Abstract
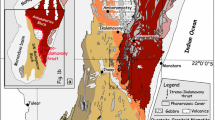
The Nanxiong red-bed basin and its adjacent Zhuguang granite form a distinctive basin-mountain landform in the Nanling region, South China. Research results suggest that the Zhuguang granite is a polyphase composite pluton developed on the metamorphic basement of the paleo-Tethys-paleo-Asian tectonic regime and possesses geometrical and kinematic features of hot-doming extensional tectonics at the middle-upper crustal level, which is considered as a magmatic complex that resulted from the collision-orogeny during the Indosinian Period, the subduction-consuming during the Early Yanshanian Period and the intra-continental basaltic underplating and deep-seated geodynamics during the Late Yanshanian Period. The Nanxiong basin is a Late Cretaceous-Paleogene asymmetric faulted basin that is characterized by a fault boundary on the northern side and an uncomformable boundary on the southern side, its deposit center was migrated gradually from south to north. Structural kinematic results on the basin-mountain coupled zone demonstrate that the ductile and the brittle rheological layers show a quite coincident sense of shear, implying that it is a continuous process from the ductile extensional deformation followed by locally sinistral strike-slip shear at a middle-crustal level to the brittle tensional deformation at a upper-crustal level during formation of granitic doming extensional tectonics. The Zhuguang granite and the Nanxiong faulted basin constructed a semi-graben tectonic system. Lithological and geochemical results suggest that the Late Triassic to Jurassic granitic bodies in the Zhuguang have some similar features: high SiO2, Al2O3, K2O contents, alkalinity index > 2.8, ANKC value > 1.1, LREE-enriched pattern with high REE contents, marked negative Eu anomalies, enrichment in Rb and Th, depletion in Ba and Nb, showing a K-rich and Al-rich calc-alkaline affinity, which suggest a continuous magmatic evolution from Late Triassic to Jurassic. Formation of Nanxiong basin and evolution of basin-mountain system were controlled both by the Zhuguang granitic-doming and the regional extensional tectonics. Development of the olivine basalt in the basin suggests that tension action was very strong during lava eruption. The magma-type zircon grains of basalt from the Nanxiong basin yielded the SHRIMP age of 96±1Ma, providing reliable geochronological constraint on the tectono-thermal event and basin-mountain evolution in the Nanling region, South China.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Department of Geology of Nanjing University, Granidoids with Different Ages and Metallogenesis in South China (in Chinese), Beijing: Science Press, 1981, 1–395.
Mo Zhuxun, Preliminary discussion on the origin mechanism of some composite granitic zones in South China, Geology of Guangdong (in Chinese with English abstract), 1987, 2(2): 1–12.
Grgnpmgmr: The granite research group of the Nanling Project of the Ministry of Geology and Mineral Resources, Granitic Geology, Its Origin and Metallogenesis in Nanling Region (in Chinese with English abstract), Beijing: Geol. Publ. House, 1989, 1–182
Yang Shufeng, Chen Hanlin, Zhang Baiyou et al., Petro-physics and Geotectonics of the Granitic Rocks in the Nanling Region (in Chinese with English abstract), Beijing: Encyclopedia Press of China, 1996, 1–113.
Lu Zhigang, Tao Kuiyuan, Xie Jiayin et al., The Volcanic Geology and Ore Deposits in the East China Continent (in Chinese with English abstract), Beijing: Geol. Publ. House, 1997, 1–118.
Chen Zuyi, Zhang Linsu, Chen Shukun et al., Fault-block movement: Development period of continental red beds and regional uranium metallogenesis in South China, Acta Geologica Sinica (in Chinese), 1983, 57(3): 294–303
Chen Yuehui, Chen Zhaobo, Chen Zuyi et al., Meso-Cenozoic Extensional Tectonics and Uranium Metallogenesis in Southeast China (in Chinese with English abstract), Beijing: Atomic Energy Publishing House, 1998, 1–262.
Deng Ping, Shu Liangshu, Tan Zhengzhong et al., Mesozoic tectonomagmatic activity and uranium metallogenetic sequence in mid-Nanling tectonic belt, Uranium Geology (in Chinese with English abstract), 2002, 18(5): 257–263.
Chen Yuehu, The fault detachment and uranium metallogenesis in Nanxiong region, South China, Uranium Geology (in Chinese with English abstract), 1994, 10(3): 168–174.
Pan Yongzheng, Zhang Jianxin, A search on the extensional tectonics and the uranium metallogenesis in the southern part of the Zhuguang granitic body, Uranium Geology (in Chinese with English abstract), 1994, 10(3): 138–143.
Zhou Xinmin, Li Wuxian, Origin of Late mesozoic igneous rocks in Southeastrn China: implications for lithosphere subduction and underplating of mafic magmas, Tectonophysics, 2000, 326: 269–287.
Shu Liangshu, Zhou Xinming, Late Mesozoic tectonic framework of Southeast China, Geological Review (in Chinese with English abstract), 2002, 48(3): 249–260.
Chen Peirong, Hua Renmin, Zhang Bangdong et al., Post-orogenic Early Yanshanian granotoids in the Nanling Region: Petrological constraints and geodynamic settings, Science in China, Ser. D, 2002, 32(4): 279–289.
