Abstract
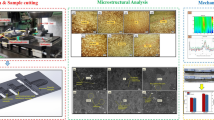
Particle reinforced aluminum-matrix composites are particularly attractive for the automobile and air-craft industries, due to their light weight, high strength, and good wear resistance. In the present work, silicon carbide (SiC) particulates have been incorporated into a pure Al matrix with the help of mechanical milling in a planetary ball-mill. Composite powders were prepared using both raw as well as premilled SiC powders. The effect of milling time on the SiC particulate size was investigated. Systematic analysis of x-ray diffraction data revealed a reinforcement particle size of about 30 nm in a composite containing 50 vol.% SiC. It has been observed that the size reduction occurs at a faster rate when indirect milling is used.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.N. Fridlyander, Ed., Metal Matrix Composite, Chapman & Hall, London, 1995
T.W. Clyne and P.J. Withers, An Introduction to Metal Matrix Composites, Cambridge University Press, 1993
W.S. Miller and F.J. Humphreys, Strengthening Mechanism in Metal Matrix Composites, Fundamental Relationships Between Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Metal Matrix Composites, P.K. Liaw and M.N. Gungor, Ed., The Minerals, Metals & Materials Society, 1990
L. Lu, M.O. Lai, and C.W. Ng, Enhanced Mechanical Properties of an Al Based Metal Matrix Composite Prepared Using Mechanical Alloying, Mater. Sci. Eng, A, Vol 252, 1998, p 203–211
R.D. Evans and J.D. Boyd, Near-Interface Microstructure in a SiC/Al Composite, Scr. Mater., Vol 49, 2003, p 59–63
P.N. Bindumadhavan, H.K. Wah, and O. Prabhakar, Assessment of Particle-Matrix Debonding in Particulate Metal Matrix Composites Using Ultrasonic Velocity Measurements, Mater. Sci. Eng, A, Vol 323, 2002, p 42–51
F.Y.C. Boey, Z. Yuan, and K.A. Khor, Mechanical Alloying for the Effective Dispersion of Sub-Micron Sicp Reinforcements in Al-Li Alloy Composite, Mater. Sci. Eng, A, Vol 252, 1998, p 276–287
L. Lu and M.O. Lai, Mechanical Alloying, Kluwer Academic Publishers, 1998
C. Suryanarayana, Mechanical Alloying and Milling, Proc. Mater. Sci., Vol 46, 2001, p 1–184
B.D. Cullity and S.R. Stock, Elements of X-Ray Diffraction, 3rd ed., Prentice Hall, 2001
B.E. Warren, X-Ray Diffraction, Addison-Wesley, 1969
D.L. Zhang, Processing of Advanced Materials Using High-Energy Mechanical Milling, Prog. Mater. Sci., Vol 49, 2004, p 537–560
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mujahid, M., Friska, I. Influence of mechanical milling on the SiC particulate size in an Al-SiC composite. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 14, 69–74 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1361/10599490522284
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1361/10599490522284