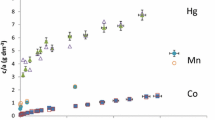
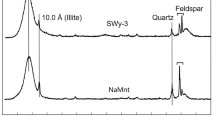
Abstract
We applied the hard and soft acid-base (HSAB) model (Xu and Harsh 1990a, 1990b) to bivalent cation exchange on a purified Ca-montmorillonite. As a result, a satisfactory model is proposed to describe the gradual selectivity of exchange with Ca for 4 of the 6 metals studied (Cd, Cu, Pb, Zn). The selectivity is predicted as a function of the differences of electronegativity and softness of the metals. The deviation of Ni and Co data from the predicting model is interpreted in terms of hydration (Ni and Co being the most strongly hydrated ions). The fitting parameters of the model, α and β, are related to the electronegativity and softness characteristics of the surface, respectively. Their ratio gives information on the nature of bonding. Results suggest that covalent bonding modifies electrostatic interactions, which in turn affect selectivity, with an increasing influence of covalent bondings in the order: Pb < Cd < Zn < Cu.
To balance the lack of representativity of the model for the small molar fraction (NM), we propose to associate to the HSAB model an equation describing the variation of the Vanselow selectivity coefficient as a function of the molar fraction of metal on clay.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Auboiroux M, Baillif P, Touray JC, Bergaya F. 1996. Fixation of Zn2+ and Pb2+ by a Ca-montmorillonite in brines and dilute solutions: Preliminary results. Appl Clay Sci 11:117–126.
Babcock KL, Duckart EC. 1980. The standard state for exchangeable cations. Soil Sci 130:64–67.
Benjamin MM, Leckie JO. 1981. Multiple-site adsorption of Cd, Cu, Zn and Pb on amourphous iron oxyhydroxyde. J Colloid Interface Sci 79:209–221.
Bergaya F, Vayer M. 1997. CEC of clays: Measurement by adsorption of a copper ethylenediamine complex. Appl Clay Sci 12:275–280.
Bertin C, Bourg ACM. 1995. Trends in the heavy metal content (Cd, Pb, Zn) of river sediments in the drainage basin of smelting activities. Wat Res 29:1729–1736.
Bleam WF. 1990a. Electrostatic potential at the basal (001) surface of talc and pyrophyllite as related to tetrahedral sheet distortions. Clays Clay Miner 38:522–526.
Bleam WF. 1990b. The nature of cation-substitution sites in phyllosilicates. Clays Clay Miner 38:527–536.
Bleam WF. 1993. Atomic theorie of phyllosilicates: Quantum chemistry, statistical mechanics, electrostatic theory, and crystal chemistry. Rev Geophys 31:51–73.
Brigatti MF, Corradini F, Franchini GC, Mazzoni S, Medici L, Poppi L. 1995. Interaction between montmorillonite and pollutants from industrial waste-water: Exchange of Zn2+ and Pb2+ from aqueous solutions. Appl Clay Sci 9:383–395.
Briiemmer GW, Gerth J, Tiller KG. 1988. Reaction kinetics of the adsorption and desorption of nickel, zinc and cadmium by goethite. I. Adsorption and difusion of metals. J Soil Sci 39:37–52.
CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 78th edition. 1997. Lide DR, editor. Boca Raton, FL: CRC Pr. p 12-1412–16.
Delville A. 1991. Modeling the clay-water interface. Langmuir 7:547–555.
Eisenman G. 1962. Cation selective glass electrodes and their mode of operation. Biophys J. 2:259–323.
Farrah H, Hatton D, Pickering WF. 1980. The affinity of metal ions for clay surfaces. Chem Geol 28:55–68.
Fripiat JJ, Cloos P, Poncelet A. 1965. Comparaison entre les propriétés d’échange de la montmorillonite et d’une résine vis-à-vis des cations alcalins et alcalino-terreux:, I.-Réversibilité des processus. Bull Soc Chim France: 208–215.
Gaines GL, Thomas HC. 1953. Adsorption studies on clay mineral: II. A formulation of thermodynamics of exchange adsorption. J Chem Phys 21:714–718.
Godfrin JM, Cloos P, Van Bladel R. 1989. Sélectivité des échangés ioniques Ca-Cu et Ca-Zn dans quelques sols belges. Pedol XXXIX-1:89–110.
Goldberg S, Glaubig RA. 1986. Boron adsorption and silicon release by the clay minerals kaolinite, montmorillonite, and illite. Soil Sci Soc Am J 50:1442–1448.
