Abstract
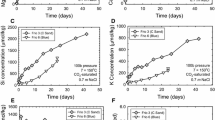
Nontronite NAu-1 was exposed to moderate temperature and pressure conditions (250 and 300°C at 100 MPa pressure) in KCl brine to simulate burial diagenetic systems over accelerated time periods appropriate for laboratory experiments. Powder X-ray diffraction and transmission electron microscopy analysis of the coexisting mixed-layer and discrete 10 Å clay reaction products, and inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry analysis of the remaining fluids, indicated that the clay retained octahedral Fe and was identified as Fe-celadonite. The release of Fe from smectite during burial diagenesis has been hypothesized as a mechanism for magnetite authigenesis. High Al activity relative to Fe may be critical to the formation of an aluminous illite and any associated authigenic magnetite.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abercrombie, H., Hutcheson, I., Bloch, J., and de Caritat, P. (1994) Silica activity and the smectite illite reaction. Geology, 22, 539–542.
Ahn, H. and Peacor, D.R. (1986) Transmission and analytical electron microscopy of the smectite-to-illite transition. Clays and Clay Minerals, 34, 165–179.
Allen, V.T. and Scheid, V.E. (1946) Nontronite in the Columbia river region. American Mineralogist, 31, 294–312.
Altaner, S.P. and Ylagan, R.F. (1997) Comparison of structural models of mixed-layer illite/smectite and reaction mechanisms of smectite illitization. Clays and Clay Minerals, 45, 517–533.
Andrews, A.J. (1980) Saponite and celadonite in layer 2 basalts, DSDP Leg 37. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 73, 323–340.
Banerjee, S., Elmore, R.D., and Engel, M.H. (1997) Chemical remagnetization and burial diagenesis: Testing the hypothesis in the Pennsylvanian Belden Formation, Colorado. Journal of Geophysical Research. 102, 24,825–24,842.
Bartels, J.M., editor (1996) Methods of Soil Analysis: Part 3 Chemical Methods. Soil Science of America, Madison, Wisconsin.
Blumstein, A.M., Elmore, R.D., Engel, M.H., Elliot, C., and Basu, A. (2004) Paleomagnetic dating of burial diagenesis in Mississippian carbonates, Utah. Journal of Geophysical Research, 109, 1–16.
Brothers, L.A., Engel, M.H., and Elmore, R.D. (1996) The late diagenetic conversion of pyrite to magnetite by organically complexed ferric iron. Chemical Geology, 130, 1–14.
Chevrier, V., Poulet, F., and Bibring, J.-P. (2007) Early geochemical environment of Mars as determined from thermodynamics of phyllosilicates. Nature, 448, 60–63.
Chipera, S. and Bish, D. (2001) Baseline studies of the Clay Minerals Society Source Clays: Powder X-ray diffraction analyses. Clays and Clay Minerals, 49, 398–409.
Cogoini, M. (2001) Magnetic minerals: Understanding the processes of formation in soils and clays and identifying their presence in the rock record. PhD thesis, University of Oklahoma, Norman, Oklahoma, USA.
D’Antonio, M. and Kristensen, M.B. (2005) Hydrothermal alteration of oceanic crust in the West Phillippine Sea Basin (Ocean Drilling Program Leg 195, Site 1201): inferences from a mineral chemistry investigation. Mineralogy and Petrology, 83, 87–112.
Dainyak, L.G., Drits, V.A., Zviagina, B.B., and Lindgreen, H. (2006) Cation redistribution in the octahedral sheet during diagenesis of illite-smectites from Jurassic and Cambrian oil source rock shales. American Mineralogist, 91, 589–603.
Dekov, V.M., Kamenov, G.D., Stummeyer, J., Thiry, M., Savelli, C., Shanks, W.C., Fortin, D., Kuzmann, E., and Vértes, A. (2007) Hydrothermal nontronite formation at Eolo Seamount (Aeolian volcanic arc, Tyrrhenian Sea). Chemical Geology, 245, 103–119.
Dennie, D., Elmore, R.D., Deng, J., Manning, E., and Pannalal, J. (2012) Palaeomagnetism of the Mississippian Barnett Shale, Fort Worth Basin, Texas. In: Remagnetization and Chemical Alteration of Sedimentary Rocks (R.D. Elmore, A.R. Muxworthy, M. Aldana, and M. Mena, editors). Special Publications, 371, Geological Society, London (DOI: https://doi.org/10.1144/SP371.10).
Dong, H., Peacor, D., and Freed, R.L. (1997) Phase relations among smectite, R1 illite-smectite, and illite. American Mineralogist, 82, 379–391.
