Abstract
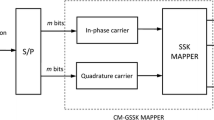
Next generation communication systems will be expected to operate under environment with high-speed motion and increasing number of antennas where it will be difficult or even impractical to estimate the real-time channel coefficients. For this reason, the DSTM (differential space time modulation) and USTM (unitary space time modulation) approaches that do not require the channel estimation became hot topics in recent years. In this paper, we propose a general approach to designing high spectral-efficiency signaling schemes. A novel modulation, dual constellations space-time modulation (DCSTM), is derived by extending DSTM and USTM theoretically. DCSTM preserves the good features of USTM such as low error rate and the capability of being demodulated without channel estimation. At the same time, it enhances the spectral efficiency and reduces the complexity of the modulation/demodulation. It can be adapted to different data rates and thus has a wider applicable area. Simulation results verify the theoretical analysis and the design of the new modulation method.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hochwald, B. M., Marzetta, T. L., Unitary space-time modulation for multiple-antenna communication in Rayleigh flat fading, IEEE Trans. Inform. Theory, 2000, 46(Mar.): 543–564.
Hochwald, B. M., Sweldens, W., Differential unitary space-time modulation, IEEE Trans. Communication, 2000, 48(Dec.): 2041–2052.
Hughes, B. L., Differential space-time modulation, IEEE Trans. Information Theory, 2000, 46(7): 2567–2578.
Marzetta, T. L., Hochwald, B. M., Capacity of a mobile multiple-antenna communication link in Rayleigh flat-fading, IEEE Trans. Inform. Theory, 1999, 45: 139–157.
Hochwald, B. M., Marzetta, T. L., Babak, H., Space-time autocoding, IEEE Trans. Inform. Theory, 2001, 47(7): 2761–2781.
Hassibi, S. B., Hochwald, B. M., Sweldens, W., Representation theory for high-rate multiple-antenna code design, IEEE Trans. on Inform. Theory, 2001, 47(6): 2335–2367.
Tarokh, V., Jafarkhani, H., A differential detection scheme for transmit diversity, IEEE J. Select. Area Commun., 2000, 18(7): 1169–1174.
Jakes, W. C., Microwave Mobile Communications, Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 1993.
Hochwald, B. M., Marzetta, T. L., Richardson, T. J. et al., Systematic design of unitary space-time constellations, IEEE Trans. Inform. Theory, 2000, 46(Sept.): 1962–1973.
Chen, Y. P., Matrix Theory (in Chinese), 2nd ed., Xi’an: Northwestern Polytechnic University Publishing Company, 2001, 126.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zou, L., Zhao, Y., Wang, B. et al. Dual constellations space-time modulation. Sci China Ser F 48, 452–466 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1360/03yf0189
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1360/03yf0189