Abstract
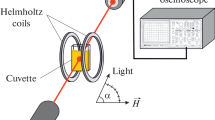
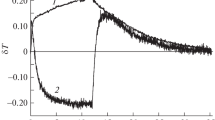
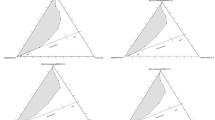
It has been shown that optical activity can occur in microemulsion under external electric field and rotation angle can also be tuned by the electric field. A set of microemulsions (water/Span80/transformer oil) with different water concentration were prepared and their optical activity was measured with the changes of applied electric field and θ, the angle between the electric vector of the incident linearly polarized light and the external electric field, using an automatic polarimeter. The experiments indicate that when none of the external electric field, water concentration and θ are zero, there is optical activity in microemulsions. For a given concentration, rotation angle ψ increases with electric field, and it firstly increases, passes through a maximum atC=C 0, then monotonically decreases asC increases when electric field keeps constant. The relationship between the rotation angle and θ is also obtained. It is thought that the electric field-induced destroy of spatial symmetry of microemulsion is responsible for the optical activity of microemulsion.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Degennes, P. G., Soft matter, Rev. Mod. Phys., 1992, 64(3): 645–648.
Yamamobo, J., Tanaka, H., Transparent nematic phase in a liquid-crystal-based microemulsion, Nature, 2001, 409(6818): 321–325.
Huang, J. S., Safran, S. A., Kim, M. W. et al., Attractive interactions in micelles and microemulsions, Phys. Rev. Lett., 1984, 53(6): 592–595.
Degiorgio, V., Bellini, T., Piazza, R. et al., Stretched-experimental relation of electric birefringence in polymer solutions, Phys. Rev. Lett., 1990, 64(9): 1043–1046.
Wu, X.-L., Pine, D. J., Dixon, P. K., Enhanced concentration fluctuations in polymer solutions under shear flow, Phys. Rev. Lett., 1991, 66 (18): 2408–2411.
Wu, X.-L., Yeung, C., Kim, M. W. et al., Study of internal modes of a “living polymer” by transient electric birefringence, Phys. Rev. Lett., 1992, 68(9): 1426–1429.
Edwards, M. E., Wu, X. L., Wu, J.-S. et al., Electric-field effects on a droplet microemulsion, Phys Rev. E., 1998, 57(1): 797–803.
Edwards, M. E., Hwang, Y. H., Wu, X. L., Large deviations from the Clausius-Mossotti equation, Phys. Rev. E, 1994, 49(5): 4263–4267.
Vicari, L., Laser beam self-phase modulation by a film of water-in-oil microemulsion, Europhys. Lett., 2000, 49(5): 564–568.
van der Linden, E., Geiger, S., Bedeaux, D., The kerr constant of a microemulsion for a low volume fraction of water, Physica A, 1989, 156: 130–143.
Borkovec, M., Eicke, H. F., Surfactant monolayer rigidities from kerr effect measurements on microemulsion, Chem. Phys. Lett., 1989, 157: 457–461.
Mayer, G., On negative kerr effects in microemulsions, Chem. Phys. Lett., 1990, 168(6): 575–578.
Pan, X. D., Mckinley, G. H., Electrorheological response of emulsion system, J. Colloid. Interface Science, 1997, 195: 101–113.
Zhao, X. P., Luo, C. R., Zhang, Z. D., Optical characteristics of electrorheological and magnetorheological fluids, Opt. Eng., 1998, 37(5): 1589–1592.
Liu, X. H., Zhao, X. P., An adjustable property of electrorheological fluids, Acta Optica Sinica (in Chinese), 1996, 16(8): 1211–1214.
Fan, J. J., Zhao, X. P., Gao, X. M. et al., Electric field regulating behavior of microwave propagation in ER fluids, J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys., 2002, 35: 88–94.
Zhao, X. P., Qu, C. Z., Ma, Y., Double refraction phenomenon of electrorheological fluids, Int. J. Mod. Phy. B, 2001, 15(7): 1057–1061.
Chen, S. H., Rouch, J., Sciortino, F. et al., Static and dynamic properties of water-in-oil microemulsions near the critical and percolation points, J. Phys.: Condens. Matter., 1994, 6: 10855–10883.
Hudson, A., Nelson, R., University Physics, New York: Harcourt Brace Jovanovich, Inc., 1982, 865–867.
Zhao, Q., Gao, X. M., Zhao, X. P., Optical activity of electrorheological fluids, Acta Optica Sinica (in Chinese), 2002, 22(5): 616–621.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiaopeng, Z., Qian, Z. & Liqin, X. Optical activity of microemulsion induced by electric field and its tunable behaviors. Sci China Ser G: Phy & Ast 46, 164–172 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1360/03yg9022
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1360/03yg9022