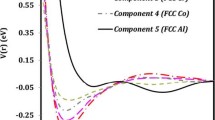
Abstract
To assist the science-based design of alloys with martensitic microstructure, a multicomponent database kMART (kinetics of MARtensitic Transformation) encompassing the components Al, C, Co, Cr, Cu, Fe, Mn, Mo, N, Nb, Ni, Pd, Re, Si, Ti, V, and W has been developed to calculate the driving force for martensitic transformation. Built upon the SSOL database of the Thermo-Calc software system, a large number of interaction parameters of the SSOL database have been modified, and many new interaction parameters, both binary and ternary, have been introduced to account for the heat of transformation, T 0 temperatures, and the composition dependence of magnetic properties. The critical driving force for face-centered cubic (fcc) → body-centered cubic (bcc) heterogeneous martensitic nucleation in multicomponent alloys is modeled as the sum of a strain energy term, a defect-size-dependent interfacial energy term, and a composition-dependent interfacial work term. Using our multicomponent thermodynamic database, a model for barrierless heterogeneous martensitic nucleation, a model for the composition and temperature dependence of the shear modulus, and a set of unique interfacial kinetic parameters, we have demonstrated the efficacy of predicting the fcc → bcc martensitic start temperature (M s ) in multicomponent alloys with an accuracy of ± 40 K over a very wide composition range.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
L.A. Carapella: Met. Progr., 1944, vol. 46, p. 108.
P. Payson and C.H. Savage: Trans. ASM, 1944, vol. 33, p. 261.
E.S. Rowland and S.R. Lyle: Met. Progr., 1945, vol. 47, p. 907.
R.A. Grange and H.M. Stewart: Trans. AIME, 1946, vol. 167, p. 467.
A.E. Nehrenberg: Trans. AIME, 1946, vol. 167, p. 494.
G.H. Eichelmann, Jr. and F.C. Hull: Trans. ASM, 1953, vol. 45, p. 77.
W. Steven and A.G. Haynes: J. Iron Steel Inst., 1956, vol. 183, p. 349.
K.J. Irvine, F.B. Pickering, and J. Garstone: J. Iron Steel Inst., 1960, vol. 198, p. 66.
K.W. Andrews: J. Iron Steel Inst., 1965, vol. 203, p. 721.
G.B. Olson: Proc. M.E. Fine Symp., P.K. Liaw, J.R. Weertman, H.L. Marcus, and J.S. Slater, eds., TMS, Warrendale, PA, 1991, p. 41
Thermo-Calc, version M, Foundation of Computational Thermodynamics, Royal Institute of Technology, Stockholm, 1998.
B. Sundman and J. Ågren: J. Phys. Chem. Solids, 1985, vol. 42, p. 297.
M. Hillert and M. Jarl: CALPHAD, 1978, vol. 2, p. 227.
O. Redlich and A. Kister: Ind. Eng. Chem., 1948, vol. 40, p. 345.
G. Ghosh: kMART Database, Northwestern University, Evanston, IL, unpublished research, 2000.
Solution Database, Scientific Group Thermodata Europe, Division of Physical Metallurgy, Royal Institute of Technology, Stockholm, Sweden, 1994.
L. Kaufman and M. Cohen: Trans. AIME, 1956, vol. 206, p. 1393.
K. Ishida and T. Nishizawa: Trans. Jpn. Inst. Met., 1974, vol. 15, p. 217.
L. Kaufman and M. Hillert: in Martensite, G.B. Olson and W.S. Owen, eds., ASM International, Materials Park, OH, 1992, p. 41.
E. Scheil and E. Saftig: Arch. Eisenhüttenwes., 1960, vol. 31, p. 623.
R.G.B. Yeo: Trans. AIME, 1963, vol. 227, p. 884.
C.E. Campbell: Ph.D. Thesis, Northwestern University, Evanston, IL, 1997.
E. Scheil and W. Normann: Arch. Eisenhüttenwes., 1959, vol. 30, p. 751.
A.J. Goldman and W.D. Robertson: Acta Metall., 1965, vol. 13, p. 391.
M. Peschard: Rev. Met., 1925, vol. 22, p. 581.
J. Crangle and G.C. Hallam: Proc. R. Soc., 1963, vol. 272, p. 119.
Y.-Y. Chuang, Y.A. Chang, R. Schmid, and J.-C. Lin: Metall. Trans. A, 1987, vol. 17A, p. 1361.
K. Hoselitz and W. Sucksmith: Proc. R. Soc. (London), 1943, vol. A181, p. 303.
Y.I. Kondorskiy and L.N. Fedotov: Izv. Akad. Nauk SSSR, 1952, vol. 16, p. 432.
