Abstract
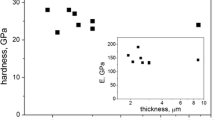
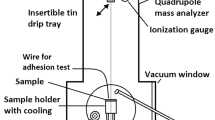
This article discusses the effect of applying diamond coatings on the response characteristics of certain infrared (IR) transmitting materials. The predicted response characteristics are compared with experimental data generated using controlled liquid jet impacts produced by the multiple impact jet apparatus. The predicted response of a selection of IR transmitting materials compare well with the experimental results. The results presented in this article illustrate the importance of the first stages of liquid impact on the integrity of the surface coating applied to zinc sulfide and germanium substrates.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.E. Field, “The Deformation and Fracture of Brittle Solids,” Ph.D. dissertation, Cavendish Laboratory, University of Cambridge, 1962
F.P. Bowden and J.E. Field, The Deformation of Solids by Liquid Impact, Solid Impact and by Shock, Proc. R. Soc. London, 1964, A282, p 331–352
M.B. Lesser and J.E. Field, The Impact of Compressible Liquids, Ann. Rev. Fluid Mech., 1983, 15, p 97–122
F.J. Heymann, High Speed Impact Between a Liquid Drop and a Solid Surface, J. Appl. Phys., 1969, 40, p 5113–5122
M.B. Lesser, Analytic solutions of liquid drop impact problems, Proc. R. Soc. London, 1981, A377, p 289–308
M.C. Rochester and J. Brunton, “H: Pressure Distributions During Drop Impact,” Paper 6, Proc. 5th Int. Conf. “Erosion by Liquid and Solid Impact,”, Cavendish Laboratory, University of Cambridge, Cambridge, U.K., 1979
F.P. Bowden and J.H. Brunton, The Deformation of Solids by Liquid Impact at Supersonic Speeds, Proc. R.. Soc. London, 1961, A263, p 433–450
B. Steverding and S.H. Lehnigk, Dynamic Thresholds for Crack Propagation, Int. J. Fract. Mech., 1969, 5, p 369–370
J.E. Field, D.A. Gorham, J.T. Hagan, M.J. Matthewson, S.V. Swain, and S. van der Zwaag, “Liquid Jet Impact and Damage Assessment for Brittle Solids,” Paper 13, Proc. 5th Int. Conf. “Erosion by Liquid and Solid Impact,” Cavendish Laboratory, University of Cambridge, Cambridge, U.K., 1979
G.F. Miller and H. Pursey, On the Partition of Energy Between Elastic Waves in a Semi-Infinite Solid, Proc. R.. Soc. London, 1956, A233, p 55–69
J.E. Field, M.B. Lesser, and J.P. Dear, Studies of Two-Dimensional Liquid Wedge Impact and the Relevance to Liquid-Drop Impact Problems, Proc. R. Soc. London, 1985, A401, p 225–249
M.J. Jackson and J.E. Field, Liquid Impact Erosion of Single Crystal Magnesium Oxide, Wear, 1999, 233–235, p 39–50
T. Obara, N.K. Bourne, and J.E. Field, Liquid Jet Impact on Liquid and Solid Surfaces, Wear, 1995, 186–187, p 338–344
J.H. Brunton and J.-J. Camus, “The Application of High-Speed Photography to the Analysis of Flow in Cavitation and Drop Impact Studies,” presented at Proc. 9th Int. Congress “High Speed Photography” (Denver, CO), 1970
J.E. Field, “The Importance of Surface Topology on Erosion Damage,” presented at 2nd Int. Conf. “Rain Erosion & Assoc. Phenom.,” Royal Aircraft Establishment (Farnborough, U.K.), 1967, p 593–603
J. Denis and D. Balageas, “Rain Erosion Resistance of Infra-Red Materials,” Paper 19, presented at Proc. 5th Int. Conf. “Erosion by Liquid and Solid Impact,” Cavendish Laboratory, University of Cambridge, U.K., 1979
C.R. Seward, “Rain Erosion Testing of Infra-Red Window Materials,” Ph.D. dissertation, Cavendish Laboratory, University of Cambridge, 1992
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jackson, M.J., Field, J.E., Coad, E.J. et al. Liquid impact of chemical vapor-deposited diamond-coated germanium and zinc sulfide infrared transmitting materials. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 15, 149–154 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1361/105994906X95797
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1361/105994906X95797