Abstract
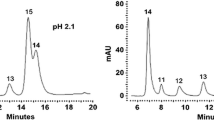
In recent years, concern about food safety has been growing. The use of food additives in different countries is limited by specific regulations. Therefore, analytical methods that simultaneously determine artificial sweeteners and preservatives are advantageous. High performance liquid chromatography has been the most popular choice for the determination of food additives. In this study, reversed-phase liquid chromatography was developed for the separation of α-aspartame, sodium saccharin, acesulfame-K, vanillin, sorbic acid and benzoic acid. The effects of the proportion of the organic modifier on the chromatographic separation were investigated in order to separate these additives. The results showed that optimum chromatographic separation for these compounds takes place when the acetonitrile content in the mobile phase was 15% containing ammonium acetate buffer (0.005 M). It was concluded that the best separation was obtained with YMC-ODS pack column by using this mobile phase at pH 4.0. All additives were separated within 40 min. The RP-HPLC-UV method was validated in terms of LOD/LOQ, linearity, recovery and repeatability. This method was used for the determination of α-aspartame, acesulfame-K and benzoic acid in cola and instant powder drinks.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Deshpande SS, Deshpande US, Salunkhe DK (1995) In: Maga JA, Tu AT (eds) Food Additive Toxicology, Marcel Dekker, New York
Hocking MB (1997) J Chem Educ 74:1055–1059
Mathlouthi M, Berssan C (1993) In: Low-Calorie Foods and Food Ingredients, Blackie, London
Summary of Evalutions Performed by the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA) 1956–1997 (first through forty-ninth meetings), FAO& WHO,1999
Veerabhadraro M, Narayan MS, Kapur O, Sastry CS (1987) J Assoc Off Anal Chem 70(3):578–582
Tyler TA (1984) J Assoc Off Anal Chem 67:745–747
Chen QC, Mou SF, Liu KN, Yang ZY, Ni ZM (1997) J Chromatogr A 771:135–143
Chen QC, Wang J (2001) J Chromatogr A 937:57–64
Tfouni SAV, Toledo MCF (2002) Food Control 13:117–123
Ferreira IMPLVO, Mendes E, Brito P, Ferreira MA (2000) Food Research International 33:113–117
Pylypiw HM Jr, Grether MT (2000) J Chromatogr A 883:299–304
Garcia I, Ortiz MC, Sarabia L, Vilches C, Gredilla E (2003) J Chromatogr A 992:11–27
Mota FJM, Ferreira IMPLVO, Cunha SC, Beatriz M, Oliveira PP (2003) Food Chemistry 82:469–473
Chen B, Fu S (1995) Chromatographia 41:43–50
Boyce MC (1999) J Chrom A 847:369–375
Cheong WJ, Carr PW (1989) AnalChem61:1524–1529
Sadek PC, Carr PW, Doherty RM, Kamlet MJ, Taft RW, Abraham MH (1985) Anal Chem 57:2971–2978
Roses M, Bosch E (1993) Anal Chim Acta 274:147–162
Barbosa J, Berges R, Sanz-Nebot V (1996) J Chromatogr A 719:27–36
Krygowski TM, Wrona PK, Zielkowska U (1985) Tetrahedron 41(20):4519–4527
Marcus Y, Migron Y (1991) J Phys Chem 95:400–406
Reichardt C (1988) Solvents and solvent effects in organic chemistry. VCH Verlagsgellschaft, Weinheim
Johnson BP, Khaledi MG, Dorsey JG (1986) Anal Chem 58:2354–2365
Michels JJ, Dorsey JG (1988) J Chromatogr 457:85–98
Barron D, Pascual JA, Segura J, Barbosa J (1995) Chromatographia 41(9/10):573–279
Rondinini S, Mussini PR, Mussini T (1987) Pure Appl Chem 59:1549–1560
Beltrán JL, Sanli N, Fonrodona G, Barrón D, Özkan G, Barbosa J (2003) Anal Chim Acta 484:253–264
Lide DR (2002–2003) C.R.C. Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, New York
AOAC Peer Verified Methods Program (1993) Manual on Policies and Procedures Arlington, VA
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Demiralay, E., Özkan, G. & Guzel-Seydim, Z. Isocratic Separation of Some Food Additives by Reversed Phase Liquid Chromatography. Chroma 63, 91–96 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1365/s10337-005-0683-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1365/s10337-005-0683-8