Abstract
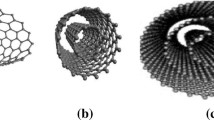
The recent progresses on constructing organic nanostructures from the self-assembly of melamine and barbituric acid derivatives are reviewed. By mediating the chemical microenvironment during the self-assembly, the information contained in the molecular components can be expressed at different levels, thus resulting in the formation of different organic nanostructures. When the assembly is carried out in anhydrous chloroform, a kind of asymmetric layered structure with a d value of 4.1 nm is obtained. When a little amount of polar solvent such as alcohol is contained in the chloroform, organic nanotubes with diameter of 6 nm and length of several hundreds of nanometers are observed. After being treated by appropriate polar solvents, the nanotubes are induced into supercoils with diameter of about 300 nm and length of several tens of microns. The sensitivity of the self-assembly process origins from the weak noncovalent intermolecular interactions between the molecular components. The enthalpy change of such interactions is pretty small, so slight change of the molecular structure or microenvironment could affect the primary equilibrium, resulting in the rearrangement and transformation of the supramolecular structure.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lehn, J.-M., Supraniolecular Chemistry, Weiheim: VCH, 1995.
Whitesides, G. M., Mathias, J. P., Seto, C. T., Molecular self-assembly and nanochemistry: A chemical strategy for the synthesis of nanostructures, Science, 1991, 254: 1312–1319.
Cao, Y. W., Chai, X. D., Chen, S. G. et al., Anew series of nonlinear optical organic materials with molecular receptor: design and synthesis, Synth. Met., 1995, 71: 1733–1734.
Johal, M. S., Cao, Y. W., Chai, X. D. et al., Spontaneously self-assembled polar asymmetric multilayers formed by complementary H-bonds, Chem. Mater., 1999, 11: 1962–1965.
Cao, Y. W., Chai, X. D., Li, T. J. et al., Self-patterned H-bond supramolecular self-assembly, Chem. Commun., 1999, 16: 1605–1606.
Ren, Y. Z., Chen, S. G., Chai, X. D. et al., Effect of interlayer molecular recognition on the structural and nonlinear optical properties of alternating Langmuir-Blodgett films of two complementary molecular components, Synth. Met., 1995, 71: 1709–1710.
Ren, Y. Z., Zhao, B., Chai, X. D. et al., Structural study on the alternating Langmuir-Blodgett films deposited with two complementary barbituric acid and melamine derivatives, Thin Solid Films, 1997, 293: 170–174.
Zerkowski, J. A., MacDonald, J. C., Seto, C. T. et al., Design of organic structures in solid state: Molecular tapes based on the network of hydrogen bonds present in the cyanuric acid-melamine comolex, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1994, 116: 2382–2387.
Yang, W. S., Chai, X. D., Li, T. J. et al., From achiral molecular components to chiral supermolecules and supercoil self-assembly, Chem. Eur. J., 1999, 5: 1144–1149.
Yang, W. S., Jiang, Y. S., Zhuang, J. Q. et al., π-π interactions in the self-assembly of melamine and barbituric acid derivatives, Science in China, Series B, 2001, 44(5): 478–485.
Yang, W. S., Lu, R., Chai, X. D. et al., Spectral study on the formation of a self-assembled mesoscopic supercoil, Supramolecular Science, 1998, 5: 741–745.
Yang, W. S., Chai, X. D., Tian, Y. Q. et al., Temperature-dependent FTIR study of a supramolecular mesophase from the self-assembly of melamine and barbituric acid derivatives, Liquid Crystals, 1997, 22: 579–583.
Chai, X. D., Yang, W. S., Cao, Y. W. et al., Formation of nanocolumn self-assembly by solvent polarity control, J. Vac. Sci. & Technol.B, 1997, 15: 1425–1428.
Lu, R., Jiang, Y. S., Duo, J. Q. et al., Aggregation behaviors of light-active barbituric acid molecular components in solution, Supramolecular Science, 1998, 5: 737–740.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhuang, J., Wang, G., Lü, N. et al. Chemical microenvironment mediated formation of organic nanostructures from self-assembly of melamine and barbituric acid derivatives. Sc. China Ser. B-Chem. 45, 509–514 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1360/02yb9067
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1360/02yb9067