Abstract
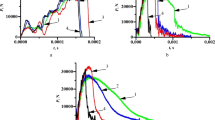
Important uses in the future for metal-matrix composites are in aerospace, weaponry, and high-speed power plants in which the inertial force produced by great acceleration is a load of high strain rate. Therefore close attention is given to the mechanical behavior of a composite at high strain rates. This paper reports a study of the behavior and mechanisms of a SiC w /7475 composite in low-cycle impact fatigue (LCIF). The LCIF and impact tension tests were conducted by using the push-pull impact fatigue apparatus developed by the authors, in which the loading assembly was actually a combination of a Hopkinson’s pressure bar and an extension bar. In the apparatus the trapezoidal stress wave loads were produced. The strain rates in specimens may reach 400 s -1 .The results show that for a SiC w /7475 composite, the strain-rate effects on yield stress, ductility, cyclic hardening and softening, δ e /2-N f relation, and transition life were slight. In low-cycle impact fatigue the cracks often initiated within or near the SiC particles, which mingled in the composite. The SiC w /7475 composite was found to be less ductile than its alloy matrix; in low-cycle fatigue brittleness appears. Therefore great attention must be given to the behavior of the composite when it is used as a structural material.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
D.L. Davidson, Tensile Deformation and Fracture Toughness of 2014+15 Vol Pct SiC Particulate Composite,Metall. Trans. A, Vol 16, 1991, p 113–123
M.H. Zhu, S.K. Liu, and W. Dong, Study on the Tensile Properties of SiCw/Al Composite,Composite Progress, S.L. Li, Ed., Aviation Industry Publishing House, Peking, China, 1994, p 527–531 (in Chinese)
X. Liu and C. Bathias, Fatigue Damage Development in A12O3/A1 Composite,Composites, Vol 24 (No. 3), 1993, p 282–287
M. Levin and B. Karlsson, Fatigue Behavior of a Saffil-Reinforced Aluminum Alloy,Composites, Vol 24 (No. 3), 1993, p 288–295
K. Cho, S. Lee, Y.W. Chang, and J. Duffy, Dynamic Fracture Behavior of SiC Whisker-Reinforced Aluminium Alloys,Metall. Trans. A, Vol 22, 1991, p 367–375
P.S. Yang, M. Zhang, F. Xu, and S.P. Gong, Effect of Strain Rate on Low-Cycle Fatigue Behaviour and Mechanism of SiCp/Lyl2 Composite,Mater. Sci. Eng. A, Vol 234–236, 1997, p 127–131
P.S. Yang, X.N. Liao, J.H. Zhu, and H.J. Zhou, High Strain-Rate Low-Cycle Impact Fatigue of a Medium-Carbon Alloy Steel,Int. J. Fatigue, Vol 16, 1994, p 327–330
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, P., Liu, Y. & Xu, F. Low-cycle impact fatigue of SiCw/7475Al composite. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 7, 677–681 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1361/105994998770347567
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1361/105994998770347567