Abstract
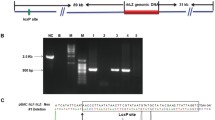
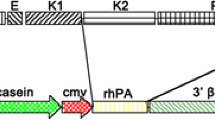
Human lysozyme is a 130-aa (amino acid) alkaline polypeptide, and has both anti-bacterial and anti-viral properties which make it an important component of human natural immunity system. As a first step toward the ultimate goal of improving the anti-bacterial properties of bovine and ovine milk, a transgenic mouse that contains the genomic DNA sequence of the human lysozme gene has been generated for the first time. From 83 mice generated by microinjection, a total of 6 positive transgenic mice were identified by PCR and Southern blot. F1 mice positive for transgene in lines were also detected by PCR. This shows that transgene could be transmitted from founder transgenic mice to their offspring. Recombinant human lysozyme (rHlys) was found in the whey of 3 female positive transgenic mice by Western blot. The highest concentration of rHlys for transgenic mice was 0.2 mg/mL. The antibacterial activity of the whey for transgenic mice was highly enhanced up to 0.4 times as much as that of human, while that of non-transgenic mouse was very low. Although the lysozyme activity of transgenic mice is still lower than that of human, the rHlys exhibits the same specific activity as that of human lysozyme. It provides a strong basis for further studies into the possible application of rHlys express in mammary gland.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fleming, A., On a remarkable bacteriolitic element found in tissues and secretions, Proc. Roy. Soc. London, 1922, B93: 306–317.
Lonnerdal, B., Biochemistry and physiological function of human milk proteins, Am. J. Clin. Nutr., 1985, 42: 1299–1317.
Maga, E., Anderson, G., Huang, M. et al., Expression of human lysozyme mRNA in the mammary gland of transgenic mice, Transgenic Research, 1994, 3: 36–42.
Maga, E., Anderson, G., Murray, J., The effect of mammary gland expression of human lysozyme on the properities of milk from transgenic mice, J. Dairy Sci., 1995, 78: 2645–2652.
Brinster, R. L., Allen, J. M., Behringer, R. R. et al., Introns increase transcriptional efficiency in transgenic mice, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 1988, 85(3): 836–840.
Palmiter, R. D., Sandgren, E. P., Avarbock, M. R. et al., Heterologous introns can enhance expression of transgene in mice, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 1991, 88: 478–482.
Kim, S. J., Sohn, B. H., Jeong, S. et al., High-level expression of human lactoferrin in milk of transgenic mice using genomic lactoferrin sequence, J. Biochem. (Tokyo), 1999, 126(2): 320–325.
Shugar, D., Measure of lysozyme activity and the ultraviolet inactivation of lysozyme, Biochem. Biophys. Acta, 1952, 8: 302.
Talbot, D., Collis, P., Antoniou, M. et al., A dominant control region from the human beta-globin locus conferring intergration site-independent gene expression, Nature, 1989, 338: 352–355.
Huang, Y., Huang, Y., Huang, Z., High expression of human serum albumin in milk of transgenic mice directed by the goat β-casein gene promoter region, Chinese Science Bulletin, 2001, 46(7): 582–586.
Roberts, B., DiTullio, P., Vitale, J. et al., Cloning of the goat beta-casein-encoding gene and expression in transgenic mice, Gene, 1992, 121: 255–262.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, Z., Fan, B., Dai, Y. et al. Expression of recombinant human lysozyme in the milk of transgenic mice. Chin.Sci.Bull. 48, 2331–2335 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1360/03wc0334
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1360/03wc0334