Abstract
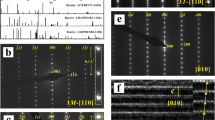
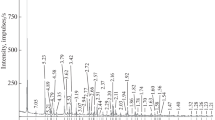
The transformation of kaolinite to halloysite-7 Å was identified in the kaolin deposit of São Vicente de Pereira (SVP), using X-ray diffraction (XRD), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). Both the 02, 1̄ and 13̄, 13 reflections show changes in the XRD patterns along the kaolinite to halloysite-7 Å transition, and the FTIR spectra show changes corresponding to both OH− and Si-O-stretching bands and Al-O-Si-bending vibrations. The interlayer water content in the kaolinite structure increases during transition. The two-layer periodicity of well-ordered kaolinite and rolling up of kaolinite plates are observed using high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM). Long and short tubes exhibit halloysite-7 Å. No structural Fe was found in the kaolinite samples. Analytical electron microscopy (AEM) indicates no substitution of Al3+ for Si4+. The Si/Al ratio shows values of ∼1 for the kaolinite and rolled kaolinite plates. The 27Al magic angle spinning neutron magnetic resonance (MAS-NMR) spectra display a resonance centered at ∼1 ppm, assigned to six-coordinated aluminum. The transformation of kaolinite to halloysite-7 Å is controlled by surface reaction.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anand, R.R., Gilkes, R.J., Armitage, T.M. and Hillyer, J.W. (1985) Feldspar weathering in a lateritic saprolite. Clays and Clay Minerals, 33, 31–43.
Bailey, S.W. (1988) Polytypism of 1:1 layer silicates. Pp. 9–27 in: Hydrous Phyllosilicates (exclusive of Micas) (S.W. Bailey, editor). Reviews in Mineralogy, 19. Mineralogical Society of America, Washington, D.C.
Bailey, S.W. (1990) Halloysite—a critical assessment. Pp. 89–98 in: Proceedings of 9th International Clay Conference, Strasbourg (V.C. Farmer and Y. Tardy, editors). Sciences Géologiques Mémoire, Strasbourg, France, 85.
Banfield, J.F. and Eggleton, R.A. (1990) Analytical transmission electron microscope studies of plagioclase, muscovite and K-feldspar weathering. Clays and Clay Minerals, 38, 77–89.
Bates, T.F., Hildebrand, F.A. and Swineford, A. (1950) Morphology and structure of endellite and halloysite. American Mineralogist, 6, 237–248.
Bobos, I. and Gomes, C. (1998) Greisen and post-greisen alteration in the kaolin deposit of São Vicente de Pereira (Portugal). Canadian Mineralogist, 36, 1621–1630.
Bobos, I. and Gomes, C. (1999) Hydrothermal alteration and kaolinization in the north western border of Ossa Morena zone. EUG 10, Abstract volume, 4. Cambridge Publications, 592 pp.
Bobos, I. and Gomes, C. (2000) Dissolution of K-feldspar into Si-Al gel and crystallization of halloysite identified in the kaolin deposit of São Vicente de Pereira (Portugal). Geologica Carpathica, 51, 49–57.
Chaminé, H.I., Ribeiro, A. and Pereira, E. (1995) Cartografia geológica e estratigrafia da faixa precâmbrica do sector Espinho—Albergaria-A-Velha (Zona de Ossa-Morena). Faculdade de Ciências, Universidade do Porto. Memoria, 4, 329–333.
Churchman, G.J. and Gilkes, R.J. (1989) Recognition of intermediates in the possible transformation of halloysite to kaolinite in weathering profiles. Clay Minerals, 24, 579–590.
Costanzo, P.M. and Giese, R.F. Jr. (1985) Dehydration of synthetic hydrated kaolinite: a model for the dehydration of halloysite (10 Å). Clays and Clay Minerals, 33, 415–423.
Costanzo, P.M., Giese, R.F. Jr. and Clemency, C.V. (1984) Synthesis of a 10 Å hydrated kaolinite. Clays and Clay Minerals, 32, 29–35.
Eswaran, H. and Bin, W.C. (1978) A study of deep weathering profile on granite in peninsular Malaysia: Mineralogy of the clay, silt and sand fractions. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 42, 149–158.
Giese, R.F. Jr. (1988) Kaolin minerals: structures and stability. Pp. 29–66 in: Hydrous Phyllosilicates (exclusive of Micas) (S.W. Bailey, editor). Reveiws in Mineralogy, 19. Mineralogical Society of America, Washington, D.C.
Gilkes, R.J., Anand, R.R. and Suddhiprakarn, A. (1986) How the microfabric of soils may be influenced by the structure and chemical composition of parent minerals. Pp. 1093–1106 in: Trans International Soil Science Conference, Hamburg, 6.
Grim, R. (1967) Clay Mineralogy. McGraw Hill, New York, 596 pp.
Hinckley, D.N. (1963) Variability in “crystallinity” values among the kaolin deposits of the coastal plain of Georgia and South Carolina. Clays and Clay Minerals, 11, 229–235.
Honjo, G., Kitamura, N. and Mihama, K. (1954) A study of clay minerals by means of single-crystal electron diffraction diagram—the structure of tubular kaolin. Clay Minerals Bulletin, 2, 133–141.
Jackson, M.L. (1975) Soil Chemical Analyses—Advanced Course. Published by the author, Madison, Wisconsin, 895 pp.
Jiang, W.T. and Peacor, D.R. (1991) Transmission electron microscopic study of the kaolinisation of muscovite. Clays and Clay Minerals, 39, 1–13.
