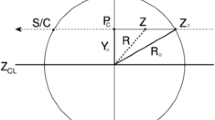
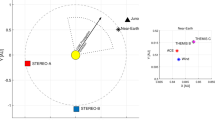
Abstract
Based on the analysis of the boundaries of 70 magnetic clouds from 1967 to 1998, and relatively complete spacercraft observations, it is indicated that the magnetic cloud boundaries are boundary layers formed through the interaction between the magnetic clouds and the ambient medium. Most of the outer boundaries of the layers, with relatively high proton temperature, density and plasma β, are magnetic reconnection boundaries, while the inner boundaries, with low proton temperature, proton density and plasma β, separate the main body of magnetic clouds, which has not been affected by the interaction, from the boundary layers. The average time scale of the front boundary layer is 1.7 h and that of the tail boundary layer 3.1 h. It is also found that the magnetic probability distribution function undergoes significant changes across the boundary layers. This new definition, supported by the preliminary numerical simulation in principle, could qualitatively explain the observations of interplanetary magnetic clouds, and could help resolve the controversy in identifying the boundaries of magnetic clouds. Our concept of the boundary layer may provide some understanding of what underlies the observations, and a fresh train of thought in the interplanetary dynamics research.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chapman, S., Ferraro, V. C. A. Solar streams of corpuscles, their geometry, absorption of light and penetration, Monthly Notices Roy. Astron. Soc., 1929, 89: 470–475.
Morrison, P., Solar-connection variations of the cosmic rays, Phys. Rev., 1954, 95: 616–620.
Cocconi, G., Gold, T., Greisen, K. et al., The cosmic ray flare effect, Nuovo Cimento, 1958, 8: 161–165.
Gold, T., Magnetic storms, Space Science Rev., 1962, 1: 100–104.
Burlaga, L. F., Mariani, S. F., Schwenn, R., Magnetic loop behind an interplanetary shock: Voyager, Helios, and IMP 8 Observations, J. Geophys. Res., 1981, 86: 6673–6684.
Klein, L. W., Burlaga, L. F., Interplanetary magnetic clouds at 1 AU, J. Geophys. Res., 1982, 87: 613–624.
Burlaga, L. F., Magnetic Clouds, Physics of the Inner Heliosphere (eds. Schwenn, R., March, E.), Berlin-Heidelberg: Springer-Verlag, 1991, 1–19.
Burlaga, L. F., Interplanetary Magnetohydrodynamics, International Series on Astronomy and Astrophysics, New York-Oxford: Oxford University Press, 1995, 112.
Geranios, A., Magnetically closed regions in the solar wind, Astrophys. Space Sci., 1982, 81: 103–109.
Smith, E. J., Identification of interplanetary tangential and rotational discontinuities, J. Geophys. Res., 1973, 78: 2054–2063.
Vandas, M. F., Pelant, P., Geranios, A., Evidence for a spheroidal structure of magnetic clouds, J. Geophys. Res., 1993, 98: 21061–21069.
Lepping, R. P., Behannon, K. W., Magnetic field directional discontinuities: 1 Minimum variance errors, J. Geophys. Res., 1980, 85: 4695–4703.
Vandas, M., Fischer, S., Odstrail, D., et al., Coronal Mass Ejections: A Numerical Study of Flux Ropes (eds. Crooker, N., Joselyn, J. A., Feynman, J.), Washington D C: American Geophysical Society, 1997, 169–176.
Marubashi, K., Coronal Mass Ejections: Interplanetary Magnetic Flux Ropes and Solar Fialaments (eds. Crooker, N., Joselyn, J. A., Feynman, J.), Washington D C: Geophysical Monography 99, 1997, 147–156.
Bothmer, V., Rust, D. M., Coronal Mass Ejections: The Field Configuration of Magnetic Clouds and the Solar Cycle (eds. Crooker, N., Joselyn, J. A., Feynmann, J.), Washington D C: American Geophysical Society, 1997, 137–146.