Xing Guangfu, Yang Zhuliang, Sun Qianghui. et al., Early Jurassic layered mafic-ultramafic intrusions in Meizhou, Guangdong Province, Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry (in Chinese with English abstract), 2001, 20(3): 172–175.
Zhou Xinming, Li Wuxian, Late Mesozoic volcanic genesis in SE-China: a model combining lithosphere subduction with basaltic magma underplating, Progress in Natureal Science, 2000, 10(3): 240–247.
Ren Jishun, Niu Baogui, He Zhengjun et al., The geotectonic framework and its dynamic evolution of the eastern ChinaThe Lithospheric Texture and Tectonic-magmatic Evolution of eastern China (eds. Ren Jishun, Yang Weiran) (in Chinese with English abstract), Beijing: Atomic Energy Publishing House, 1998, 1–12.
GBGMR: Guangdong Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources, Regional Geology of Guangdong Province (in Chinese with English abstract), Beijing: Geol. Publ. House, 1988, 1–941.
Deng Ping, Shu Liangshu, Xiao Danhong, A study of the tectonic basement of the Late Mesozoic igneous rocks in southeastern China, Geological Journal of China Universities (in Chinese with English abstract), 2002, 8(2): 169–179.
GBGMR: Guangdong Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources, Geological Map of Guangdong Province, 1:1000000, four leaves (in Chinese), Beijing: Geol. Publ. House, 1988.
Li Sitian, Lu Fengxiang, Meso-Cenozoic Basin Evolution and Geochemical Dynamical Settings in East China and Adjacent Regions (in Chinese with English abstract), Wuhan: Publishing House of China Geological University, 1997.
Liu Hefu, Liang Huishe, Li Xiaoqing et al., Meso-Cenozoic taphrogeny basins and extensional basin-range coupling mechanism, Earth Science Frontiers (in Chinese with English abstract), 2000, (7): 477–486.
Li Xianhua, Zhou Hanwen, Liu Ying et al., Mesozoic shoshonitic intrusives in the Yangchun Basin, western Guangdong, and their tectonic significance: II Trace elements and Sr-Nd isotope, Geochemistry (in Chinese with English abstract), 2001, 30(1): 57-
Chen Peirong, Kong Xinggong, Ni Qisheng et al., Ascertainment and implication of the Early Yanshanian Bimodal volcanic association from South Jiangxi Province, Geological Review (in Chinese with English abstract), 1999, 45(Sup.): 734–741.
Hong Dawei, Wang Shiguang, Han Baofu et al., Classify of tectonic environments of alkalic granite and their discriminate indicators. Science in China, Series B, 1995, 25(4): 418–426.
Zhao Zhenhua, Bao Zhiwei, Zhang Baiyou, Geochemical features of the Mesozoic basaltic rocks in the southern Hunan, Science in China, Series D (in Chinese), 1998, 28(sup.): 7–14.
Sun, S. S., McDonough, W. F., Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: implications for mantle composition and processes (eds. A. D. Saunders, M. J. Norry), Magmatism in the Ocean Basins, Geol. Soc. London, 1989, Spec. Publ.(42): 313–345.
McDonough, W. F., Sun, S S., The composition of the earth, Chemical Geology, 1995, 120: 223–253.
Condie, K. C., Plate Tectonics and Crustal Evolution: Oxford, Pergamon Press, 1989, 1–476.
Faure, M., Sun Yan, Shu Liangshu et al., Wugong dome extensional tectonics, South China, Tectonophysics, 1996, 163(1-4): 77–106.
Shu Liangshu, Sun Yan, A study of simulating experiments for the deformation and microstructures of granite in the central part of Jiangnan belt, South China, Science in China, Series D, 1996, 39(1): 82–92.
Sun Yan, Shu Liangshu, Li Benliang et al., Experimental analysis of ductile-slip rheology in shallow structural level faults, Science in China, Series D, 2000,30(5): 519–525.
Shu Liangshu, Sun Yan, Wang Dezi et al., Mesozoic extensional tectonics in the Wugongshan area, South China, Science in China, Series D, 1998, 41(6): 601–608.
Wang Dezi, Shu Liangshu, Faure, M. et al., Mesozoic magmatism and granitic dome in the Wugongshan massif, Jiangxi Province and Their genetical relationship to the tectonic events in Southeast China, Tectonophysics, 2001, 339: 259–277.
Lin Wei, Faure, M., Monie, P. et al., Tectonics of SE China: New insights from the Lushan massif (Jiangxi Province), Tectonics, 2000, 19(5): 852–871.
Xu Xisheng, Deng Ping, O’Reilly, S. Y. et al., Single zircon LAM-ICPMS U-Pb dating of Guidong complex (SE China) and its petrogenetic significance, Chinese Science Bulletin, 2003, 48(17): 1892–1899.
Sun Yan, Shu Liangshu, Zhu Wenbin et al., Three evolutionary stages of the collision orogenic deformation in the Middle Yangzi region, Science in China, Series D, 2001, 44(11): 990–1001.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shu, L., Deng, P., Wang, B. et al. Lithology, kinematics and geochronology related to Late Mesozoic basin-mountain evolution in the Nanxiong-Zhuguang area, South China. Sci. China Ser. D-Earth Sci. 47, 673–688 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1360/03yd0113
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1360/03yd0113