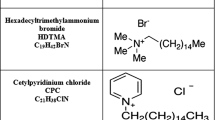
Abstract
The surface thermodynamic properties of a series of n-alkylammonium and quaternary ammonium treated clay films were determined by contact angle measurement of drops of test liquids using the Young equation for polar materials. The two clays were a Wyoming montmorillonite (SWy-1) and Laponite RD. For a series of primary n-alkyl (6 ≤ n ≤ 15) and several quaternary organic cations, the organo-clay (both SWy-1 and Laponite RD) showed very little change in the value of γLW compared to the equivalent ammonium-saturated clay. Also, γ⊕ remained small or increased slightly compared to the ammonium-saturated clay. For SWy-1 exchanged by both quaternary ammonium and primary n-alkylammonium cations, the value of γ⊖ was smaller (0.1 ≤ γ⊖ ≤ 15.8 mJ/m2) than for the ammonium-saturated clay (γ⊖ = 36.2 mJ/m2) and decreased linearly with the number of carbon atoms. The γ⊖ values for the organic cation-exchanged Laponite RD samples (24.2 ≤ γ⊖ ≤ 31.2 mJ/m2) were smaller than or comparable to the ammonium saturated clay (γ⊖ = 30.7 mJ/m2), and were relatively insensitive to the number of carbon atoms in the organic cation. Thus, for both clays the increased adsorption of organic molecules resulting from replacement of inorganic cations by organic cations is due primarily to the decrease in the value of the Lewis base parameter, γ⊖.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chassin P., Jouany C., and Quiquampoix H. (1986) Measurement of the surface free energy of Ca-montmorillonite: Clay Miner. 21, 899–907.
Chibowski E. and Staszczuk P. (1988) Determination of surface free energy of kaolinite: Clays & Clay Minerals 36, 455–461.
Costanzo P. M., Giese R. F., Norris J., and van Oss C. J. (1991a) Effect of exchangeable cations on the surface properties of clay minerals: in abstracts American Chemical Society Meeting, Atlanta, Georgia.
Costanzo P. M., Giese R. F., and van Oss C. J. (1991b) Determination of the acid-base characteristics of clay mineral surfaces by contact angle measurements—Implications for the adsorption of organic solutes from aqueous media: J. Adhesion Sci. Technol. 4, 267–275.
Costanzo P. M., Giese R. F., and van Oss C. J. (1991c) The determination of surface tension parameters of powders by thin layer wicking: in Advances in Measurement and Control of Colloidal Processes, International Symposium on Colloid & Surface Engineering, R. A. Williams and N. C. de Jaeger, eds., Butterworth Heinemann, London, 223–232.
Cowan C. T. and White D. (1962) Adsorption by organoclay complexes, I: Proc. 9th National Clay Conf, 459–467.
Giese R. F., Costanzo P. M., and van Oss C. J. (1991) The surface free energies of talc and pyrophyllite: Phys. Chem. Minerals 17, 611–616.
Giese R. F., van Oss C. J., Norris J., and Costanzo P. M. (1989) Surface energies of some smectite minerals: Proc. 9th Int. Clay Conf. Strasbourg, Sci. Geol. Mem. 86, 33–41.
Girifalco L. A. and Good R. J. (1957) A theory for the estimation of surface and interfacial energy. I. Derivation and application to interfacial tension: J. Phys. Chem., 64, 904–909.
Hofmann U., Endell K., and Wilm D. (1934) Röntgenographische und kolloidchemische Untersuchungen über T on: Angew. Chem. 47, 539–547.
Holysz L. and Chibowski E. (1992) Surface free energy components and floatability of barite precovered with sodium dodycyl sulfate: Langmuir 8, 303–308.
Janczuk B. and Bialopiotrowicz T. (1988) Components of surface free energy of some clay minerals: Clays & Clay Minerals 36, 243–248.
Jasper J. J. (1972) The surface tension of pure liquid compounds: J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data 1, 841–1010.
Johnson R. E. and Dettre R. H. (1964) Contact angle hysteresis: Advan. Chem. Ser. 43, 112–135.
Jouany C. (1991) Surface free energy components of claysynthetic humic acid complexes from contact angle measurements: Clays & Clay Minerals 39, 43–49.
Jouany C. and Chassin P. (1987) Determination of the surface energy of clay-organic complexes by contact-angle measurements: Colloids and Surfaces 27, 289–303.
Lagaly G. and Weiss A. (1969) Determination of the layer charge in mica-type layer silicates: Proc. Intern. Clay Conf., Tokyo, VI, 61–80.
Li Z., Giese R. F., van Oss C. J., and Eberl D. (1991) Surface thermodynamic properties of some illites: in abstracts, Clay Mineral Society Annual Meeting, Houston, Texas.
Mortland M. M., Shaobai S., and Boyd S. A. (1986) Clayorganic complexed as adsorbents for phenol and chlorophenols: Clays & Clay Minerals 34, 581–585.
Murphy K., van Oss C. J., and Giese R. F. (1991) Surface free energies of kaolinites: in abstracts Clay Minerals Society Annual Meeting, Houston, Texas.
Norris J. G. (1987) Layer charge magnitude and homogeneity and their relationship to the thixotropic properties of bentonites: Ph.D. thesis, State University of New York at Buffalo, 111 pp.
Ruelicke G. and Kohler E. E. (1981) A simplified procedure for determining layer charge by the n-alkylammonium method: Clay Miner. 16, 305–307.
Smith C. R. (1936) Base exchange reactions of bentonites and salts of organic bases: J. Am. Chem. Soc. 56, 1561–1563.
van Oss C. J. and Good R. J. (1992) Prediction of the solubility of polar polymers by means of interfacial tension combining rules: Langmuir, submitted.
van Oss C. J., Chaudhury M. K., and Good R. J. (1988) Interfacial Lifshitz-van der Waals and polar interactions in macroscopic systems: Chem. Rev. 88, 927–941.
van Oss C. J., Chaudhury M. K., and Good R. J. (1989) The mechanism of phase separation of polymers in organic media—Apolar and polar systems: Separation Sci. Tech. 24, 15–30.
van Oss C. J., Giese R. F., and Costanzo P. M. (1990) DLVO and non-DLVO interactions in hectorite: Clays & Clay Minerals 38, 151–159.
van Oss C. J., Giese R. F., Li Z., Murphy K., Norris J., Chaudhury M. K., and Good R. F. (1992) Determination of contact angles and pore sizes of porous media by column and thin layer wicking: J. Adhesion Sci. Technol., 6, 413–428.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Norris, J., Giese, R.F., van Oss, C.J. et al. Hydrophobic Nature of Organo-Clays as a Lewis Acid/Base Phenomenon. Clays Clay Miner. 40, 327–334 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1346/CCMN.1992.0400313
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1346/CCMN.1992.0400313