Abstract
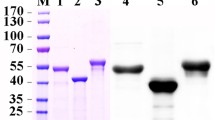
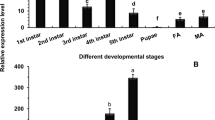
Cadherins belong to one of the families of animal glycoproteins responsible for calcium-dependent cell-cell adhesion. Recent literatures showed that the cadherin-like in midgut of several insects served as the receptor of Bt toxin Cry1A and the variation of cadherin-like is related to insect’s resistance to Cry1A. The full-length cDNA encoding cadherin-like of Helicoverpa armigera is cloned by degenerate PCR and RACE techniques and the gene was designated as BtR-harm, which is 5581 bp in full-length, encoding 1730 amino acid residues (BtR-harm was deposited in GenBank and the accession number is AF519180). Its predicted molecular weight and isoelectric point were 195.39 kDa and 4.23, respectively. The inferred amino acid sequence includes a signal sequence, 11 cadherin repeats, a membrane-proximal region, a transmembrane region and a cytoplasmic region. Sequence analysis indicated that the deduced protein sequence was most similar to the cadherin-like from Heliothis virescens with 84.2% identity and highly similar to three other lepidopteran cadherin from Bombyx mori, Manduca sexta and Pectinophora gossypiella, with the sequence identities of 60.3.6%, 57.5% and 51.0%, respectively. The cDNA encoding cadherin gene was expressed successfully in E. coli and the recombinant proteins can bind with Cry1Ac. Truncation analysis and binding experiment of BtR-harm revealed that the Cry1A binding region was a contiguous 244-amino acid sequence, which located between amino acid 1217 and 1461. Semi-quantitative RT-PCR analysis showed that BtR-harm was highly expressed in midgut of H. armigera, very low expressed in foregut and hindgut and was not expressed in other tissues. After H. armigera producing resistance to Cry1Ac, the expression quantity of BtR-harm significantly decreased in midgut of H. armigera. It is the first confirmation that BtR-harm can function as receptor of Cry1Ac in H. armigera and the binding region was located on a contiguous 244 amino acid sequence, suggesting that the decrease of expression quantity of BtR-harm is one of the main reasons for H. armigera resistance to Cry1Ac.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yu, Z. N., Bacillus thuringiensis (in Chinese), Beijing: Science Press, 1990.
Schnepf, E., Crickmore, N., Van Rie J. et al., Bacillus thuringiensis and its pesticidal crystal protein, Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev., 1998, 62:755–806.
Zhang, B.H., Feng, R., ed., Cotton Insect Resistance and Insect-resistant Cotton (in Chinese), Beijing: China Agricultural Science Press, 2000, 306–326.
Jia, S. R., Guo, S. D., An, D. C., ed., Transgenic Cotton (in Chinese), Beijing: Science Press, 2001, 15–57.
Huang, D.F., Lin, M., ed., Gene Engineering of Agricultural Microorganism, Beijing: Science Press, 2001
McGaughey, W. H., Insect resistance to the biological insecticide Bacillus thuringiensis, Science, 1985, 229: 193–195.
Tabashnik, B. E., Cushing, N. L., Finson, N. et al., Field development of resistance to Bacillus thuringiensis in diamonback moth (Lepidoptera: Plutellidae), J. Econ. Entomol., 1990, 83: 1671–1676
Liang, G. M., Tan, W. J., Guo, Y. Y., Study on screening and inheritance mode of resistance to Bt transgenic cotton in cotton bollworm, Acta Entomologica Sinica (in Chinese), 2000, 43(Suppl.): 57–62.
Liang, G. M., Tan, W. J., Guo, Y. Y., Study on the resistance screening and cross-resistance of Cotton Bollworm to Bacillus thuringiensis (Berliner), Scientia Agricultura Sinica (in Chinese), 2000, 33(4): 46–53.
Ferré, J., Van Rie, J., Biochemistry and genetics of insect resistance to Bacillus thuringiensis, Annu. Rev. Entomol., 2002, 47: 501–533.
Vadlamudi, R. K., Ji, T. H., Bulla, L. A. Jr., A specific Binding Protein from Manduca sexta for the insecticidal toxin of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. Berliner, J. Biol. Chem., 1993, 268: 12334–12340.
Vadlamudi, R. K., Weber, E., Ji, I. et al., Cloning and expression of a receptor for an insecticidal toxin of Bacillus thuringiensis, J. Biol. Chem., 1995, 270: 5490–5494.
Takeichi, M., Cadherin cell adhesion receptors as a morphogenetic regulator, Science, 1991, 251: 1451–1455.
Takeichi, M., Morphogenetic roles of classic cadherins, Curr. Opin. Cell Biol., 1995, 7: 619–627.
Vleminckx, K., Vakaet, L., Jr Mareel, M. et al., Genetic manipulation of E-cadherin expression by epithelial tumor cells reveals an invasion suppressor role, Cell, 1991, 66: 107–119.
