Abstract
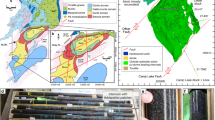
A field-mapping and crystal-chemical study of two alunite- and halloysite-rich deposits in the Turplu area, situated northwest of Balıkesir on the Biga Peninsula of northwest Turkey reveals a mineralogically diverse and a potentially economic clay deposit. The mineral assemblage along fault zones is dominated by halloysite and sometimes alunite. The alunite is nearly end-member in composition (a = 6.995 Å, c = 17.195 Å) often occurring with a minor Ca phosphate phase. Of the two deposits studied, the more northerly mine contains more alunite relative to halloysite. Geochemical alteration indices suggest that the northern mine has experienced a slightly greater degree of hydrothermal modification. Halloysite is found in both hydrated and dehydrated states and assumes a tubular morphology. Observations by transmission and scanning electron microscopy are consistent with a model of halloysite dehydration, where the shapes transform from an open-hole tubular morphology to a closed-hole unfurled morphology.
Mineral paragenesis includes the effects of initial deposition of volcanic tuffs and andesite on top of karstic terrain. The contact between altered volcanics and underlying limestones is irregular and appears to have provided a mechanism to flush both hydrothermal and meteoric waters through the volcanics. Periods of hydrothermal alteration (hypogene) contemporaneous with extensional and strike-slip faulting have resulted in alunite and halloysite deposits. Hydrothermal alteration is concentrated near the fault zones. Because of subsequent weathering (supergene) away from the fault zones, much of the andesitic volcanic rocks have been altered to a more smectite-rich and kaolinite-bearing assemblage. The deposits continue to be both plastically deformed in the alunite/halloysite regions and to undergo brittle deformation in the saprolitized volcanics. Tectonic deformation has mixed the contacts, such that limestone blocks are entrained into parts of the alteration zones. Gibbsite and gypsum are common weathering products associated with limestone block inclusions. Genetic models for the origins of alunite-halloysite deposits in NW Turkey should consider as possible influencing factors the underlying lithologies, the extent of hydrothermal alteration, and recent weathering by meteoric fluids. In the case of the Turplu deposits, karstic limestones, hydrothermal circulation of sulfate-rich waters, and a post-alteration history of meteoric weathering were all important factors in their formation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altaner, S.P., Ylagan, R.F., Savin, S.M., Aronson, J.L., Belkin, H.E. and Pozzuoli, A. (2003) Geothermometry, geochronology, and mass transfer associated with hydrothermal alteration of a rhyolitic hyaloclastite from Ponza Island, Italy. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 67, 275–288.
Altunkaynak, Ş. and Yılmaz, Y. (1998) The Mount Kozak magmatic complex, Western Anatolia. Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, 85, 211–231.
Altunkaynak, Ş. and Yılmaz, Y. (1999) The Kozak Pluton and its emplacement. Geological Journal, 34, 257–274.
Bozzola, J.J. and Russell, L.D. (1999) Electron Microscopy. Principles and Techniques for Biologists. Jones and Bartlett Publishers, Boston, Massachusetts, USA, 670 pp.
Churchman, G.J. (1990) Relevance of different intercalation tests for distinguishing halloysite from kaolinite in soils. Clays and Clay Minerals, 38, 591–599.
Churchman, G.J., Whitton, J.S. and Claridge, G.G.C. (1984) Intercalation method using formamide for differentiating halloysite from kaolinite. Clays and Clay Minerals, 32, 241–248.
Ciesla, K. and Rudnicki, R. (1993) Thermal-decomposition of Ca10(PO4)6(OH)2 at ambient-pressure in air and in nitrogen. Polish Journal of Chemistry, 67, 2103–2111.
Davidson, J.P., Harmon, R.S. and Worner, G. (1991) The source of central Andean magmas: some considerations. Pp. 233–243 in: Andean Magmatism and its Tectonic Setting (R.S. Harmon and C. Rapela, editors). Geological Society of America Special Paper, 265.
Dill, H.G. (2001) The geology of aluminium phosphates and sulphates of the alunite group minerals: a review. Earth Science Reviews, 53, 35–93.
