Abstract
Clinoptilolite from the Fort LaClede deposit in Sweetwater County, Wyoming, shows a moderate selectivity for NH4− over Na+ in aqueous solution. At 30°C, the standard free energy of this replacement reaction is −0.7 kcal/mole at an ionic strength of 0.05 M and −0.8 kcal/mole at 0.5 M. The Na+-NH4+ exchange is complete within 3 days in agitated solution and proceeds to the same extent from the clinoptilolite saturated with either cation.
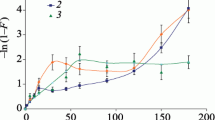
The Ca2+-Na+ exchange also is complete within 3 days in agitated aqueous solution and proceeds to the same extent from either the calcium or the sodium form of the zeolite. Using test methods which take into account the slower equilibration of Ca2+-loaded clinoptilolite, the cation-exchange capacity is substantially the same over the full range of loading by Ca2+ and Na+. Ca2+ replaces Na+ with decreasing selectivity as Ca2+ loading increases to about 80% at 30°C (95% at 63°C), above which the selectivity reverses. The standard free energy of replacement of two Na+ ions by one Ca2+ ion in 0.05 M solution is −1.2 ± 0.2 kcal/mole at 63°C and −0.3 to −0.8 kcal/mole at 30°C.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ames, L. L., Jr. (1960) The cation sieve properties of clinoptilolite: Amer. Mineral. 45, 689–700.
Ames, L. L., Jr. (1961) Cation sieve properties of the open zeolites chabazite, mordenite, erionite and clinoptilolite: Amer. Mineral. 46, 1120–1131.
Barrer, R. M., Papadopoulos, R., and Rees, L. V. C. (1967) Exchange of sodium in clinoptilolite by organic cations: J. Inorg. Nucl. Chem. 29, 2047–2063.
Barrer, R. M., Rees, L. V. C, and Shamsuzzoha, M. (1966) Thermochemistry and thermodynamics of ion exchange in a near-faujasite: J. Inorg. Nucl. Chem. 28, 629–643.
Barrer, R. M., Rees, L. V. C, and Ward, D. J. (1963) Thermochemistry and thermodynamics of ion exchange in a crystalline exchange medium: Proc. Royal Soc, Ser. A 273, 180–197.
Black, C. A., ed. (1965) Methods of Soil Analysis: Amer. Soc. Agron., Madison, Wisconsin, 894–899.
Breck, D. W. (1974) Zeolite Molecular Sieves: Wiley, New York, 533–534.
Curry, H. D. and Samini, K. (1983) Washakie basin, Wyoming, zeolites: in Genesis and Exploration of Metallic and Nonmetallic Minerals and Ore Deposits of Wyoming and Adjacent Areas, W. D. Hausel and R. E. Harris, eds., Public Inf. Circ. 19, Geol. Soc. Wyoming, Laramie, Wyoming, 32–33.
Dyer, A. (1984) Uses of natural zeolites: Chemistry & Industry, 241–245.
Gaines, G. L., Jr. and Thomas, H. C (1953) Adsorption studies on clay minerals. II. A formulation of the thermodynamics of exchange adsorption: J. Chem. Phys. 21, 714–718.
Howery, D. G. and Thomas, H. C (1965) Ion exchange on the mineral clinoptilolite: J. Phys. Chem. 69, 531–537.
Laitinen, H. A. (1960) Chemical Analysis: McGraw-Hill, New York, 10–12.
Llenado, R. A. (1984) The use of sodium type A zeolite in laundry detergents: in Proc. 6th Int. Zeolite Conf, D. Olson and A. Bisio, eds., Butterworths, Guildford, Surrey, United Kingdom, 940–956.
McNair, D. R., Sims, R. C, and Grenney, W. J. (1986) An evaluation of clinoptilolite amended slow rate sand filtration economics at higher than standard flow rates: Proc. 1986 Annual Conference, Amer. Water Works Assn., Denver, Colorado, 285–300.
Mumpton, F. A. (1978) Natural zeolites: A new industrial mineral commodity: in Natural Zeolites: Occurrence, Properties, Use, L. B. Sand and F. A. Mumpton, eds., Pergamon Press, Elmsford, New York, 3–27.
Rees, L. V. C. (1984) Binary and ternary exchange in zeolite A: in Proc. 6th Int. Zeolite Conf, D. Olson and A. Bisio, eds., Butterworths, Guildford, Surrey, United Kingdom, 626–640.
Roehler, H. W. (1973) Stratigraphy of the Washakie Formation in the Washakie basin, Wyoming: U.S. Geol. Surv. Bull. 1369, 40 pp.
Semmens, M. J. and Seyfarth, M. (1978) The selectivity of clinoptilolite for certain heavy metals: in Natural Zeolites: Occurrence, Properties, Use, L. B. Sand and F. A. Mumpton, eds., Pergamon Press, Elmsford, New York, 517–526.
Vaughan, D. E. W. (1978) Properties of natural zeolites: in Natural Zeolites: Occurrence, Properties, Use, L. B. Sand and F. A. Mumpton, eds., Pergamon Press, Elmsford, New York, 353–371.
Wiers, B. H., Grosse, R. J., and Cilley, W. A. (1982) Divalent and trivalent ion exchange with zeolite A: Envir. Sci. Tech. 16, 617–624.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hulbert, M.H. Sodium, Calcium, and Ammonium Exchange on Clinoptilolite from the Fort Laclede Deposit, Sweetwater County, Wyoming. Clays Clay Miner. 35, 458–462 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1346/CCMN.1987.0350606
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1346/CCMN.1987.0350606