Dorsch, J. A., Candas, M., Griko, N. B. et al., Cry1A toxins of Bacillus thuringiensis bind specifically to a region adjacent to the membrane-proximal extracellular domain of BT-R1 in Manduca Sexta: Involvement of a cadherin in the entomopathogenicity of Bacillus thuringiensis, Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol., 2002, 32: 1025–1036.
Hara, H., Atsumi, S., Yaoi, K. et al., A cadherin-like protein functions as a receptor for Bacillus thuringiensis Cry1Aa and Cry1Ac toxins on midgut epithelial cells of Bombyx mori larvae, FEBS Lett., 2003, 538(1–3): 29–34.
Nagamatsu, Y., Toda, S., Yamaguchi, F. et al., Identification of Bombyx mori midgut receptor for Bacillus thuringiensis insecticidal CryIA(a) toxin, Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem., 1998, 62(4): 718–726.
Gahan, L. J., Gould, F., Heckel, D. G., Identification of a gene associated with Bt resistance in Heliothis virescenes, Science, 2001, 293: 857–860.
Morin, S., Biggs, R. W., Sisterson, M. S. et al., Three cadherin alleles associated with resistance to Bacillus thuringiensis in pink bollworm, PNAS, 2003, 100(9): 5004–5009.
Liang, G. M., Tan, W. J., Guo, Y. Y., An improvement in the technique of artificial raring cotton bollworm, Plant Protection (in Chinese), 1999, 25: 15–17.
Luo, K., Lu, Y. J., Adang, M. J., A 106-kDa form of aminopeptidase is a receptor for Bacillus thuringiensis Cry1C deltaen-dotoxin in the brush border membrane of Manduca Sexta, Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol., 1996, 26: 33–40.
Wang, G. R., Liang, G. M., Wu, K. M. et al., Cloning and sequencing of a gene encoding aminopeptidase N in the mid-gut of Helicoverpa armigera (Hübner), Agricultural Sciences in China, 2003, 2(7): 760–767.
Sambrook, K. J., Fritsch, E. F., Maniatis, T., Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, 2nd ed., New York: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, 1989.
Pagni, M., Iseli, C., Junier, T. et al., TrEST, trGEN and Hits: Access to databases of predicted protein sequences, Nucleic Acids Research, 2001, 29: 148–151.
Nielsen, H., Engelbrecht, J., Brunak, S., von Heijne, G., Identification of prokaryotic and eukaryotic signal peptides and prediction of their cleavage sites, Protein Engineering, 1997, 10: 1–6.
Wang, G. R., Wu, K. M., Guo, Y. Y., Cloning, expression and immunocytochemical localization of a general odorant-binding protein gene from Helicoverpa armigera (Hübner), Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol., 2003, 33: 115–124.
Cao, W. H., Dong, Y., Zhang, J. S., Chen, S. Y., Characterization of an ethylene receptor homolog gene from rice, Science in China, Ser. C, 2003, 46 (4): 370–378.
Hofte, H., Whigeley, H. R., Insecticidal crystal proteins of Bacillus thuringiensis, Microbiol. Rev., 1989, 53: 242–255.
English, L., Slatin, S. L., Mode of action of delta-endotoxins from Bacillus thuringiensis: A comparison with other bacterial toxins, Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol., 1992, 22(1): 1–7.
Gill, S. S., Cowles, E. A., Pietrantonio, P. V., The mode of action of Bacillus thuringiensis endotoxins, Annu. Rev. Entomol., 1992, 37: 615–636.
Knight, P. J., Knowles, B. H., Ellar, D. J., Molecular cloning of an insect aminopeptidase N that serves as a receptor for Bacillus thuringiensis CryIA(c) toxin, J. Biol. Chem., 1995, 28: 270(30): 17765–17770.
Garner, K. J., Hiremath, S., Lehtoma, K., Valaitis, A. P., Cloning and complete sequence characterization of two gypsy moth aminopeptidase-N cDNAs, including the receptor for Bacillus thuringiensis Cry1Actoxin, Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol., 1999, 29(6): 527–535.
Wu, K., Guo, Y., Geographic variation in susceptibility of Helicoverpa armigera (Lepidoptra: Noctuidae) to Bt insecticidal protein in China, Journal of Economic Entomology, 1999, 92(2): 273–278.
Wu, K., Guo, Y., Lv, N. et al., Resistance monitoring of Helicoverpa armigera (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) to Bt insecticidal protein in China, Journal of Economic Entomology, 2002, 95(4): 826–831.
Environmental Protection Agency, The Environmental Protection Agency’ White Paper on Bt Plant-Pesticide Resistance Management, Washington: EPA Publication, 1998, 739-S-98-001.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, G., Wu, K., Liang, G. et al. Gene cloning and expression of cadherin in midgut of Helicoverpa armigera and its Cry1A binding region. Sci. China Ser. C.-Life Sci. 48, 346–356 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1360/03yc0273
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1360/03yc0273