Drief, A., Martinez-Ruiz, F., Nieto, F., and Sanchez, N.V. (2002) Transmission electron microscopy of smectite in K-enriched seawater solution at 50°C and basic pH. Clays and Clay Minerals, 50, 746–756.
Drits, V.A., Zviagina, B.B., McCarty, D.K., and Salyn, A.L. (2010) Factors responsible for crystal-chemical variations in the solid solutions from illite to aluminoceladonite and from glauconite to celadonite. American Mineralogist, 95, 348–361.
Eberl, D.D., Whitney, G., and Khoury, H. (1978) Hydrothermal reactivity of smectite. American Mineralogist, 63, 401–409.
Ehlmann, B.L., Mustard, J.F., Murchie, S.L., Bibring, J.P., Meunier, A., Fraeman, A.A., and Langevin, Y. (2011) Subsurface water and clay mineral formation during the early history of Mars. Nature, 479, 53–60.
Elliott, W.C., Osborn, S., O’Brien, V., Elmore, R.D., Engel, M.H., and Wampler, M. (2006) A comparison of K-Ar ages of diagenetic illite and the age implications of a remagnetization in the Cretaceous Marias River Shale, Disturbed Belt, Montana. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 89, 92–95.
Elmore, R.D. and Leach, M.C. (1990) Remagnetization of the Rush Springs Formation, Cement, Oklahoma: Implications for dating hydrocarbon migration and aeromagnetic exploration. Geology, 18, 124–127.
Elmore, R.D., Engel, M.H., Crawford, L., Nick, K., Imbus, S., and Sofer, Z. (1987) Evidence for a relationship between hydrocarbons and authigenic magnetite. Nature, 325, 428–430.
Elmore, R.D., Kelley, J., Evans, M., and Lewchuk, M. (2001) Remagnetization and Orogenic Fluids: Testing the hypothesis in the central Appalachians. Geological Journal International, 144, 568–576.
Eslinger, E. and Pevear, D. (1988) Clay Minerals for Petroleum Geologists and Engineers. SEPM Short Course No. 22.
Fernández-Caliani, J.C., Crespo, E., Rodas, M., Barrenechea, J.F., and Luque, F.J. (2004) Formation of nontronite from oxidative dissolution of pyrite disseminated in Precambrian felsic metavolcanics of the southern Iberian Massif (Spain). Clays and Clay Minerals, 52, 106–114.
Ferrage, E., Vidal, O., Mosser-Ruck, R., Cathelineau, M., and Cuadros, J. (2011) A reinvestigation of smectite illitization in experimental hydrothermal conditions: Results from X-ray diffraction and transmission electron microscopy. American Mineralogist, 96, 207–223.
Gill, J.D., Elmore, R.D., and Engel, M.H. (2002) Chemical remagnetization and clay diagenesis: Testing the hypothesis in the Cretaceous sedimentary rocks of northwestern Montana, Physics and Chemistry of the Earth,27/25-31, 1131–1139.
Guthrie, D.G. and Veblen, D.R. (1989) High Resolution Transmission Electron Microscopy of mixed layer illite/ smectite: Computer simulation. Clays and Clay Minerals, 37, 1–11.
Güven, N. and Huang, W. (1991) Effects of octahedral Mg and Fe substitutions on hydrothermal illitization reactions. Clays and Clay Minerals, 39, 387–399.
Henning, K. and Störr, M. (1986) Electron Micrographs (TEM, SEM) of clays and clay minerals. Akademi-Verlag, Berlin, Germany.
Hirt, A., Banin, A., and Gehring, A. (1993) Thermal generation of ferromagnetic minerals from iron-enriched smectites. Geophysics Journal International, 115, 1161–1168.
Holloway, J.R. (1984) Graphite-CH4-H2O-CO2 equilibria at low-grade metamorphic conditions. Geology, 12, 455–458.
Hower, J., Eslinger, W.V., Hower, M., and Perry, E.A. (1976) Mechanism of burial metamorphism of argillaceous sediments: I. Mineralogical and chemical evidence. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 87, 725–737
Huang, W., Longo, J.M., and Pevear, D.R. (1993) An experimentally derived kinetic model for smectite-to-illite conversion and its use as a geothermometer. Clays and Clay Minerals, 41, 162–177.
Hugget, J.M., Gale, A.S., and Clauer, N. (2001) The nature and origin of non-marine 10 Å clay from the Late Eocene and Early Oligocene of the Isle of Wright (Hampshire Basin), UK. Clay Minerals, 36, 447–464.
Inoue, A. (1983) Potassium fixation by clay minerals during hydrothermal treatment. Clays and Clay Minerals, 31, 81–92.
