Abstract
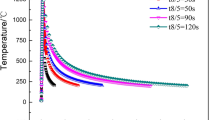
The effects of austenite stabilizers, such as nitrogen, nickel, and manganese, and cooling time on the microstructure of the Gleeble simulated heat-affected zone (HAZ) of 22% Cr duplex stainless steels were investigated. The submerged are welding was performed for comparison purposes. Optical microscopy (OM) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) were used for microscopic studies. The amount of Cr2N precipitates in the simulated HAZ was determined using the potentiostatic electrolysis method. The experimental results indicate that an increase in the nitrogen and nickel contents raised the δ to transformation temperature and also markedly increased the amount of austenite in the HAZ. The lengthened cooling time promotes the reformation of austenite. An increase in the austenite content reduces the supersaturation of nitrogen in ferrite matrix as well as the precipitation tendency of Cr2N. The optimum cooling time from 800 to 500 °C (Δt 8/5) obtained from the Gleeble simulation is between 30 and 60 s, which ensures the austenite content in HAZ not falling below 25% and superior pitting and stress corrosion cracking resistance for the steels. The effect of manganese on the formation of austenite can be negligible.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
T. Kudo, H. Tsuge, and T. Moroishi: Corr. J., 1989, vol. 45, p. 831.
W.A. Baeslack and J.C. Lippold: Met. Const., 1988, vol. 20, p. 26R.
L. Karlsson, L. Ryen, and S. Pak: Weld. J., 1995, vol. 74, p. 28.
R.M. Davison and J.D. Redmond: Mater. Selection Design, 1990, vol. 11, p. 57.
T. Omura, T. Kushida, T. Kudo, T. Hayashi, Y. Matsuhiro, and T. Hikida: Tetsu-to-Hagané, 1997, vol. 83, p. 37.
B.E.S. Lindblom, B. Lundquivst, and N. Hannerz: Scand. J. Metall., 1991, vol. 20, p. 305.
G.L. Leone and H.W. Kerr: Weld. J., 1982, vol. 61, p. 13.
N. Suutala, T. Talkalo, and T. Moisio: Metall. Trans. A, 1980, vol. 11A, p. 717.
S. Hertzman, P.J. Ferreira, and B. Brolund: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1997, vol. 28A, p. 277.
S. Atamert and J.E. King: Mater. Sci. Technol., 1992, vol. 8, p. 896.
B. Sundman, B. Jansson, and J.O. Andersson: CALPHAD, 1985, vol. 9, p. 153.
R.N. Gunn: Duplex Stainless Steels—Microstructure, Properties and Applications, Woodhead Publishing Ltd., Cambridge, United Kingdom, 1997.
H. Tsuge, Y. Tarutani, and T. Kudo: Corr. J., 1988, vol. 44, p. 305.
M.J. Huh, S.B. Kom, K.W. Paik, and Y.G. Kim: Scripta Mater., 1997, vol. 36, p. 775.
R.W.K. Honeycombe: Steels Microstructure and Properties, Edward Arnold Ltd., London, 1981.
H.Y. Liou, R.I. Hsieh, and W.T. Tsai: Materials Chemistry and Physics, to be published.
H. Lee, C.H. Yoo, and H.M. Lee: Mater. Technol., 1998, vol. 14, p. 54.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hsieh, RI., Liou, HY. & Pan, YT. Effects of cooling time and alloying elements on the microstructure of the gleeble-simulated heat-affected zone of 22% Cr duplex stainless steels. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 10, 526–536 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1361/105994901770344665
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1361/105994901770344665