Abstract
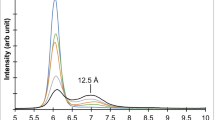
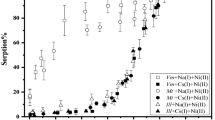
The conversion of Malawi vermiculite into K-vermiculite by treatment with bi-ionic K-Mg solutions of 1 N total ion concentration (KCl and MgCl2 mixed solutions of ionic strength equal to 0.5) was studied by following the 00l X-ray powder diffraction (XRD) reflections. Flakes of Mg-saturated samples were treated at 160°C during 24 hr with bi-ionic solutions, with the K concentration varying from zero to pure 1 N KCl solution. The K-Mg interlayer exchange began at a critical value xK = .0196 (K/Mg = 1/100) of the molar fraction of K in the solution. Above the critical concentration and extending to pure 1 N KCl, the XRD diagrams were characteristic of a 10-Å/14-Å interstratification that had a marked tendency towards regularity. Experiments with KCl and MgCl2 mixed solutions of ionic strength equal to 0.75 and 1.0 showed that the exchange began at the same critical value xK as the experiments with ionic strength equal to 0.5, if the K added was equivalent. X-ray fluorescence analysis further showed that the amount of K adsorbed was proportional to the molar fraction xK and to the proportion of K-saturated layers (10 Å) in the interstratification. To explain the mechanism of this quasi-regular interstratification, a crystallochemical rather than a thermodynamic mechanism is proposed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bailey, S. W. (1982) Nomenclature for regular interstrati-fication: Clay Miner. 17, 243–248.
Basset, W. A. (1959) The origin of vermiculite at Libby: Amer. Mineral. 35, 590–595.
Boettcher, A. L. (1966) Vermiculite, hydrobiotite and bio-tite in the Rainy Creek igneous complex near Libby, Montana: Clay Miner. 6, 283–296.
Brindley, G. W. and Gillery, F. M. (1956) X-ray identification of chlorite species: Amer. Mineral. 41, 169–181.
Brindley, G. W., Zalba, P. E., and Bethke, C. M. (1983) Hydrobiotite, a regular 1:1 interstratification of biotite and vermiculite layers: Amer. Mineral. 68, 420–425.
de la Calle, C., Suquet, H., and Pons, C. H. (1988) Stacking order in a 14.3-A Mg-vermiculite: Clays & Clay Minerals 36, 481–490.
Farmer, V. C., Russell, J. D., Machardy, W. J., Newman, A. C. D., Ahlrich, J. L., and Rimsaite, J. Y. H. (1971) Evidence for loos of octahedral iron from oxidised biotites and vermiculites: Mineral. Mag. 38, 1–37.
Giese, R. F. (1971) Hydroxyl orientation in muscovite as indicated by electrostatic calculations: Science 172, 263–264.
Guinier, A. (1964) Théorie et Technique de la Radio-Cristallographie: Dunod, Paris, 740 pp.
Jackson, M. L., Hseung, Y., Corey, R. B., Evans, E. J., and Vanden Heuvel, R. C. (1952) Weathering sequence of clay size minerals in soils and sediments. II. Chemical weathering of layer silicate: Soil Sci. Soc. Amer. Proc. 16, 3–6.
MacEwan, D. M. C., Ruiz-Amil, A., and Brown, G. (1961) Interstratified clay minerals: in The X-Ray Identification and Crystal Structures of Clay Minerals, G. Brown, ed., Mineralogical Society, London, 393–445.
MacEwan, D. M.C. and Ruiz-Amil, A. (1975) Interstratified clay minerals: in Soil Components. I. Inorganic Components, G. E. Gieseking, ed., Springer-Verlag, New York, 265–334.
Méring, J. (1949) Interference des rayons X dans les systèmes désordonnée: Acta Crystallogr. 2, 371–377.
Morel, S. W. (1955) Biotite in the basement complex of southern Nyasaland: Geol. Mag. 92, 241–255.
Newman, A. C. D. and Brown, G. (1987) The chemical constitution of clays: in Chemistry of Clays and Clay Minerals, A. C. D. Newman, ed., Mineralogical Society, London, 1–128.
Norrish, K. (1973) Factors in the weathering of mica to vermiculite: in Proc. Int. Clay Confi, Madrid, 1972, J. M. Serratosa, ed., Div. Ciencias C.S.I.C., Madrid, 417–432.
Pons, C. H. (1980) Mise en évidence des relations entre la structure et la texture dans les systèmes eau-smectites par la diffusion aux petits angles du rayonnement X synchrotron: Ph.D. thesis, Univ. Orleans, Orleans, France, 175 pp.
Pons, C. H., Pozzuoli, A., Rausell-Colom, J. A., and Calle, C., de la (1989) Mécanisme de passage de l’état hydraté à une couche à l’état zéro couche d’une vermiculite-Li de Santa Olalla: Clay Miner. 24, 479–494.
Radoslovich, E. W. (1960) The structure of muscovite: Acta Cristallogr. 13, 919–925.
Radoslovich, E. C. (1963) The cell dimensions and symmetry of layer-lattice silicates. IV. Interatomic forces: Amer. Mineral. 48, 76–99.
Reynolds, R. C. (1980) Interstratified clay minerals: in Crystal Structures of Clay Minerals and their X-Ray Identification, G. W. Brindley and G. Brown, eds., Mineralogical Society, London, 249–303.
Rhoades, J. D. and Coleman, N. T. (1967) Interstratification in vermiculite and biotite produced by potassium sorption. I. Evaluation by simple X-ray diffraction pattern inspection: Soil Sci. Soc. Amer. Proc. 31, 366–372.
Sato, M. (1965) Structure of interstratified (mixed-layer) minerals: Nature 208, 70–80.
Sawhney, B. L. (1967) Interstratification in vermiculite: in Clays & Clay Minerals, Proc. 15th Natl. Conference, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania 1966, S. W. Bailey, ed., Pergamon Press, New York, 75–84.
Sawhney, B. L. (1969) Regularity of interstratification as affected by charge density in layer silicates: Soil Sci. Soc. Amer. Proc. 33, 42–46.
Sawhney, B. L. and Reynolds, R. C. (1985) Interstratified clays as fundamental particles: A discussion: Clays & Clay Minerals 33, p. 559.
Stephen, I. (1952) A study of rock weathering with reference of the Malvern Hills. Part I. Weathering of biotite and granite: J. Soil Sci. 87, 20–33.
Vila, E. and Ruiz-Amil, A. (1988) Computer program for analysing interstratified structures: Powder Diffraction 3, 7–11.
Vila, E., Ruiz-Amil, A., and Martin de Vidales, J. L. (1988) Computer program for X-ray powder diffraction analysis: Internal Report, C.S.I.C., Madrid, Spain.
Walker, G. F. (1950) Trioctahedral minerals in the soil clays of northeast Scotland: Mineral. Mag. 29, 72–84.
Weed, S. B. and Leonard, R. A. (1968) Effect of K-uptake by K-depleted micas on the basal spacing: Soil Sci. Soc. Amer. Proc. 32, 335–340.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Martin de Vidales, JL., Vila, E., Ruiz-Amil, A. et al. Interstratification in Malawi Vermiculite: Effect of Bi-Ionic K-Mg Solutions. Clays Clay Miner. 38, 513–521 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1346/CCMN.1990.0380508
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1346/CCMN.1990.0380508