Gorgeon L. 1994. Contribution à la modélisation physicochimique de la rétention de radioéléments a vie longue par des matériaux argileux [3eme cycle], Paris 6.
Guse MP. 1981. An atoms in molecules approach to density functional theory. J Chem Phys 75:828–833.
Güven N. 1992. Molecular aspects of clay-water interactions. In: Güven N, Pollastro RM, editors. Clay-water interface and its rheological implications. Boulder, CO: Clay Miner Soc. p 1–79.
Halen H, Van Bladel R, Cloos P. 1991. Relations pH-adsorption du cuivre, du zinc et du cadmium pour quelques sols et minéraux argileux. Pedol XL-1:47–68.
Helios Rybicka E, Calmano W, Breeger A. 1995. Heavy metal sorption/desorption on competing clay minerals; An experimental study. Appl Clay Sci 9:369–381.
Helios Rybicka E, Kyziol J. 1991. Clays and clay minerals as the natural barries for heavy metals in pollution mech anisms—Illustrated by Polish rivers and soils. Mitt Ôsterr Geol Ges 83:163–176.
Hewitt CN, Rashed MB. 1992. Removal rates of selected pollutants in the runoff waters from a major rural highway. Wat Res 26:311–319.
Hirsch D, Nir S, Banin A. 1989. Prediction of cadmium complexation in solution and adsorption to montmorillonite. Soil Sci Soc Am J 53:716–721.
Inskeep WP, Baham J. 1983. Adsorption of Cd(II) and Cu(II) by Na-montmorillonite at low surface coverage. Soil Sci Soc Am J 47:660–665.
John MK, Van Laerhaven CJ, Cross CH. 1975. Cadmium, lead and zinc accumulation in soil near a smelter complex. Environ Lett 10:25–35.
Kanungo SB. 1994. Adsortion of cations on hydrous oxides of iron. J Colloid Interface Sci 162:93–102.
Klopman G. 1968. Chemical reactivity and the concept of charge-and-frontier controlled reaction. J Am Chem Soc 90:223–234.
Langmuir D. 1997. Aqueous environmental geochemistry. New York: Prentice-Hall. 600 p.
Lee PK, Baillif P, Touray JC, Lepiller M, Gallet M. 1996. Un système de décantation-filtration des eaux pluviales dans le domaine autoroutier (A71). Rev Gén Rout et Aérod 741:24–30.
Lee PK, Touray JC, Baillif P, Ildefonse JP. 1997. Heavy metal contamination of settling particles in a retention pond along the A-71 motorway in Sologne, France. Sci Tot Environ 201:1–15.
Liu J, Howard SM, Han KN. 1993. Adsorption behavior of cadmium and zinc ions on oxide/water interfaces. Langmuir 9:3635–3639.
Makov G. 1995. Chemical hardness in density functional theory. J Phys Chem 99:9337–9339.
Maza-Rodriguez J, Oliver-Pastor P, Bruque S, Jimenez-Lopez A. 1992. Exchange selectivity of lanthanide ions in montmorillonite. Clay Miner 27:81–89.
Misono M, Ochiai E, Saito Y, Yoneda Y. 1967. A new dual parameter scale for the strength of Lewis acids and bases with the evaluation of their softness. J Inorg Nucl Chem 29:2685–2691.
Nagle JK. 1990. Atomic polarizability and electronegativity. J Am Chem Soc 112:4741–4747.
Nir S. 1986. Specific and nonspecific cation adsorption to clays: Solution concentrations and surface potentials. Soil Sci Soc Am J 50:52–57.
Nwankwo JN, Elinder CG. 1979. Cadmium, lead and zinc concentrations in soils and in food grown near a zinc and lead smelter in Zambia. Bull Environ Contamin Tox 22:625–631.
Parr RG, Pearson RG. 1983. Absolute hardness: Companion parameter to absolute electronegativity. J Am Chem Soc 105:7512–7516.
Parr RG, Yang W. 1989. Density-functional theory of atoms and molecules. New York: Oxford Univ Pr. 333 p.
Pearson RG. 1963. Hard and soft acids and bases. J Am Chem Soc 85:3533–3539.
Pearson RG. 1968a. Hard and soft acids and bases, HSAB, Part I. J Chem Educ 45:581–587.
Pearson RG. 1968b. Hard and soft acids and bases, HSAB, Part II. J Chem Educ 45:643–648.
