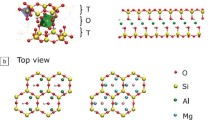
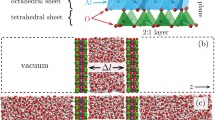
Abstract
X-ray diffraction has been used to study the sorption of water by multilayer films containing ordered stacks of alternating layers of an organic polyelectrolyte and individual platelets of a smectite. The position and shape of the 001 reflections due to the ordered polyelectrolyte/platelet stacks were essentially the same when in air at low relative humidity (23–25% RH) and under water. These data indicate that swelling occurs exclusively in X-ray amorphous regions within the film, and that the ordered polyelectrolyte/clay domains themselves are not ‘swellable’ by water.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bailey, S.W. (1982) Nomenclature for regular interstratifications. American Mineralogist, 67, 394–398.
Barrer, R.M. and MacLeod, D.M. (1954) Intercalaction and sorption by montmorillonite. Transactions of the Faraday Society, 50, 980–989.
Berend, I., Cases, J.-M., François, M., Uriot, J.-P., Michot, L., Masion, A. and Thomas, F. (1995) Mechanism of adsorption and desorption of water vapor by homoionic montmorillonites: 2. The Li+, Na+, K+, Rb+, and Cs+-exchanged forms. Clays and Clay Minerals, 43, 324–336.
Bradley, W.F., Grim, R.E. and Clark, G.L. (1937) A study of the behavior of montmorillonite upon wetting. Kristallographia, 97, 216–222.
Cases, J.-M., Bérend, I., Besson, G., François, M., Uriot, J.P., Michot, L., Thomas, F. and Porier, J.E. (1992) Mechanism of adsorption and desorption of water vapor by homoionic montmorillonites: 1. The sodium-exchanged form. Langmuir, 8, 2730–2739.
Drits, V.A. and Tchoubar, C. (1990) X-ray Diffraction by Disordered Lamellar Structures. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, pp. 40–43.
Grim, R.E. (1968) Clay Mineralogy, 2nd edition. McGraw-Hill, New York, chapter 3.
Hendricks, S.B., Nelson, R.A. and Alexander, L.T. (1940) Hydration mechanism of the clay mineral montmorillonite saturated with various cations. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 62, 1457–1464.
Hofmann, U., Endell, K. and Wilm, D. (1933) Kristallstruktur und Quellung von Montmorillonit (Das Tonmineral der Bentonittone). Kristallographia, 83, 340–348.
Kleinfeld, E.R. and Ferguson, G.S. (1994) Stepwise formation of multilayered nanostructural films from macromoleclular precursors. Science, 265, 370–373.
Kleinfeld, E.R. and Ferguson, G.S. (1995) Rapid, reversible sorption of water from the vapor by a multilayered composite film: A nanostructured humidity sensor. Chemistry of Materials, 7, 2327–2331.
Kotov, N.A., Haraszti, T., Turi, L., Zavala, G., Geer, R.E., Dekany, I. and Fendler, J.H. (1997) Mechanism of and defect formation in the self-assembly of polymeric polycation-montmorillonite ultrathin films. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 119, 6821–6832.
MacNeill, B.A., Simmons, G.W. and Ferguson, G.S. (1999) The sorption of water vapor by multilayered composite films measured using infrared spectroscopy. Materials Research Bulletin, 34, 455–461.
Mooney, R.W., Keenan, A.G. and Wood, L.A. (1952a) Adsorption of water vapor by montmorillonite. I. Heat of desorption and application of BET theory. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 74, 1367–1370.
Mooney, R.W., Keenan, A.G. and Wood, L.A. (1952b) Adsorption of water vapor by montmorillonite. II. Effect of exchangeable ionsand lattice swelling as measured by X-ray diffraction. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 74, 1371–1374.
Rouse, J.H., MacNeill, B.A. and Ferguson, G.S. (2000) Sol-gel processing of ordered multilayers to produce composite filmsof controlled thickness. Chemistry of Materials, 8, 2502–2507.
Rouse, J.H., White, S.T. and Ferguson, G.S. (2004) A method for imaging single clay platelets by scanning electron microscopy. Scanning, 26, 131–134.
Tompkins, H.G. (1993) A User’s Guide to Ellipsometry. Academic Press, New York.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rouse, J.H., Ferguson, G.S. Does water swell the ordered domains in polyelectrolyte/clay multilayers?. Clays Clay Miner. 55, 160–164 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1346/CCMN.2007.0550205
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1346/CCMN.2007.0550205