Abstract
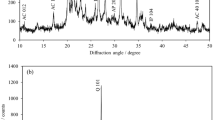
Low-angle X-ray powder diffraction (XRD) measurements of soil samples, made at controlled relative humidities, showed the presence of major reflections at 20–33, 10–27, and 7–8 Å. The first reflection, which increased in intensity but did not shift in spacing with decreasing relative humidity, represents curved smectite layers. This spacing was also observed by high-resolution transmission electron microscopy. The value of 10–27 Å for the second reflection, the 001 reflection of smetite, is unusually high, probably due to poorly stacked, irregularly curved layers. The 7–8-Å reflection originates from kaolinite or dehydrated halloysite, which also contain curved layers. The more curved the layer structure of the smectite, the more difficult it is to detect this phase; therefore the XRD relative peak heights are not directly proportional to the percentages of the smectite.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chapman, J. A. and Zussman, J. (1959) Further electron optical observations on crystals of antigorite: Acta Crys-tallogr. 12, 550–552.
De Wit, H. A. (1978) Soils and grassland types of the Ser-engeti plain (Tanzania): Their distribution and interrelations: Ph.D. Thesis, Agricultural University, Wageningen, The Netherlands, 300 pp.
Gilley, F. H. and Hill, V. G. (1959) X-ray study of synthetic Mg-Al serpentines and chlorites: Amer. Mineral. 44, 143–152.
Jager, Tj. (1982) Soils of the Serengeti woodlands, Tanzania: Agric. Res. Rep. 912, PUDOC., Wageningen, 239 pp.
Kunze, G. (1956) Die gewelte Struktur des Antigorites. I: Z. Kristallogr. Kristallgeom. 108, 83–107.
Kunze, G. (1958) Die gewelte Struktur des Antigorites. II: Z. Kristallogr. Kristallgeom. 110, 282–320.
Kunze, G. (1961) Antigorit. Strukturtheoretische Grundla-gen und ihre Bedeutung fur Serpentin-Forschung: Fortschr. Miner. 39, 206–324.
McKee, T. R., Dixon, J. B., Whitehouse, U. G., and Harling, D. F. (1973) Study of Te Puke halloysite by a high resolution electron microscope: 31st Ann. Electron Microscopy Soc. of America Meeting.
Mizota, C. and van Reeuwijk, L. P. (1986) Clay mineralogy and chemistry of Andisols and related soils from diverse climatic regimes: International Soil Reference and Information Centre, Wageningen, The Netherlands, Monograph (in press).
Pauling, L. (1930) The structure of the chlorites: Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 16, 578–582.
Roy, D. M. and Roy, R. (1954) Experimental study of the formation and properties of synthetic serpentines and related layer silicate minerals: Amer. Mineral. 39, 957–975.
Van der Gaast, S. J. and Kühnel, R. A. (1986) Effects of different cations and relative humidity on hydration-de-hydration mechanisms of Wyoming montmorillonite: Applied Clay Science (in press).
Van der Gaast, S. J. and Vaars, A. J. (1981) A method to eliminate the background in X-ray diffraction patterns of oriented clay mineral samples: Clays & Clay Minerals 16, 383–393.
Van der Gaast, S. J., Wada, K., Wada, S.-L., and Kakuto, Y. (1985) Small-angle X-ray diffraction, morphology, and structure of allophane and imogolite: Clays & Clay Minerals 33, 237–243.
Wada, K. and Kakuto, Y. (1983) Intergradient vermiculite-kaolin mineral in a Korean Ultisol: Clays & Clay Minerals 31, 183–190.
Wielemaker, W. G. and Wakatsuki, T. (1984) Properties, weathering and classification of some soils formed in per-alkaline volcanic ash in Kenya: Geoderma 32, 21–44.
Zussman, J. (1954) Investigation of the crystal structure of antigorite. Mineral. Mag. 30, 498–512.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
van der Gaast, S.J., Mizota, C. & Jansen, J.H.F. Curved Smectite in Soils from Volcanic ash in Kenya and Tanzania: A Low-Angle X-Ray Powder Diffraction Study. Clays Clay Miner. 34, 665–671 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1346/CCMN.1986.0340607
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1346/CCMN.1986.0340607