Inoue, A., Kohyama, N. Kitagawa, R., and Watanabe, T. (1987) Chemical and morphological evidence for the conversion of smectite to illite. Clays and Clay Minerals, 35, 111–120.
Jackson, M., McCabe, C., Ballard, M.M., and Van der Voo, R. (1988) Magnetite authigenesis and diagenetic paleotemperatures across the northern Appalachian basin. Geology, 16, 592–595.
Jaisi, D.P., Dong, H., and Morton, J.P. (2008) Partitioning of Fe(II) in reduced nontronite (NAu-2) to reactive sites: reactivity in terms of Tc(VII) reduction. Clays and Clay Minerals, 56, 175–189.
Jaisi, D.P., Eberl, D.D., Dong, H., and Kim, J. (2011) The formation of illite from nontronite by mesophilic and thermophilic bacterial reaction. Clays and Clay Minerals, 59, 21–33.
Katz, B., Elmore, R.D., Engel, M.H., Cogoini, M., and Ferry, S. (2000) Associations between burial diagenesis of smectite, chemical remagnetization and magnetite authigenesis in the Vocontian Trough of SE-France. Journal of Geophysical Research, 105, 851–868.
Katz, B., Elmore, R.D., Engel, M.H., Cogoini, M., and Ferry, S. (1998) Widespread chemical remagnetization: Orogenic fluids or burial diagenesis of clays? Geology, 26, 603–606.
Keeling, J.L., Raven, M.D., and Gates, W.P. (2000) Geology and characterization of two hydrothermal nontronites from weathered metamorphic rocks at the Uley graphite mine, South Africa. Clays and Clay Minerals, 48, 537–548.
Kennedy, M.J., Pevear, D.R., and Hill, R.J. (2002) Mineral surface control of organic carbon in black shale. Science, 295, 657–660.
Kim, J., Furukawa, Y., Daulton, T.L., Lavoie, D., and Newell, S.W. (2003) Characterization of microbially Fe(III)-reduced nontronite: environmental cell-transmission electron microscopy study. Clays and Clay Minerals, 51, 382–389.
Kim, J., Dong, H., Seabaugh, J., Newell, S.W., and Eberl, D.D. (2004) Role of microbes in the smectite-to-illite reaction. Science, 303, 830–832.
Köhler, B., Singer, A., and Stoffers, P. (1994) Biogenic nontronite from marine white smoker chimneys. Clays and Clay Minerals, 42, 689–701.
Kostka, J.E., Haefele, E., Viehweger, R., and Stucki, J.W. (1999) Respiration and dissolution of iron(III)-containing clay minerals by bacteria. Environmental Science & Technology, 33, 3127–3133.
Lanson, B., Sakharov, B.A., Claret, F., and Drits, V. (2009) Diagenetic smectite-to-illite transition in clay-rich sediments: A reappraisal of X-ray diffraction results using the multispecimen method. American Journal of Science, 309, 476–516.
Li, G., Peacor, D.R., Coombs, D.S., and Kawachi, Y. (1997) Solid solution in the celadonite family: The new minerals ferroceladonite K2(Fe2+)2(Fe3+)2Si8O20(OH)4, and ferroaluminoceladonite, K2(Fe2+)2Al2Si8O20(OH)4. American Mineralogist, 82, 503–511.
Li, Y., Vali, H., Sears, S.K., Yang, J., Deng, B., and Zhang, C.L. (2004) Iron reduction and alteration of nontronite NAu-2 by a sulfate-reducing bacterium. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 68, 3251–3260.
Lindgreen, H., Drits, V.A., Sakharov, B.A., Salyn, A.L., Wrang, P., and Dainyak, L.G. (2000) Illite-smectite structural changes during metamorphism in black Cambrian Alum shales from the Baltic area. American Mineralogist, 85, 1223–1238.
Longuépeé, H. and Cousineau, P.A. (2006) Constraints on the genesis of ferrian illite and aluminum-rich glauconite: potential impact on sedimentology and isotopic studies. The Canadian Mineralogist, 44, 967–980.
Lorimer, G. (1987) Quantitative X-ray microanalysis of thin specimens in the transmission electron microscope; a review. Mineralogical Magazine, 51, 49–60.
Lovley, D.R. and Chapelle, F.H. (1995) Deep surface microbial processes. Reviews of Geophysics, 33, 365–381.
Lynch, F.L., Mack, L.E., and Land, L.S. (1997) Burial diagenesis of illite/smectite in shales and the origin of authigenic quartz and secondary porosity in sandstones. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 61, 1995–2006.
