Abstract
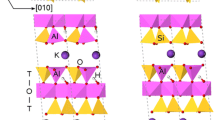
Plane-wave pseudopotential total energy calculations have been applied to investigate the structure and energetics of the Cs/K exchange into interlayer sites in muscovite mica. Novel muscovite structures were designed to isolate the effects of 2:1 layer charge, cation size/interlayer site shape, and tetrahedral Al/Si substitutions on the exchange. All atom and cell-parameter optimizations were performed with the intention to mimic the constant pressure, non-isovolumetric exchange conditions thought to be found at frayed-edge sites. Under conditions where the cell parameters are allowed to relax, the overall Cs/K exchange reaction is surprisingly close to isoenergetic. The forward reaction is more strongly favored with increasing layer charge. For the condition of zero layer charge and no interlayer site distortion, the difference in the optimal interlayer spacing for Cs relative to K is very small, indicating a baseline indifference of the muscovite structure to cation size. The presence of 2:1 layer charge or tetrahedral rotations arising from Al/Si substitutions clearly change this outcome. Analysis of the dependence of the interlayer spacing on layer charge shows that while the spacing collapses with increasing layer charge for K as the interlayer cation, the reverse is true for Cs. We attribute the contrasting behavior to inherent differences in the ability of these cations to screen 2:1 layer-layer repulsions. Such effects might be involved during exchange at frayed-edge sites where interlayer spacings are increased. This is known, from experiment, to be very selective for Cs. Overall, the exchange energetics are so low that the Cs/K exchange rate and degree of irreversibility are likely to be dominated by diffusion kinetics.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, K. and Allard, B. (1983) Sorption of radionuclides on geologic media. Report No. SKBF-KBS-TR-83-07. Svensk Karnsbransterforjning.
Bailey, S.W. (1984) Crystal chemistry of the true micas. Pp. 13–57 in: Micas (S.W. Bailey, editor). Mineralogical Society of America, Washington, D.C.
Bradbury, M.H. and Baeyens, B. (2000) A generalised sorption model for the concentration dependent, uptake of caesium by argillaceous rocks. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 42, 141–163.
Bridgeman, C.H. and Skipper, N.T. (1997) A Monte Carlo study of water at an uncharged clay surface. Journal of Physics—Condensed Matter, 9, 4081–4087.
Bridgeman, C.H., Buckingham, A.D., Skipper, N.T. and Payne, M.C. (1996) Ab initio total energy study of uncharged 2:1 clays and their interaction with water. Molecular Physics, 89, 879–888.
Brueeuwsma, A. and Lyklema, J. (1971) Interfacial electrochemistry of hematite (α-Fe2O3). Discussions of the Faraday Society, 52, 324–333.
Burns, A.F. and White, J.L. (1963) Removal of potassium alters b-dimension of muscovite. Science, 139, 39–40.
Cerius2 User Guide (1997) Cerius2. Molecular Simulations Inc.
Chang, F.R.C., Skipper, N.T. and Sposito, G. (1995) Computer simulation of interlayer molecular structure in sodium montmorillonite hydrates. Langmuir, 11, 2734–2741.
Chatterjee, A., Iwasaki, T. and Ebina, T. (2000) A novel method to correlate layer charge and the catalytic activity of 2:1 dioctahedral smectite clays in terms of binding the interlayer cation surrounded by monohydrate. Journal of Physical Chemistry A, 104, 8216–8223.
Comans, R.N.J., Haller, M. and Depreter, P. (1991) Sorption of cesium on illite—nonequilibrium behavior and reversibility. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 55, 433–440.
Comans, R.N.J, and Hockley, D.E. (1992) Kinetics of cesium sorption on illite. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 56, 1157–1164.
Cremers, A., Elsen, A., Depreter, P. and Maes, A. (1988) Quantitative analysis of radiocesium retention in soils. Nature 335, 247–249.
De Carvalho, R. and Skipper, N.T. (2001) Atomistic computer simulation of the clay-fluid interface in colloidal laponite. Journal of Chemical Physics, 114, 3727–3733.
De Preter, P., Vanloon, L., Maes, A. and Cremers, A. (1991) Solid liquid distribution of radiocesium in boom clay—a quantitative interpretation. Radiochimica Acta, 52-3, 299–302.