Keller, W.D. (1978) Classification of kaolins exemplified by their textures in scanning electron microscopy. Clays and Clay Minerals, 26, 1–20.
Kohyama, N., Fukushima, K. and Fukami, A. (1978) Observation of the hydrated form of tubular halloysite by an electron microscope equipped with an environmental cell. Clays and Clay Minerals, 26, 25–40.
Ma, C. and Eggleton, R.A. (1999) Surface layer types of kaolinite: A high resolution transmission electron microscopy study. Clays and Clay Minerals, 47, 181–191.
Ma, C., FitzGerald, J.D., Eggleton, R.A. and Llewellyn, D.J. (1998) Analytical electron microscopy in clays and other phyllosilicates: Loss of elements from a 90-nm stationary beam of 300 KeV electrons. Clays and Clay Minerals, 46, 301–317.
MacEwan, D.M.C. and Wilson, M.J. (1980) Interlayer and intercalation complexes of clay minerals. Pp. 197–249 in: Crystal Structures of Clay Minerals and Their X-ray identification (G.W. Brindley and G. Brown, editors). Monograph 5. Mineralogical Society, London.
McBride, M.B. (1976) A critique of diffuse double layer models applied to colloid and surface chemistry. Clays and Clay Minerals, 24, 598–608.
Meunier, A. and Velde, B. (1979) Weathering mineral facies in altered granites: The importance of local small-scale equilibrium. Mineralogical Magazine, 43, 261–268.
Newman, R.H., Childs, C.W. and Churchman, G.J. (1994) Aluminium co-ordination and structural disorder in halloysite and kaolinite by 27Al NMR spectroscopy. Clay Minerals, 29, 305–312.
Plançon, A. and Tchoubar, C. (1977) Determination of structural defects in phyllosillicates by X-ray powder diffraction. Clays and Clay Minerals, 25, 436–450.
Plançon, A. and Zacharie, C. (1990) An expert system for the structural characterization of kaolinites. Clay Minerals, 25, 249–260.
Plançon, A., Giese, R.F. and Snyder, R. (1988) The Hinckley index for kaolinites. Clay Minerals, 23, 249–260.
Rand, B. and Melton, I.E. (1976) Particle interactions in aqueous kaolinite suspensions, I. Effect of pH and electrolyte upon the mode of particle interaction in homoionic sodium kaolinite suspensions. Journal of Colloidal Interface Science, 60, 308–320.
Range, K.J., Range, A. and Weiss, A. (1969) Fire clay type kaolinite or fire clay minerals? Experimental classification of kaolinite-halloysite minerals. Pp. 3–13 in: Proceedings International Clay Conference Tokyo, Volume 1. (L. Heller and A. Weiss, editors). Israel University Press, Jerusalem.
Ribeiro, A., Pereira, E. and Severo, L. (1980) Análise da deformação da zona de cisalhamento Porto-Tomar na transversal de Oliveira de Azeméis. Comunicação de Servicio Geologico de Portugal, 66, 3–9.
Robertson, I.D. and Eggleton, R.A. (1991) Weathering of granitic muscovite to kaolinite and halloysite and plagioclase-derived kaolinite to halloysite. Clays and Clay Minerals, 39, 113–126.
Rocha, J. and Klinowski, J. (1990) 29Si and 27Al magic-angle-spinning NMR studies of the thermal transformation of kaolinite. Physics and Chemistry of Minerals, 17, 179–186.
Rocha, J. and Pedrosa de Jesus, J.D. (1994) 27A1 satellite transition MAS NMR spectroscopy of kaolinite. Clay Minerals, 29, 287–291.
Singh, B. (1996) Why does halloysite roll?—A new model. Clays and Clay Minerals, 44, 191–197.
Singh, B. and Gilkes, R.J. (1992) An electron optical investigation of the alteration of kaolinite to halloysite. Clays and Clay Minerals, 40, 212–229.
Singh, B. and Mackinnon, I. (1996) Experimental transformation of kaolinite to halloysite. Clays and Clay Minerals, 44, 825–834.
Stoch, L. and Sikora, W. (1976) Transformation of micas in the process of kaolinization of granites and gneisses. Clays and Clay Minerals, 24, 156–162.
Stumm, W. (1992) Chemistry of the Solid-Water Interface. Wiley & Sons, New York, 346 pp.
Sunagawa, I. (1975) Morphology of minerals. Pp. 509–587 in: Morphology of Crystals (I. Sunagawa, editor). Terra Science Publishes Co., Tokyo.
Tari, G., Bobos, I., Gomes, C. and Ferreira, J.M. (1999) Modification of charge density during the kaolinite to hallosyite-7 Å transformation. Journal of Colloid Interface Surface, 209, 360–366.
Wada, K. (1961) Lattice expansion of kaolin minerals by treatment with potassium acetate. American Mineralogist, 46, 78–91.
Wilke, B.S., Schwertmann, U. and Murad, E. (1978) An occurrence of polymorphic halloysite in granite saprolite of the Bayerischer Wald, Germany. Clay Minerals, 13, 67–77.
Zvyagin, B.B. (1967) Electron Diffraction Analysis of Clay Minerals Structures. Plenum Press, New York, 364 pp.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bobos, I., Duplay, J., Rocha, J. et al. Kaolinite to halloysite-7 Å transformation in the kaolin deposit of São Vicente de Pereira, Portugal. Clays Clay Miner. 49, 596–607 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1346/CCMN.2001.0490609
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1346/CCMN.2001.0490609