT (2007) J Chromatogr A 1163:96–104
Kite GC, Porter EA, Simmonds MS-J (2007) J Chromatogr A 1148:177–183
Liu TY, Zhang SQ, Shi T, Shen LH (2006) J Southeast Univ (Med Sci Edi) 25:24–27
Lee HS, Eom YE, Eom DO (1999) J Pharm Biomed Anal 21:59–63
Chana CO, Chua CC, Moka DK-W, Chau FT (2007) Anal Chim Acta 592:121–131
Jong TT, Lee MR, Chiang YC, Chiang ST (2006) J Pharm Biomed Anal 40:472–477
Lu T, Liang Y, Song J, Xie L, Wang GJ, Liu XD (2006) J Pharm Biomed Anal 40:1218–1224
Zhang YB, Sze CZ, He Q, Wang ZT, Tong Y (2006) J Chin Med Mat 29:859–860
Acknowledgments
The research was supported by the Small Project Funding (200807176144) from the Committee on Research and Conference Grants, Li Ka Shing Faculty of Medicine, the University of Hong Kong. The authors would also like to thank the Physical & Chemical Testing Center at the Jinan University, Guangzhou, for their assistance in NMR and ESIMS experiments and the Aomei’ Company in Hong Kong for supplying the EXD samples.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, Y.M., Sze, S.CW., Zhang, X.Q. et al. Simultaneous Analysis of Lipid-Soluble Constituents of Erxian Decoction by GC–MS. Chroma 70, 1171–1177 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1365/s10337-009-1295-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1365/s10337-009-1295-5