Dolcater, D.L., Lotse, E.G., Syers, J.K. and Jackson, M.L. (1968) Cation exchange selectivity of some clay-sized minerals and soil materials. Proceedings of the Soil Science Society of America, 32, 795–798.
Feller, D., Glendening, E.D., Woon, D.E. and Feyereisen, M.W. (1995) An extended basis set ab initio study of alkali metal cation water clusters. Journal of Chemical Physics, 103, 3526–3542.
Garcia, A., Elsasser, C., Zhu, J., Louie, S.G. and Cohen, M.L. (1992) Use of gradient-corrected functionals in total energy calculations for solids. Physical Review B, 46, 9829–9832.
Gibbs, G.V. (1982) Molecules as models for bonding in silicates. American Mineralogist, 67, 421–450.
Giese, R.F., Jr. (1975) The effect of F/OH substitution on some layer-silicate minerals. Zeitschift für Kristallographie, 141, 138–144.
Giese, R.F., Jr. (1984) Electrostatic energy models of micas. Pp. 105–144 in: Micas (S.W. Bailey, editor). Mineralogical Society of America, Washington, D.C.
Gillan, M.J. (1989) Calculation of the vacancy formation energy in aluminum. Journal of Physics–Condensed Matter, 1, 689–711.
Greathouse, J. and Sposito, G. (1998) Monte Carlo and molecular dynamics studies of interlayer structure in Li(H2O)3-smectites. Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 102, 2406–2414.
Gutierrez, M. and Fuentes, H.R. (1996) A mechanistic modeling of montmorillonite contamination by cesium sorption. Applied Clay Science, 11, 11–24.
Hewitt, D.A. and Wones, D.R. (1975) Physical properties of some synthetic Fe-Mg-Al trioctahedral biotites. American Mineralogist, 60, 854–862.
Hobbs, J.D., Cygan, R.T., Nagy, K.L., Schultz, P.A. and Sears, M.P. (1997) All-atom ab initio energy minimization of the kaolinite crystal structure. American Mineralogist, 82, 657–662.
Jackson, M.L. (1963) Interlayering of expansible layer silicates in soils by chemical weathering. Clays and Clay Minerals, 11, 29–46.
Kim, Y. and Kirkpatrick, R.J. (1997) Na-23 and Cs-133 NMR study of cation adsorption on mineral surfaces: local environments, dynamics, and effects of mixed cations. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 61, 5199–5208.
Kim, Y., Kirkpatrick, R.J. and Cygan, R.T. (1996) Cs-133 NMR study of cesium on the surfaces of kaolinite and illite. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 60, 4059–4074.
Kinniburgh, D.G. and Jackson, M.L. (1981) Cation adsorption by hydrous metal oxides and clay. Pp. 91–160 in: Adsorption of Inorganics at Solid-Liquid Interfaces. (M.A. Anderson and A.J. Rubin, editors). Ann Arbor Science, Michigan.
Kresse, G. and Furthmuller, J. (1996) Efficient iterative schemes for ab initio total-energy calculations using a plane-wave basis set. Physical Review B—Condensed Matter, 54, 11169–11186.
Laird, D.A. (1996) Model for crystalline swelling of 2:1 phyllosilicates. Clays and Clay Minerals, 44, 553–559.
Laird, D.A. (1999) Layer charge influences on the hydration of expandable 2:1 phyllosilicates. Clays and Clay Minerals, 47, 630–636.
Maes, E., Vielvoye, L., Stone, W. and Delvaux, B. (1999) Fixation of radiocaesium traces in a weathering sequence mica → vermiculite → hydroxy interlayered vermiculite. European Journal of Soil Science, 50, 107–115.
Mortland, M.M. (1958) Kinetics of potassium release from biotite. Proceedings Soil Science Society of America, 22, 503–508.
Ni, Y.X. and Hughes, J.M. (1996) The crystal structure of nanpingite-2M2, the Cs end-member of muscovite. American Mineralogist, 81, 105–110.
