Abstract
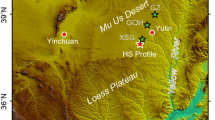
The history of groundwater recharge and climatic changes during the last 1000 years has been estimated and reconstructed using environmental chloride from unsaturated zone profile in the southeast Badain Jaran Desert, NW China. By using a steady-state model for duplicate unsaturated zone chloride profiles, the long-term recharge at the site was estimated to be 1.3 mm yr−. From one profile, which reached the water table, the climatic change events of 10–20 years duration were well preserved. There were 3 wet phases and 4 dry episodes during the recent 800 years according to the peaks and troughs of recharge rate calculated via chloride concentration and moisture content. There was a dry episode before 1290 AD. At ca. 1500–1530 AD, which is an important date, there was an abrupt change from drought to wet conditions. At the beginning of the 1800s, local climate changed from wet to dry occurred and subsequently deteriorated over the past 200 years. The unsaturated profile was compared with the Guliya ice core records. The agreement of wet and dry phases from 1200 to 1900 AD is quite good, whilst trends diverged during the last 100 years. It seems that the large-scale climate difference took place between mountain regions and the desert basin in NW China during the 20th century, which closely correspond to the water table reduction of some 1 metre.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Norin, E. S. H., Central Asia Atlas, Memoir on Maps, Vol. III, Stockholm: Statens Etnografiska Museam, 1980, 94–110.
Yu, S., Li, B., Cai, W., Research on Badain Jaran Desert and Gobi in the western Inner Mongliar, Desert-Control Research, 1962, 3: 96–107.
Sun, P., Sun, D., Study on the hydrogeology of western Inner Mongolia, Desert Control Research, 1962, 3: 245–317.
Geyh, M. A., Gu, W. Z., Jakel, D., Groundwater recharge study in the Gobi Desert, China, Geowissenschaften, 1996, 7/8: 279–280.
Hofmann, J., The lakes in the SE part of Badain Jaran Shamo, their limnology and geochemistry, Geowissenschaften, 1996, 7/8: 275–278.
Jakel, D., The Badain Jaran Desert: its origin and development, Geowissenschaften, 1996, 7/8: 272–274.
Pachur, H. J., Wunnemann, B., Zhang, H. C., Lake evolution in the Tengger Desert, Northwestern China, during the last 40000 years, Quaternary Research, 1995, 44: 171–180.
Wunnemann, B., Pachur, H. J., Zhang, H. C., Climatic and environmental changes in the deserts of Inner Mongolia China since the Late Pleistocene, in Quaternary Deserts and Climates Changes (eds. Alsharhan, A. S., Glennie, K. W., Whittle, G. L. et al.), Rotterdam: Balkeman, 1998, 381–394.
Dong, G., Gao, Q., Zou, X., The climatic change during the last Pleistocene in the Badain Jaran Desert, Chinese Science Bulletin, 1995, 40(13): 1214–1218.
An, Z., Kukla, G. L., Porter, S. C. et al., Magnetic susceptibility evidence of monsoon variation on the loess plateau of central China during the last 130000 years, Quaternary Research, 1991, 36: 29–36.
Zhang, H. C., Ma, Y., Wunnemann, A., Holocene climatic record from arid northwestern China, Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2000, 162: 389–401.
Fan, X., The characteristics of groundwater and environment problems resulted from water resources development in the arid areas of northwest China, Hydrogeology and Engineering Geology, 1990, 15: 12–16.
Ma, J. Z., Sustainable exploitation and utilization of water resources in the inland river basin of arid northwest China, Chinese Geographical Science, 1997, 7: 38–42.
Allison, G. B., Gee, G. W., Tyler, S. W., Vadose-zone techniques for estimating groundwater in arid and semi arid regions, Soil Sci. Am. J., 1994, 58: 6–14.
Edmunds, W. M., Recharge to groundwater in arid and semi-arid regions from the Holocene to the present, in Quaternary Deserts and Climates Changes (eds. Alsharhan, A. S., Glennie, K. W., Whittle, G. L. et al.), Rotterdam: Balkeman, 1998, 419–431.
Edmunds, W. M., Walton, N. R. G., A geochemical and isotope approach to recharge evaluation in semi-arid zones-past and present. IAEA, Application of Isotope techniques in Arid Zone Hydrology, Proc. Advisory Group Meeting, Vienna, 1978, 47–68.
Allison, G. B., Hughes, M. W., The use of environmental chloride and tritium to estimate total recharge of an unconfined aquifer, Aust. J. Soil Res., 1978, 16: 181–195.
Edmunds, W. M., Gaye, C. B., Fontes, J. C., A record of climatic and environmental change contained in interstitial waters from the unsaturated zone of northern Senegal, In Isotope Techniques in Water Resources Development 1991, Proceedings, Symposium of the IAEA, Vienna: IAEA, 1992, 533–549.
Cook, P. G., Edmunds, W. M., Gaye, C. B., Estimating paleorecharge and paleoclimate from unsatured zone profiles, Water Resour. Res., 1992, 28: 2721–2731.
Zhu, Z., Desert and Desertification Rehabilitation in China, Beijing: Chinese Environmental Science Press, 1999, 137–142.
Zhang, J., Lin, Z., Climate of China, New York: Wiley, 1992.
Darling, W. G., Talbot, J. C., Extraction method for the isotopic analysis of porewaters. Rep. WD/89/66, British Geological Survey, England: Wallingford, 1989, 13.
Tandia, A. A., Revue critique des methods d’evaluation de la recharge des nappes. Contribution de approche geochemique et isotopique, Louga Nord Senegal, University of Daker, 1990, 138.
Barnes, C. J., Allison, G., The distribution of deuterium and 18O in dry soil, l.Theory, J. Hydrol., 1983, 60: 141–156.
Edmunds, W. M., Gaye, C. B., Kinniburgh, D. G., Solute profile techniques for recharge estimation in semi-arid and arid terrain, in Estimation of Natural Groundwater Recharge (ed. Simmers, I.), Dordrecht: Reidel, 1988, 136–157.
Yao, T., Qing, D., Tian, L. et al., Temperature and precipitation fluctuations in Tibetan Plateau during the last 2000 years: record in Guliya ice core, Science in China, Ser. D, 1996, 26(4): 348–353.
Shi, Y., Yao, T., Yang, B., 10 a scale climatic change during the last 2000 a recorded in Guliya ice core and compared to East China references records, Science in China, Ser. D, 1999, 29: 79–86.
Zhang, P., The Climatic Change in China, Jinan: Shandong Scientific and Technique Press, 1996, 231–436.
Shi, Y. F., Zhang, X. S., The influence of climate changes on the water resources in the arid areas of northwest China, Science in China, Ser. B, 1995, 25: 968–977.
Chen, L., Shao, Y., Zhang, Q., The research on climatic change during the recent 40 a, J. Application Meteorology, 1991, 2(2): 164–173.
Herczeg, A. L., Edmunds, W. M., Inorganic ions as tracers, in Environmental Tracers in Subsurface Hydrology, CSIRO Land and water (eds. Cook, P. G., Herczeg, A. L.), Glen Osmond, Austrilia, 2000, 31–76.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, J., Li, D., Zhang, J. et al. Groundwater recharge and climatic change during the last 1000 years from unsaturated zone of SE Badain Jaran Desert. Chin.Sci.Bull. 48, 1469–1474 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1360/02wd0262
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1360/02wd0262