C.G. Shull and M.K. Wilkinson: Phys. Rev., 1955, vol. 97, p. 304.
M.F. Collins, R.V. Jones, and R.D. Lowde: J. Phys. Soc. Jpn., 1962, vol. 17, p. 19.
Y. Bando: J. Phys. Soc. Jpn., 1964, vol. 19, p. 237.
D.A. Colling: J. Appl. Phys., 1969, vol. 40, p. 1379.
M. Nishi, Y. Nakai, and N. Kunitomi: J. Phys. Soc. Jpn., 1974, vol. 37, p. 570.
H. Asano: Honda Mem. Ser. Mater. Sci., 1978, No. 3, p. 457.
A.N. Moisin: Phys. Status Solidi, A, 1978, vol. 47, p. 305.
I. Nakai: J. Phys. Soc. Jpn., 1983, vol. 52, p. 1781.
I. Nakai, F. Ono, and O. Yamada: J. Phys. Soc. Jpn., 1983, vol. 52, p. 1791.
D.H. Martin: in Magnetism in Solids, MIT Press, Cambridge, MA, 1967, p. 10.
C.E. Guilleaume: Compt. Rend. Acad. Sci (Paris), 1897, vol. 125, p. 235.
G. Gossels: Z. Anorg. Chem., 1929, vol. 182, p. 19.
R.J. Wakelin and E.L. Yates: Proc. R. Soc. (London), 1953, vol. B66, p. 221.
G.F. Bolling and R.H. Richman: Acta Metall., 1970, vol. 18, p. 673.
R.G. Davies and C.L. Magee, Metall. Trans., 1970, vol. 1, p. 2927.
R.G. Davies and C.L. Magee: Metall. Trans., 1971, vol. 2, p. 1939.
C.L. Magee and R.G. Davies: Acta Metall., 1972, vol. 20, p. 1031.
C. Kantner, G. Ghosh, and G.B. Olson: Northwestern University, Evanston, IL, research in progress, 2000.
G.B. Olson and M. Cohen: Metall. Trans. A, 1976, vol. 7A, pp. 1905–15.
G.B. Olson and M. Cohen: in Dislocations in Solids, F.R.N. Nabarro, ed., North-Holland, Amsterdam, 1986, vol. 7, p. 297.
G.B. Olson, K. Tsuzaki, and M. Cohen: Turnbull Symp.: Phase Transtions in Condensed Systems, G.S. Cargill, F. Spaepen, and K.N. Tu, eds., Materials Research Society, Pittsburgh, PA, 1987, p. 129.
A.C.E. Reid and G.B. Olson: Mater. Sci. Eng., 1998, vols. A273–A275, p. 257.
A.C.E. Reid, G.B. Olson, and B. Moran: Phase Transitions, 1999, vol. 69, p. 309.
L. Kaufman and M. Cohen: Progr. Met. Phys., 1958, vol. 7, p. 165.
G. Ghosh and G.B. Olson: Acta Metall. Mater., 1994, vol. 42, p. 3361.
G. Ghosh and G.B. Olson: Acta Metall. Mater., 1994, vol. 42, p. 3371.
G. Ghosh and G.B. Olson: submitted to Acta Mater., 2001.
M. Lin, G.B. Olson, and M. Cohen: Metall. Trans. A, 1992, vol. 23A, p. 2991.
T.J. Koppenaal and D. Kuhlmann-Wilsdorf: Appl. Phys. Lett., 1964, vol. 4, p. 59.
A.J. Goldman and W.D. Robertson: Acta Metall., 1964, vol. 12, p. 1265.
Atlas for Time-Temperature Diagrams for Iron and Steels, G.F. Vander Voort, ed., ASM International, Materials Park, OH, 1991.
U.R. Lenel and B.R. Knott: Metall. Trans. A, 1987, vol. 18A, p. 767.
J.C. Brachet: J. Phys. IV, 1995, Coll. C8, vol. 5, pp. C8–339.
T. Cool and H.K.D.H. Bhadeshia: Mater. Sci. Technol., 1996, vol. 12, p. 40.
H. Finkler and M. Schirra: Steel Res., 1996, vol. 67, p. 328.
H. Nakagawa and T. Miyazaki: Tetsu-to-Hagańe, 1999, vol. 85, p. 49.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ghosh, G., Olson, G.B. Computational thermodynamics and the kinetics of martensitic transformation. JPE 22, 199–207 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1361/105497101770338653
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1361/105497101770338653