Payne, M.C., Teter, M.P., Allan, D.C., Arias, T.A. and Joannopoulos, J.D. (1992) Iterative minimization techniques for ab initio total-energy calculations: molecular dynamics and conjugate gradients. Reviews of Modern Physics, 64, 1045–1097.
Perdew, J.P. and Wang, Y. (1992) Accurate and Simple Analytic Representation of the Electron-Gas Correlation-Energy. Physical Review B—Condensed Matter, 45, 13244–13249.
Rich, C.I. and Black, W.R. (1964) Potassium exchange as affected by cation size, pH, and mineral structure. Soil Science, 97, 384–390.
Rothbauer, R. (1971) Untersuchung eines 2M1-muscovits mit Neutronenstrahlen. Neues Jahrbüch für Mineralogie, Monatshefte, 4, 143–154.
Scott, A.D. and Reed, M.G. (1964) Expansion of potassium-depleted muscovite. Proceedings of the 13th National Conference of the Clay Minerals Society, Clays and Clay Minerals, 13, 247–273.
Shannon, R.D. (1976) Revised effective ionic radii and systematic studies of interatomic distances in halides and chalcogenides. Acta Crystallographica Section A: Crystal Physics, Diffraction Theoretical & General Crystallography, 5, 751–767.
Shroll, R.M. and Smith, D.E. (1999) Molecular dynamics simulations in the grand canonical ensemble: application to clay mineral swelling. Journal of Chemical Physics, 111, 9025–9033.
Skipper, N.T., Refson, K. and McConnell, J.D.C. (1991) Computer simulation of interlayer water in 2:1 clays. Journal of Chemical Physics, 94, 7434–7445.
Smith, D.E. (1998) Molecular computer simulations of the swelling properties and interlayer structure of cesium montmorillonite. Langmuir, 14, 5959–5967.
Tamura, T., Bonner, W.E., Brinkley, F.S., Jacobs, D.G., Myers, O.H. and Murano, T. (1963) Mineral exchange studies. Report—Oak Ridge National Laboratory, ORNL-3492, pp. 62–70.
Vanderbilt, D. (1990) Soft self-consistent pseudopotentials in a generalized eigenvalue formalism. Physical Review B, 41, 7892–7895.
Venkataramani, B., Venkateswarlu, K.S. and Shankar, J. (1978) Sorption properties of oxides. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 67, 187–194.
Wagman, D.D., Evans, W.H., Parker, V.B., Halow, I., Bailey, S.M. and Schumm, R.H. (1968) Selected values of chemical thermodynamic properties. Tables for the first thirty-four elements in the standard order of arrangement. United States National Bureau of Standards Technical Note, 270–3, 1–264.
Wagman, D.D., Evans, W.H., Parker, V.B., Halow, I., Bailey, S.M. and Schumm, R.H. (1969) Selected values of chemical thermodynamic properties. Tables for elements 35 through 53 in the standard order of arrangement. United States National Bureau of Standards Technical Note, 270–4, 1–141.
Wang, J.W., Kalinichev, A.G., Kirkpatrick, R.J. and Hou, X.Q. (2001) Molecular modeling of the structure and energetics of hydrotalcite hydration. Chemistry of Materials, 13, 145–150.
Weiss, C.A., Kirkpatrick, R.J. and Altaner, S.P. (1990) Variations in interlayer cation sites of clay minerals as studied by Cs-133 MAS nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. American Mineralogist, 75, 970–982.
White, J.A. and Bird, D.M. (1994) Implementation of gradient-corrected exchange-correlation potentials in Car-Parrinello total energy calculations. Physical Review B—Condensed Matter, 50, 4954–4957.
White, J.L., Bailey, G.W., Brown, C.B. and Ahlrichs, J.L. (1962) Migration of lithium ions into empty octahedral sites in muscovite and montmorillonite. Special Paper—Geological Society of America, 295 pp.
Young, D.A. and Smith, D.E. (2000) Simulations of clay mineral swelling and hydration: dependence upon interlayer ion size and charge. Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 104, 9163–9170.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rosso, K.M., Rustad, J.R. & Bylaska, E.J. The Cs/K exchange in muscovite interlayers: An Ab Initio treatment. Clays Clay Miner. 49, 500–513 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1346/CCMN.2001.0490603
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1346/CCMN.2001.0490603