Abstract
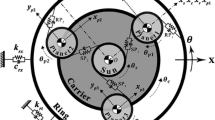
Planetary gears are widely used in aeronautic and industrial applications that require compactness and high torque-to-weight ratios. Despite these advantages, the severe conditions under which such gears are typically used may lead to failure. Tooth pitting and cracking are frequently encountered failure modes. The defects are modeled and discussed for a planetary gear set. The influence of tooth defects on gear mesh stiffness is scrutinized. Healthy planetary gear dynamic response and the response of planetary gears containing tooth defects are compared in both the time and frequency domains and in the joint time-frequency domains by use of the Wigner-Ville distribution.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
F.K. Choy, V. Polyshchuk, J.J. Zakrajsek, R.F. Handschuh, and D.P. Townsend: “Analysis of the Effects of Surface Pitting and Wear on the Vibrations of a Gear Transmission System,” Tribol. Int., 1996, 29, pp. 77–83.
F. Chaari, T. Fakhfakh, and M. Haddar: “Simulation Numérique du Comportement Dynamique d’une Transmission par Engrenages en Présence de Défauts de Denture,” Méc. Ind., 2006, 6(6), pp. 625–33.
T. Hidaka, Y. Terauchi, and K. Dohi: “On the Relation Between the Run-Out Errors and the Motion of the Centre of Sun Gear in a Stoeckicht Planetary Gear,” Bull. Jpn. Soc. Mech. Eng., 1979, 22, pp. 748–54.
R. Kasuba and R. August: “Gear Mesh Stiffness and Load Sharing in Planetary Gearing,” ASME Paper 84-DET-229, ASME Fourth Power Transmission Conference (Cambridge, MA), 1984.
I. Yesilyurt, F. Gu, and A.D. Ball: “Gear Tooth Stiffness Reduction Measurement Using Modal Analysis and Its Use in Wear Fault Severity Assessment of Spur Gears,” NDTE Int., 2003, 36(5), pp. 357–72.
A. Kahraman: “Load Sharing Characteristics of Planetary Transmissions,” Mech. Mach. Theory, 1994, 29, pp. 1151–65.
A. Saada and P. Velex: “An Extended Model for the Analysis of the Dynamics of Planetary Trains,” J. Mech. Des. (Trans. ASME), 1995, 117, pp. 241–47.
P. Velex and L. Flamand: “Dynamic Response of Planetary Trains to Mesh Parametric Excitations,” J. Mech. Des. (Trans. ASME), 1996, 118, pp. 7–14.
F. Chaari, R. Hbaieb, J. Louati, T. Fakhfakh, and M. Haddar: “Influence of Manufacturing Errors on the Dynamical Behavior of Planetary Gear,” Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 2006, 6(6), pp. 738–46.
J. Lin and R.G. Parker: “Analytical Characterization of the Unique Properties of Planetary Gear Free Vibration,” ASME J. Vib. Acoust., 1999, 121, pp. 316–21.
P. Ma and M. Botman: “Load Sharing in a Planetary Gear Stage in the Presence of Gear Errors and Misalignment,” J. Mech. Trans. Auto. Des., 1984, 104, pp. 1–7.
Y.S. Shin and J.J. Jeon: “Pseudo Wigner-Ville Time Frequency Distribution and Its Application to Machinery Condition Monitoring,” J. Shock Vib., 1993, 1(1), pp. 65–76.
G. Touzot and G. Dhatt: Une Présentation de la Méthode des Eléments Finis, Editions Maloine, France, 1984.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chaari, F., Fakhfakh, T. & Haddar, M. Dynamic analysis of a planetary gear failure caused by tooth pitting and cracking. J Fail. Anal. and Preven. 6, 73–78 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1361/154770206X99343
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1361/154770206X99343