Abstract
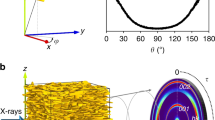
Homoionic Ca-saturated clay pastes were prepared and drying curves were obtained by applying suction pressures from 1 kPa to 100 MPa, A transmission device was used to study particle orientation by placing the clay in a cell specially designed to obtain diagrams corresponding to different sample orientations. The 00l and hk0 reflections were compared to determine the best reflections for studying clay-particle orientation. Depending on the clay, 00/ reflections or the 020 reflection and/or hkl bands can be used to analyze orientation. In many cases the 020 reflection is preferred because the intensity of the peak is high and appears to be independent of the H2O content and the degree of stacking order of layers along the [001] direction.
For interstratified clays, the conditions required to obtain 00l reflections depended on several factors, the most important of which is the water content. Also, the intensity relating to particie orientation depends on (1) particle extension (size) in the (001) plane and (2) the crystal structure. Illite crystals of <1000 A gave a poorly oriented clay matrix. In contrast, large aggregates of illite, smectite, and kaolinite particles (>10,000 Å) showed a strongly oriented system. The particles of smectites may be curved and the dry material was poorly oriented owing to weak cohesion forces between the layers in comparison to illite.
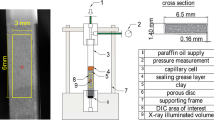
The study of the orientation of particles by X-ray diffraction on hydrated samples may be affected by sample mounting techniques. Any change in the content or the way the sample is mounted may modify the microstructure of a material.
Clay containing a high water content affects the disorientation of particles, whereas, for the dry samples, pore size, pore volume, and solid continuity are associated with the geometry and crystal structure of the clay matrix.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Assouline, S., Tavares-Filho, J., and Tessier, D. (1997) Effect of compaction on soil physical and hydraulic properties: Experimental results and modeling. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 61, 390–398.
Aylmore, L.A.G. and Quirk, J.P. (1959) Swelling of claywater systems. Nature, 183, 1752–1753.
Ben Rhaïem, H., Pons, C.H., and Tessier, D. (1987) Factors affecting the microstructure of smectites. In Role of Cation and History of Applied Stresses. Proceedings of International Clay Conference, Denver, Colorado The Clay Minerals Society, Boulder, Colorado, 292–297.
Brindley, G.W. (1980) Order-disorder in clay minerals structures. In Crystal Structures of Clay Minerals and Their X-ray Identification, G.W. Brindley and G. Brown, eds., Mineralogical Society, London, 125–195.
Brindley, G.W. and Brown, G. eds. (1980) Crystal Structures of Clay Minerals and Their X-ray Identification. Mineralogical Society, London, 495 pp.
Courville, J., Tchoubar, D., and Tchoubar, C. (1979) Détermination expérimentale de la fonction d’orientation. Son application dans les calculs des bandes de diffraction. Journal of Applied Crystallography, 12, 322–338.
Djéran-Maigre, I., Tessier, D., Grunberger, D., Velde, B., and Vasseur, G. (1998) Evolution of microstructures and of macroscopie properties of some clays during experimental compaction. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 15, 109–129.
Elsass, F., Beaumont, A., Pemes, M., Jaunet, A.M., and Tessier, D. (1998) Changes in layer organization of Na- and Ca-exchanged smectite materials during solvent exchanges for embedment in resin. The Canadian Mineralogist, 36, 1475–1483.
Grossman, R.B. and Millet, J.C. (1961) Carbonate removal from soils by a modification of the acetate buffer method. Soil Science Society of America Proceedings, 25, 325–326.
Inigo, A.C. and Tessier, D. (1996) Crystal structure and particle orientation in relation to behavior of clays during drying. Advances in Clay Minerals, 70–72.
Kim, J.M., Peacor, D.R., Tessier, D., and Elsass, F. (1995) A technique for maintaining texture and permanent expansion of smectite interlayer spacings for TEM observations. Clays and Clay Minerals, 43, 51–57.
Kunze, G.W. and Rich, C.I. (1959) Mineralogical methods. In Certain Properties of Selected Southeastern United States Soils and Mineralogical Procedures for Their Study, C.I. Rich, L. Seatz, and F. Kunze, eds., Southern Cooperation Series Bulletin 61, 135–146.
Mamy, J. (1975) Les phéomènes de diffraction des rayonnements X et électroniques par les réseaux atomiques: Application à l’étude de l’ordre cristallin dans les minéraux argileux. Annales Agronomiques, 26, 625–650.
McBride, M.B. (1989) Reactions controlling heavy metal solubility in soils. Advances in Soil Science, 10, 1–56.