Dill, H.G., Bosse, H.R., Henning, K.H., Fricke, A. and Ahrendt, H. (1997) Mineralogical and chemical variations in hypogene and supergene kaolin deposits in a mobile fold belt, the Central Andes of northwestern Peru. Mineralium Deposita, 32, 149–163.
Dixon, J.B. and McKee, T.R. (1974) Internal and external morphology of tubular and spheroidal halloysite particles. Clays and Clay Minerals, 22, 127–137.
Ece, Ö.I. and Nakagawa, Z. (2003) Alteration of volcanic rocks and genesis of kaolin deposits in Şile Region, northern Istanbul, Turkey. Part II. Differential mobility of elements. Clay Minerals, 38, 529–550.
Freeman, T. (1999) Procedure in Field Geology. Blackwell Science, Inc., Malden, Massachusetts, USA, 95 pp.
Genç, C.Ş. (1998) Evolution of the Bayramiç magmatic complex, northwestern Anatolia. Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, 85, 233–249.
Grant, J.A. (1986) The isocon diagram — A simple solution to Gresen’s equation for metasomatic alteration. Economic Geology, 81, 1976–1982.
Gresens, R.L. (1967) Composition-volume relationships of metasomatism. Chemical Geology, 2, 47–55.
Harris, N.B.W., Pearce, J.A. and Tindle, A.G. (1986) Geochemical characteristics of collision-zone magmatism. Pp. 67–81 in: Collision Tectonics (M.P. Coward and A.C. Ries, editors). Special Publication, 19, Geological Society, London.
Harris, N.B.W., Kelley, S. and Okay, A.I. (1994) Post-collision magmatism and tectonics in northwest Anatolia. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 117, 241–252.
Hurst, V.J. and Pickering, S.M. (1997) Origin and classification of coastal plain kaolins, southeastern USA, and the role of groundwater and microbial action. Clays and Clay Minerals, 45, 274–285.
Jambor, J.L. (1999) Nomenclature of the alunite supergroup. The Canadian Mineralogist, 37, 1323–1341.
Joussein, E., Petit, S., Churchman, J., Theng, B., Righi, D. and Delvaux, B. (2005) Halloysite clay minerals — a review. Clay Minerals, 40, 383–426.
Karacık, Z. and Yılmaz, Y. (1998) Geology of the ignimbrites and the associated volcano-plutonic complex of the Ezine area, northwestern Anatolia. Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, 85, 251–264.
Kohyama, N., Fukushima, K. and Fukami, A. (1978) Observation of the hydrated form of tubular halloysite by an electron microscope equipped with an environmental cell. Clays and Clay Minerals, 26, 25–40.
Küçük, A. and Gülaboğlu, M.S. (2002) Thermal decomposition of Saphane alunite ore. Industrial Engineering and Chemical Resources, 41, 6028–6232.
Okay, A.I., Siyako, M. and Burkan, K.A. (1991) Geology and tectonic evolution of the Biga Peninsula, northwest Turkey. Bulletin of Istanbul Technical University, 44, 191–256.
Okay, A.I., Demirbağ, E., Kurt, H., Okay, N. and Kuşçu, I. (1999) An active, deep marine strike-slip basin along the North Anatolian Fault in Turkey. Tectonics, 18, 129–147.
Okay, A.I., Kaşlılar-Özcan, A., İmren, C., Boztepe-Güney, A., Demirbağ, E. and Kuşçu, I. (2000) Active faults and evolving strike-slip basins in the Marmara Sea, northwest Turkey: a multichannel seismic reflection study. Tectonophysics, 321, 189–218.
Pearce, J.A., Bender, J.F., De Long, S.E., Kidd, W.S.F., Low, P.J., Güner, Y., Saroglu, F., Yılmaz, Y., Moorbath, S. and Mitchell, J.J. (1990) Genesis of collision volcanism in eastern Anatolia Turkey. Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, 44, 189–229.
Pysiak, J. and Glinka, A. (1981) Thermal decomposition of basic aluminum potassium sulphate. Part I. Stages of decomposition. Thermochimica Acta, 44, 21–28.
Railsback, B. (2003) Earth scientist’s periodic table of the elements and their ions. Geology, 31, 737–740.
Rattray, K.J., Taylor, M.R. and Bevan, D.J.M. (1996) Compositional segregation and solid solution in the lead-dominant alunite-type minerals from Broken Hill, N.S.W. Mineralogical Magazine, 60, 779–785.