Pearson RG. 1986. Absolute electronegativity and hardness correlated with molecular orbital theory. Proc Natl Acad Sci (USA) 83:8440–8441.
Pearson RG. 1997. Chemical hardness. weinheim: Wiley-VCH. 198 p.
Peigneur P, Maes A, Cremers A. 1975. Heterogeneity of charge density in montmorillonite as inferred from cobalt adsorption. Clays Clay Miner 23:71–75.
Rashin AA, Honig B. 1985. Reevaluation of the Bom model of the ion hydration. J Phys Chem 89:5588–5593.
Robles J, Bartolotti LJ. 1984. Electronegativities, electron affinities, ionization potentials, and hardness of the elements within spin polarized density functional theory. J Am Chem Soc 106:3723–3727.
Rose AW, Bianchi-Mosquera GC. 1993. Adsorption of Cu, Pb, Zn, Co, Ni, and Ag on goethite and hematite: A control on metal mobilization from red beds into stratiform copper deposits. Econ Geol 88:1226–1236.
Schindler PW, Liechti P, Westall JC. 1987. Adsorption of copper, cadmium and lead from aqueous solution to the kaolinite/water interface. Neth J Agr Sci 35:219–230.
Schultess CP, Huang CP. 1990. Adsorption of heavy metal by silicon and aluminium oxydes surfaces on clay minerals. Soil Sci Soc Am J 54:679–688.
Siantar DP, Fripiat JJ. 1995. Lead retention and complexation in a magnesium smectite. J Colloid Interface Sci 169:400–407.
Skipper NT, Refson K, McConnell JDC. 1991. Computer simulation of interlayer water in 2:1 clays. J Chem Phys 94:7434–7445.
Skipper NT, Soper AK, McConnell JDC. 1991. The structure of interlayer water in vermiculite. J Chem Phys 94:5751–5760.
Sposito G. 1984. The surface chemistry of soils. New York: Clarendon Pr.
Stadler M, Schindler PW. 1993. The effect of dissolved ligands on the sorption of Cu(II) by Ca-montmorillonite. Clays Clay Miner 42:148–160.
Staunton S, Roubaud M. 1997. Adsorption of 137Cs on montmorillonite and illite: Effect of charge compensating cation, ionic strength, concentration of Cs, K and fulvic acid. Clays Clay Miner 45:251–260.
Sullivan PJ. 1997. The principle of Hard and Soft Acids and Bases as applied to exchangeable cation selectivity in soils. Soil Sci 124:117–121.
Tiller KG, Gerth J, Briimmer G. 1984. The sorption of Cd, Zn and Ni by soil clay fractions: Procedure for partition of bound forms and their interpretation. Geoderm 34:1–16.
Trichet J, Disnar JR, Bonnamy S, Gauthier B, Nakashima S, Oberlin A, Perruchot A, Rouzaud JN. 1987. Le comportement mutuel de la matière organique et des métaux: Implications géochimiques et métallogéniques. Mém Soc Géol Fr 151:143–162.
Van Bladel R, Halen H, Cloos P. 1993. Calcium-zinc and calcium-cadmium exchange in suspensions of various types of clays. Clay Miner 28:33–38.
Viraraghavan T, Kapoor A. 1994. Adsorption of mercury from wastewater by bentonite. Appl Clay Sci 9:31–49.
Wada K, Kakuto Y. 1980. Selective adsorption of zinc on halloysite. Clays Clay Miner 28:321–327.
Xu S, Harsh JB. 1990a. Monovalent cation selectivity quantitatively modeled according to Hard/Soft Acid/Base theory. Soil Sci Soc Am J 54:357–363.
Xu S, Harsh JB. 1990b. Hard and Soft Acid-Base model verified for monovalent cation selectivity. Soil Sci Soc Am J 54:1596–1601.
Xu S, Harsh JB. 1992. Alkali cation selectivity and surface charge of 2:1 clay minerals. Clays Clay Miner 40:567–574.
Yang W, Parr RG. 1985. Hardness, softness, and the fukui function in the electronic theory of metals and catalysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 82:6723–6726.
Zachara JM, Kittrick JA, Harsh JB. 1988. The mechanism of Zn2+ adsorption on calcite. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 52:2281–2291.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Auboiroux, M., Melou, F., Bergaya, F. et al. Hard and Soft Acid-Base Model Applied to Bivalent Cation Selectivity on a 2:1 Clay Mineral. Clays Clay Miner. 46, 546–555 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1346/CCMN.1998.0460508
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1346/CCMN.1998.0460508