Wei Feingsi, Schwenn, R., Hu Qiang, Magnetic reconnection events in the interplanetary space, Science in China, Series E, 1997, 40: 463–471.
Burlaga, L. F., Lepping, R., Weber, R. et al., Interplanetary particles and fields, November 22 to December 6, 1977: Helios, Voyager and IMP observations between 0.6 AU and 1.6 AU, J. Geophys. Res., 1980, 85: 2227–2242.
Marsden, R. G., Sanderson, T. R., Tranquiller, C., Wenzel K-P ISEE-3 observations of low energy proton bidriectional events and their relation to isolated interplanetary magnetic structures, J. Geophys. Res., 1987, 92: 11009–11019.
Gosling, J. T., Baker, D. N., Bame, S. J., et al., Bidirectional solar wind electron heat flux events, J. Geophys. Res., 1987, 92:8519–8535.
Osherovich, V. A., Farrugia, C. J., Burlaga, L. F. et al., Polytropic relationship for magnetic clouds, J. Geophys. Res., 1993, 98: 15331–15342.
Farrugia, C. J., Fitzenreiter, R. J., Burlaga, L. F. et al., Observations in the sheath region ahead of magnetic clouds and in the dayside magnetosheasth during cloud passage, Adv. Space Res., 1994, 114: 105–109.
Fainberg, J., Osherovich, V. A., Stone, R. G. et al., Solar Wind Eight: Observations of electron and proton components in a magnetic cloud and related wave activity, in AIP Conference Proceedings, 382 (eds. Winterhalter, D., Gosling, J., Habbal, S. R., et al.), 1995, 554–560.
Tsurutani, B. T., Christian, H. M., A review of discontinuities and Alfven waves in interplanetary space: Ulyssess results, Review of Geophysics, 1999, 37: 517–532.
Farrugia, C. J., Burlaga, L. F., Lepping, L. F., Magnetic Storms: Magnetic clouds and the quiet-storm effect at earth, in Tsurutani Geophysical Monograph 98 (eds. Walter, B. T., Kamide, D. G., Araballo, J.), New York: American Geophysical Society, 1997, 91–106.
Gonzalez, W. D., Tsurutani, B. T., Crteria of interplanetary parameters causing intense magnetic stoms (Dst ≤100 nT) Planet Space Sci., 1987, 35: 1101–1109.
Zhang, G., Burlaga, L. F., Magnetic clouds, geomagnetic disturbances, and cosmic ray decreases, J. Geophys. Res., 1988, 95: 2511–2518.
Tsurutani, B. T., Gonzalez, W. D., Tang, F., et al., Great magnetic storms, Geophys. Res Lett., 1992, 19: 73–76.
Lepping, R. P., Jones, J. A., Burlaga, L. F., Magnetic field structure of interplanetary magnetic clouds at 1AU, J. Geophys. Res., 1990, 95: 11957–11965.
Wilson, R. M., On the behavior of the Dst geomagnetic index in the vicinity of magnetic clouds passages at Earth, J. Geophys. Res., 1990, 95: 215–219.
Burlaga, L. F., Magnetic clouds: Constant alpha force-free Configurations, J. Geophys. Res., 1988, 93: 7217–7224.
Feng Xueshang, Wu, S. T., Fan Quanlin et al., A class of TVD type combined numerical scheme for MHD equations and its application to MHD numerical simulation, Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2002, 22, in press.
Vands, M., Fischer, S., Dryer, M., et al., Simulation of magnetic cloud propagation in the inner heliosphere in two dimensions 2. A loop perpendicular to the ecliptic plane, Geophys. Res., 1995, 100:12285–12292.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, F., Liu, R., Fan, Q. et al. Characteristics of the boundary layer of magnetic clouds and a new definition of the cloud boundary. Sci. China Ser. E-Technol. Sci. 46, 19–32 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1360/03ye9002
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1360/03ye9002