Rudolph, W.W., Mason, R. and Schmidt, P. (2003) Synthetic alunites of the potassium-oxonium solid solution series and some other members of the group: synthesis, thermal and X-ray characterization. European Journal of Mineralogy, 15, 913–924.
Schroeder, P.A., Pruett, R.J. and Melear, N.D. (2004a) Crystal-chemical changes in an oxidative weathering front in a middle Georgia kaolin deposit. Clays and Clay Minerals, 52, 212–220.
Schroeder, P.A., Smilley, M.J., Ece, Ö.I. and Wampler, M. (2004b) Sulfur isotope and potassium argon analysis of minerals from the Turplu halloysite mine, Balikesir region, northwest Turkey. The Clay Minerals Society, 41st Annual meeting, Richland, WA. Abstract with programs, p. 134.
Shelobolina, E. (2000) Role of microorganisms in development of commercial grade kaolins. Pp. 45–59 in: Guidebook — Geology of the commercial kaolin mining district of central and eastern Georgia (J. Elzea-Kogel, S.M. Pickering Jr., E. Shelobolina, J. Yuan and T.M. Chowns, editors). Volume 20, Georgia Geological Society, Georgia, USA.
Singh, B. (1996) Why does halloysite roll? — A new model. Clays and Clay Minerals, 44, 191–196.
Slansky, E. (1973) The thermal investigation of alunite and natroalunite. Neues Jahrburch für Mineralogie, 3, 124–138.
Stoffregen, R., Alpers, C.N. and Jambor, J.L. (2000) Alunite-jarosite crystallography, thermodynamics and geochronology. Pp. 453–479 in: Sulfate Minerals (C.N. Alpers, J.L. Jambor and D.K. Nordstrom, editors). Reviews in Mineralogy & Geochemistry, 40, Mineralogical Society of America, Chantilly, Virginia and the Geochemical Society, Washington, D.C.
Taylor, S.R. and McLennan, S.M. (1985) The Continental Crust: Its Composition and Evolution. Blackwell Scientific, Oxford, UK, 312 pp.
Theng, B.K.G., Churchman, G.J. and Whitton, J.S. (1984) Comparison of intercalation methods for differentiating halloysite from kaolinite. Clays and Clay Minerals, 32, 249–258.
Thorpe, R.S., Francis, P.W., Hammill, M. and Barker, M.C.W. (1982) The Andes. Pp. 187–205 in: Andean Magmatism and its Tectonic Setting (R.S. Thorpe, editor). John Wiley & Sons.
Thorpe, R.S., Francis, P.W. and O’Callaghan, L. (1984) Relative roles of source composition, fractional crystallisation and crustal contamination in the petrogenesis of Andean volcanic rocks. Philosophical Transaction of the Royal Society, London, A310, 675–692.
Walker, J.A., Moulds, T.N., Zentilli, M. and Feigenson, M.D. (1991) Spatial and temporal variations in volcanics of the Andean central volcanic zone (26 to 28). Pp. 139–155 in: Andean Magmatism and its Tectonic Setting (R.S. Harmon and C. Rapela, editors). Geological Society of America Special Paper, 265.
Winchester, J.A. and Floyd, P.A. (1977) Geochemical discrimination of different magma series and their differentiation products using immobile elements. Chemical Geology, 20, 325–343.
Yalçın, T.H. (1997) Hydrogeological investigation of Gönen and Ekçidere (Balıkesir) thermal waters (NW Turkey). Pp. 275–300 in: Active Tectonics of Northwestern Anatolia — The Marmara Poly-Project (C. Schindler and M. Pfister, editors). vdf, Hochschulverlag AG an der ETH Zürich.
Yau, Y.C., Peacor, D.R. and Essene, E.J. (1987) Authigenic anatase and titanite in shales from the Salton Sea Geothermal Field, California. Neues Jahrbuch für Mineralogie Monatshefte, 19, 441–452.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ece, Ö.I., Schroeder, P.A. Clay mineralogy and chemistry of halloysite and alunite deposits in the Turplu area, Balikesir, Turkey. Clays Clay Miner. 55, 18–35 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1346/CCMN.2007.0550102
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1346/CCMN.2007.0550102