Mas, A., Meunier, A., Beaufort, D., Patrier, P., and Dudoignon, P. (2008) Clay minerals in basalt-hawaiite rocks from Mururoa Atoll (French Polynesia). I. Mineralogy. Clays and Clay Minerals, 56, 711–729.
McCabe, C., Van der Voo, R., Peacor, D.R., Scotese, C.R., and Freeman, R. (1983) Diagenetic magnetite carries ancient yet secondary remanence in some Paleozoic sedimentary carbonates. Geology, 11, 221–223.
McCabe, C., Sassen, R., and Saffer, B. (1987) Occurrence of secondary magnetite within biodegraded oil. Geology, 15, 7–10.
McCarty, D.K., Sakharov, B.A., and Drits, V.A. (2008) Early clay diagenesis in gulf coast sediments: New insights from XRD profile modeling. Clays and Clay Minerals, 56, 359–379.
McCarty, D.K., Sakharov, B.A., and Drits, V.A. (2009) New insights into smectite illitization: A zoned K-bentonite revisited. American Mineralogist, 94, 1653–1671.
Meunier, A. (2005) Clays. Springer, Berlin, 472 pp.
Meunier, A. and Velde, B. (2004) Illite. Springer, Berlin, 286 pp.
Meunier, A., Petit, S., Cockell, C.S., El Albani, A., and Beaufort, D. (2010) The Fe-rich clay microsystems in basalt-komatiite lavas: importance of Fe-smectites for prebiotic molecule catalysis during the Hadean Eon. Origin of Live and Evolutionary Biospheres, 40, 253–272.
Moore, D.M. and Reynolds, R.C. (1997) X-ray Diffraction and the Identification of Clay Minerals. Oxford University Press, New York, 371 pp.
Moreau, M.G., Adera, M., and Enkin, R.J. (2005) The magnetization of clay-rich rocks in sedimentary basins: low-temperature experimental formation of magnetic carriers in natural samples. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 230, 193–210.
Murakami, T., Inoue, A., Lanson, B., Meunier, A., and Beaufort, T. (2005) Illite-smectite mixed layer minerals in the hydrothermal alteration of volcanic rocks: II. One dimensional High Resolution Transmission Electron Microscopy structure images and formation mechanisms. Clay and Clay Minerals, 53, 440–451.
Mustard, J.F., Murchie, S.L., Pelkey, S.M., Ehlmann, B.L., Milliken, R.E., Grant, J.A., Bibring, J.P., Poulet, F., Bishop, J., Dobrea, E.N., Roach, L., Seelos, F., Arvidson, R.E., Wiseman, S., Green, R., Hash, C., Humm, D., Malaret, E., McGovern, J.A., Seelos, K., Clancy, T., Clark, R., Marais, D.D., Izenberg, N., Knudson, A., Langevin, Y., Martin, T., McGuire, P., Morris, R., Robinson, M., Roush, T., Smith, M., Swayze, G., Taylor, H., Titus, T., and Wolff, M. (2008) Hydrated silicate minerals on Mars observed by the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter CRISM instrument. Nature, 454, 305–309.
Odin, G.S. (1988) Developments in Sedimentology: Green Marine Clays. Elsevier, Amsterdam.
Odom, I.E. (1984) Glauconite and celadonite minerals. Pp. 545–572 in: Micas (S.W. Bailey, editor). Reviews in Mineralogy, 13, Mineralogical Society of America, Washington, D.C.
Olives, J., Amouric, M., and Perbost, R. (2000) Mixed layering of illite-smectite: Results from high-resolution transmission electron microscopy and lattice-energy calculations. Clays and Clay Minerals, 48, 282–289.
O’Reilly, S.E., Watkins, J., and Furukawa (2005) Secondary mineral formation associated with respiration of nontronite, NAu-1 by iron reducing bacteria. Geochemical Transactions, 6, 67–76.
Paul, H.J., Gillis, K.M., Coggon, R.M., and Teagle, D.A.H. (2006) ODP Site 1224: A missing link in the investigation of seafloor weathering. Geochemistry Geophysics Geosystems, 7Q02003, doi:https://doi.org/10.1029/2005GC001089.
Pevear, D.R. (1999) Illite and hydrocarbon exploration. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, U.S.A., 96, 3440–3446.
Pollastro, R.M. (1985) Mineralogical and morphological evidence for the formation of illite at the expense of illite/smectite. Clays and Clay Minerals, 33, 265–274.
Potter, P., Maynard, J., and Depetris, P. (2005) Mud and Mudstones: Introduction and Overview. Springer, New York, pp. 128–154.
