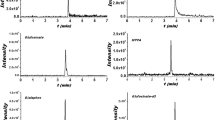
Abstract
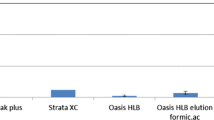
The development and optimization of analytical methods for the better monitoring of disinfection by-products especially haloacetic acids in water are key step in order to estimate human exposure to such products after chlorination. A reliable and accurate analytical method is needed in order to reach the levels of concentration required by United States Environmental Protection Agency regulations. In this study a method was developed for determining halogenated acetic acids in drinking water, involving solid phase extraction, methylation derivatization, and GC-MS. The new SPE-GC-MS-SIM method is capable of analyzing all nine acids at extremely low μg L–1 level. Run time is significantly reduced without compromising analytical results. The major advantages of the method are the simplicity of the chromatography, short run time and low detection limits. The method performance, limits of detection and spiking recovery were evaluated and the results proved that the accuracy and precision were good. This method outperforms previous GC-MS methods especially for the determination of dibromoacetic, dibromochloroacetic, dichlorobromoacetic and tribromoacetic acids. The method has been used to analyse domestic tap water and water samples collected at a local water treatment plant.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ozawa H (1993) J Chromatogr A 644:375–385. doi:10.1016/0021-9673(93)80722-K
Martinez D, Borrull F, Calull M, Ruana J, Colom A (1998) Chromatographia 48:811–816. doi:10.1007/BF02467653
Paull B, Barron L (2004) J Chromatogr A 1046:1–9
USEPA (1995) Method 552.2: determination of haloacetic acids and dalapon in drinking water by liquid–liquid extraction, derivatization and gas chromatography with electron capture detection. Environmental monitoring and System Laboratory, Cincinnanti
Carrero H, Rusling JF (1999) Talanta 48:711–718. doi:10.1016/S0039-9140(98)00295-1
Martinez D, Borrull F, Calull M (1998) J Chromatogr A 827:105–112. doi:10.1016/S0021-9673(98)00752-3
Sarzanini C, Bruzzoniti MC, Mentasti E (1999) J Chromatogr A 850:197–211. doi:10.1016/S0021-9673(99)00199-5
Loos R, Barcelo D (2001) J Chromatogr A 938:45–55. doi:10.1016/S0021-9673(01)01092-5
Ells B, Barnett DA, Purves RW, Guevremont R (2000) Anal Chem 72:4555–4559. doi:10.1021/ac000341v
Magnuson ML, Kelty CA (2000) Anal Chem 72:2308–2312. doi:10.1021/ac991469j
Roehl R, Slingsby R, Avdalovic N, Jackson PE (2002) J Chromatogr A 956:245–254. doi:10.1016/S0021-9673(02)00041-9
Xie YF (2001) Water Res 35:1599–1602. doi:10.1016/S0043-1354(00)00397-3
USEPA (1992) Method 552.1: determination of haloacetic acids and dalapon in drinking water by ion exchange liquid-solid extraction and gas chromatography with electron capture detection. Environmental monitoring and System Laboratory, Cincinnanti
Clesceri LS, Greenberg AE, Eaton AD (1998) Standard methods for examination of water and wastewater, 20th edn. APHA, AWWA, and WEF. Washington, DC
Anastasia DN, Golfinopoulos SK, Kostopoulou MN (2002) Water Res 36:1089–1094. doi:10.1016/S0043-1354(01)00300-1
Hashimoto S, Azuma T, Otsuki A (2005) Environ Toxicol Chem 17(5):798–805. doi:10.1897/1551-5028(1998)017<0798:DSASOH>2.3.CO;2
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sadia, W., Pauzi, A. SPE-GC-MS for the Determination of Halogenated Acetic Acids in Drinking Water. Chroma 69, 1447–1451 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1365/s10337-009-1065-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1365/s10337-009-1065-4