Méring, J. (1946) On the hydration of montmorillonite. Transactions of the Faraday Society, 42B, 205–219.
Méring, J. (1949) L’interférence des rayons X dans les systèmes à stratification désordonnée. Acta Crystallographica, 2, 371–377.
Nadeau, P.H., Wilson, M.J., McHardy, W.J., and Tait, J.M. (1984) Interstratified minerals as fundamental particles. Science, 225, 923–925.
Norrish, K. (1954) The swelling of montmorillonite. Discussions of the Faraday Society, 18, 120–134.
Plançon, A. (1980) The calculation of intensities diffracted by a partially oriented powder with a layer structure. Journal of Applied Crystallography, 13, 524–528.
Pons, C.H., Rousseaux, F., and Tchoubar, D. (1981) Utilisation du rayonnement synchrotron en diffusion aux petits angles pour l’étude du gonflement des smectites: 1. Etude du système eau-montmorillonite-Na en fonction de la température. Clay Minerals, 16, 23–42.
Reynolds, R.C. (1980) Interstratified clay minerals. In Crystal Structures of Clay Minerals and Their X-ray Identification, G.W. Brindley and F. Brown, eds., Mineralogical Society, London, 249–303.
Robert, M. and Tessier, D. (1974) Méthode de préparation des argiles des sols pour études minéralogiques. Annales Agronomiques, 25, 859–882.
Taylor, R.M. and Norrish, K. (1966) The measurement of orientation distribution and its application to quantitative X-ray diffraction analysis. Clay Minerals, 6, 127–142.
Tessier, D. (1978a) Etude de l’organisation des argiles calciques. Evolution au cours de la dessiccation. Annales Agronomiques, 29, 319–355.
Tessier, D. (1978b) Technique d’étude de l’orientation des particules argileuses utilisable sur des échantillons secs et humides. Annales Agronomiques, 29, 193–207.
Tessier, D. (1984) Etude Expérimentale de l’Organisation des Matériaux Argileux: Hydratation, Gonflement et Structuration au Cours de la Dessiccation et de la Réhumectation. INRA Versailles, France, 361 pp.
Tessier, D. (1991) Behavior and microstructure of clay minerals. In Soil Colloids and Their Associations in Aggregates, M.F. De Boodt, M. Hayes, and A. Herbillon eds., NATO Book Series, Plenum Publishing Corporation, New York, 387–415.
Tessier, D. and Pédro, G. (1976) Les modalités de l’organisation des particules dans les matériaux argileux. Evolution des principales argiles Ca au cours du phénomène de retrait. Science du Sol, 2, 85–99.
Tessier, D. and Pédro, G. (1987) Mineralogical Characterization of 2:1 Clays in Soils: Importance of the Clay Texture. In Proceedings of the International Clay Conference, Denver, 1985, L.G. Schultz, H. van Olphen, and F.A. Mumpton, eds., The Clay Minerals Society, Bloomington, Indiana, 78–84.
Tessier, D., Bouzigues, J.C., Favrot, J.C., and Valles, V. (1992) Influence du micro-relief sur l’évolution texturate dans les sols lessivés de la vallée de la Garonne. Différenciation des structures vertique et prismatique. Comptes Rendus Académie Sciences Paris, 315, 1027–1032.
Touret, O., Pons, C.H., Tessier, D., and Tardy, Y. (1990) Etude de la répartition de l’eau dans des argiles saturées Mg2+ aux fortes teneurs en eau. Clay Minerals, 25, 217–233.
Vasseur, G., Djéran-Maigre, I., Grunberger, D., Rousset, G., Tessier, D., and Velde, B. (1995) Evolution of structural and physical parameters of clays during experimental compaction. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 12, 941–954.
Wiewiora, A. (1982) Oblique-texture method in transmission X-ray diffractometry of clays and clay minerals. In Proceedings of the 9th Clay Mineralogy and Petrology Conference, Zvolen-Praha, Czechoslovakia, 43–51.
Wiewiora, A. and Weiss, Z. (1985) X-ray powder transmission diffractometry determination of mica polytypes: Method and application to natural samples. Clay Minerals, 20, 231–248.
Wilding, L. and Tessier, D. (1988) Genesis of vertisols: Shrink-swell phenomena. In Vertisols: Their Distribution, Properties, Classification and Management, L. Wilding and R. Puentes, eds., Texas A & M University, Texas 55–81.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Iñigo, A.C., Tessier, D. & Pernes, M. Use of X-Ray Transmission Diffractometry for the Study of Clay-Particle Orientation at Different Water Contents. Clays Clay Miner. 48, 682–692 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1346/CCMN.2000.0480609
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1346/CCMN.2000.0480609