Rask, J.H., Bryndzia, L.T., Braunsdorf, N.R., and Murray, T.E. (1997) Smectite illitization in Pliocene-age Gulf of Mexico Mudrocks. Clays and Clay Minerals, 45, 99–109.
Ribeiro, F.R., Fabris, J.D., Kostka, J.E., Komadel, P., and Stucki, J.W. (2009) Comparisons of structural iron reduction in smectites by bacteria and dithionite: II. A variable-temperature Mö ssbauer spectroscopic study of Garfield nontronite. Pure and Applied Chemistry, 81, 1499–1509.
Seyfried, Jr., W.E. and Bischoff, J.L. (1979) Low temperature basalt alteration by seawater: an experimental study at 70°C and 150°C. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 43, 1937–1947.
Środoń, J. (1980) Precise identification of illite/smectite interstratifications by X-ray powder diffraction. Clays and Clay Minerals, 28, 401–411.
Stucki, J.W. (2011) A review of the effects of iron redox cycles on smectite properties. Comptes Rendus Geoscience, 343, 199–209.
Stucki, J.W. and Kostka, J.E. (2006) Microbial reduction of iron in smectite. Comptes Rendus Geoscience, 338, 468–475.
Suk, D., Van der Voo, R., and Peacor, D.R. (1990a) Scanning and transmission electron microscope observations of magnetite and other iron phases in Ordovician carbonates from east Tennessee. Journal of Geophysical Research, 95, 12,327–12,336.
Suk, D., Peacor, D.R., and Van der Voo, R. (1990b) Replacement of pyrite framboids by magnetite in limestone and implications for paleomagnetism. Nature, 345, 611–613.
Tohver, E., Weil, A.B., Solum, J.G., and Hall, C.M. (2008) Direct dating of carbonate remagnetization by 40Ar/39Ar analysis of the smectite-illite transformation. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 274, 524–530.
Ulrey, A.L. and Drees, R.L., editors (2008) Methods of Soil Analysis: Part 5 — Mineralogical Methods. Soil Science Society of America, Madison, Wisconsin. USA.
Velde, B. (1972) Celadonite Mica: Solid solution and stability. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 37, 235–247.
Veblen, D.R., Guthrie, D.G., Livi, K.J.T., and Reynolds, R.C. (1990) High-resolution transmission electron microscopy and electron diffraction of mixed layer illite-smectite: Experimental results. Clays and Clay Minerals, 38, 1–13.
Vorhies, J.S. and Gaines, R.R. (2009) Microbial dissolution of clay minerals as a source of iron and silica in marine sediments. Nature Geoscience, 2, 221–225.
Weaver, C.E. (1960) Possible uses of clay minerals in search for oil. American Association of Petroleum Geologists Bulletin, 44, 1505–1518.
Weil, A.B. and Van der Voo, R. (2002) Insights into the mechanism for orogen-related carbonate remagnetization from growth of authigenic Fe-oxide: A scanning electron microscopy and rock magnetic study of Devonian carbonates from northern Spain. Journal of Geophysical Research, 107, 2063.
Wise, W.S. and Eugster, H.P. (1964) Celadonite: synthesis, thermal stability and occurrence. American Mineralogist, 49, 1031–1083.
Woods, S., Elmore, R.D., and Engel, M. (2002) Paleomagnetic dating of the smectite-to-illite conversion: testing the hypothesis in Jurassic sedimentary rocks, Skye, Scotland. Journal of Geophysical Research, 107, 2091, doi:https://doi.org/10.1029/2000JB000053.
Zegers, T.E., Dekkers, M.J., and Bailly, S. (2003) Late Carboniferous to Permian remagnetization of Devonian limestones in the Ardennes: Role of temperature, fluids, and deformation. Journal Geophysical Research, 108, 2357, doi: https://doi.org/10.1029/2002JB002213.
Zhang, G., Kim, J., Dong, H., and Sommer, A.J. (2007) Microbial effects in promoting the smectite to illite reaction: Role of organic matter intercalated in the interlayer. American Mineralogist, 92, 1401–1410.
Zwing, A., Clauer, N., Liewig, N., and Bachtadse, V. (2009) Identification of remagnetization processes in Paleozoic sedimentary rocks of the northeast Rhenish Massif in Germany by K/Ar dating and REE tracing of authigenic illite and Fe oxides. Journal of Geophysical Research, 114, B06104, doi:https://doi.org/10.1029/2008JB006137.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miller, M.A., Madden, A.S., Elwood Madden, M. et al. Laboratory-Simulated Diagenesis of Nontronite. Clays Clay Miner. 60, 616–632 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1346/CCMN.2012.0600607
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1346/CCMN.2012.0600607