Abstract
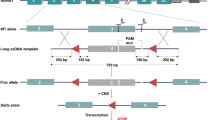
Smads is a new gene family in transforming growth factor-β (TGF- β) signaling pathway. Smad2 mutated in multiple human tumors and may be a candidate tumor suppressor gene. Targeted disruption of murine Smad2 gene resulted in embryonic lethality at E6.5. To study the function of Smad2 in vertebrate organgenesis and tumorigenesis, we constructed the Smad2 conditional targeting vector in which two LoxP sequences were placed to flank the sequences encoding the C terminal functional domain of Smad2. The validity of the LoxP sites in the targeting construct was tested in E. coli that express the Cre recombinase constitutively. The vector was electroporated into ES cells and 3 targeted ES cell clones were obtained by Southern blot screening. Targeted ES cells were introduced into C57BL/6J blastocysts by microinjection to generate germ-line chimeras. Genotyping analysis showed that 2 progeny among these chimeras carried the Smad2 conditional targeted allele. The establishment of Smad2 conditional gene targeting mouse has laid a solid foundation for producing the tissue specific Smad2 gene knockout mice.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Heldin, C. H., Miyazono, K., ten Dijke, P., TGF-beta signalling from cell membrane to nucleus through SMAD proteins, Nature, 1997, 390(6659): 465–471.
Yang, X., Huang, P. T., Huang, C. F., Progress in the function of Smad genes, Chin. J. Biochem. Mol. Biol. (in Chinese), 2000, 16(2): 145–150.
Eppert, K., Scherer, S. W., Ozcelik, H. et al., MADR2 maps to 18q21 and encodes a TGF β-regulated MAD-related protein that is functionally mutated in colorectal carcinoma, Cell, 1996, 86: 543–552.
Nomura, M., Li, E., Smad2 role in mesoderm formation, left-right patterning and craniofacial development, Nature, 1998, 393: 786–790.
Waldrip, W. R., Bikoff, E. K., Hoodless, P. A. et al., Smad2 signaling in extraembryonic tissues determines anteriorposterior polarity of the early mouse embryo, Cell, 1998, 92: 797–808.
Weinstein, M., Yang, X., Li, C. et al., Failure of egg cylinder elongation and mesoderm induction in mouse embryos lacking the tumor suppressor Smad2, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 1998, 95: 9378–9383.
Gu, H., Marth, J. D., Orban, P. C. et al., Deletion of a DNA polymerase beta gene segment in T cells using cell type-specific gene targeting, Science, 1994, 265: 103–106.
Abremski, K., Hoess, R., Sternberg, N., Studies on the properties of P1 site-specific recombination: evidence for topologically unlinked products following recombination, Cell, 1983, 32(4): 1301–1311.
Yang, X., Huang, P. T., Huang, C. F., Progress of the gene targeting in mouse, Chinese Science Bulletin, 2000, 45(15): 1584–1592.
Yang, X., Li, C., Deng, C., The tumor suppressor SMAD4/DPC4 is essential for epiblast proliferation and mesoderm induction in mice, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 1998, 95: 3667–3672.
Rucker, E. B., Piedrahita, J. A., Cre-mediated recombination at the murine whey acidic protein (mWAP) locus, Mol. Reprod. Dev., 1997, 48: 324–331.
Zhou, J., Yang, X., Sun, Y. S. et al., Production of a kind of G418 resistance fibroblast feeder layers, Bull. Acad. Mil. Med. Sci., 2001, 25(1): 59–61.
Maniatis, T., Fritsch, E. F., Sambrook, J., Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, New York: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, 1989.
Stewart, C. L., Production of chimeras between embryonic stem cells and embryos, Meth. Enzymol., 1994, 225: 823–855.
Postic, C., Shiota, M., Niswender, K. D. et al., Dual roles for glucokinase in glucose homeostasis as determined by liver and pancreatic β cell-specific gene knock-outs using Cre recombinase, J. Biol. Chem., 1999, 274(1): 305–315.
Lakso, M., Pichel, J. G., Gorman, J. R. et al., Efficient in vivo manipulation of mouse genomic sequences at the zygote stage, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 1996, 93: 5860–5865.
Takagi, Y., Koumura, H., Futamura, M. et al., Somatic alterations of the SMAD-2 gene in human colorectal cancers, Br. J. Cancer, 1998, 78(9): 1152–1155.
Yakicier, M. C., Irmak, M. B., Romano, A. et al., Smad2 and Smad4 gene mutations in hepatocellular carcinoma, Oncogene, 1999, 18(34): 4879–4883.
Tsujiuchi, T., Sasaki, Y., Tsutsumi, M. et al., Mutations of the smad2 and smad4 genes in lung adenocarcinomas induced by N-nitrosobis (2-hydroxypropyl) amine in rats, Br. J. Cancer, 1998, 78(9):1152–1155.
Prunier, C., Mazars, A., Noe, V. et al., Evidence that Smad2 is a tumor suppressor implicated in the control of cellular invasion, J. Biol. Chem., 1999, 274(33): 22919–22922.
Osaki, M., Taukazaki, T., Ono, N. et al., cDNA cloning and chromosomal mapping of rat Smad2 and Smad4 and their expression in cultured rat articular chondrocytes, Endocr J., 1999, 46(5): 695–701.
Ferguson, C. M., Schwarz, E. M., Reynolds, P. R. et al., Smad2 and 3 mediate transforming growth factor-betal-induced inhibition of chondrocyte maturation, Endocrinology, 2000, 141(12): 4728–4735.
Liu, A. M., Shang, K. G., Mutation of hprt gene in murine embryonic stem cell, Heredity, 1994, 16(5): 1–5.
Chen, W. S., Han, R., Shang, K. G., Formation of germline chimeras from murine embryonic stem cell lines, Acta Genetica Sinica, 1999, 26(2): 126–134.
Yang, X., Sun, Y. S., Zhou, J. et al., Establishment of murine Smad5 double knockout ES cells and the studies on their properties, Science in China (in Chinese), Ser. C, 2000, 30(6): 577–584.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, J., Cheng, X., Sun, Y. et al. Establishment of Smad2 conditional gene targeting mice based on the Cre-LoxP system. Sci. China Ser. C.-Life Sci. 45, 129–137 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1360/02yc9015
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1360/02yc9015