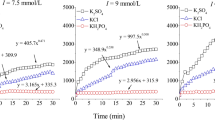
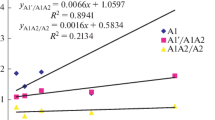
Abstract
Photon correlation spectroscopy (PCS), a dynamic light-scattering technique for particle size measurement, was used to determine the coagulation rates of aqueous dispersions of relatively monodisperse South Carolina Peerless kaolinite, Silver Hill, Montana, illite, Wyoming montmorillonite, and Florida palygorskite. This technique allows quantitative measurement of the rate of coagulation for clay particles where the traditional turbidity method gives only a qualitative measure. The critical coagulation concentrations for KCl at pH = 10.0 were: 0.199 M for kaolinite, 0.202 M for illite, 0.290 M for montmorillonite, and 0.034 M for palygorskite. The effective Hamaker constants, calculated using Derjaguin-Landau-Verwey-Overbeek theory, were: 3.1 × 10−20 J for kaolinite, 2.5 × 10−20 J for illite, 2.2 × 10−20 J for montmorillonite, and 1.63 × 10−19 J for palygorskite. Stern potentials at the critical coagulation concentration at pH 10.0 were: −42.7 mV for kaolinite, −40.7 mV for illite,‒21.2 mV for montmorillonite, and −66.9 mV for palygorskite.
Резюме
Фото-корреляцционная спектроскопия (ФКС), динамический, свет рассеивающий метод для измерений размера частиц, использовалась для определения скоростей коагуляции водных дисперсий относительно монодисперсионных каолинитов из Южной Каролины, иллита из Серебряного Холма, Монтана, монтмориллонита из Вайоминга и палыгорскита из Флориды. Этот метод позволяет из¬мерять количественно скорость коагуляции частиц глины в случае, когда традиционный метод путем мутнения дает только качественное измерение. Критические концентрации коагуляции КС1 при рН = 10 были: 0,199 М для каолинита, 0,202 М для иллита, 0,29 М для монтмориллонита, и 0,034 М для палыгорскита. Эффективные постоянные Гамакера, рассчитанные при использовании теории Дер-жагина-Ландау-Веруэя-Овербика, составляли: 3,1 × 10−20 дж для каолинита, 2,5 × 10t—20 дж для ил-лита, 2,2 × 10−20 дж для монтмориллонита, и 1,63 × 10−19 дждля палыгорскита. Потенциалы Штерна при критических концентрациях коагуляции при рН = 10,0 составляли: −42,7 мв для каолинита, −40,7 мв для иллита, −21,2 мв для монтмориллонита, и −66,9 мв для палыгорскита. [E.G.]
Resümee
Photonenkorrelationsspektroskopie (PCS), eine dynamische auf Lichtstreuung beruhende Technik zur Messung der Teilchengröße wurde verwendet, um die Koagulationsgeschwindigkeiten von wässrigen Dispersionen von relativ monodispersem South Carolina Peerless Kaolinit; Illit von Silver Hill, Montana; Montmorillonit von Wyoming; und Palygorskit von Florida zu bestimmen. Diese Methode erlaubt die quantitative Messung der Koagulationsgeschwindigkeit für Tonpartikel, während die her¬kömmliche Turbiditätsmethode nur qualitative Messungen ergibt. Die kritischen Koagulationskonzen¬trationen für KCl bei pH 10,0 waren: 0,199 m für Kaolinit; 0,202 m für Illit; 0,290 m für Montmorillonit; und 0,034 m für Palygorskit. Die wirksamen Hamaker-Konstanten, die unter Verwendung der Derjaguin-Landau-Verwey-Overbeek-Theorie berechnet wurden, waren: 3,1 × 10−20 J für Kaolinit; 2,5 × 10−20 J für Illit; 2,2 × 10−20 J für Montmorillonit; und 1,63 × 10−19 für Palygorskit. Die Stern-Potentiale bei der kritischen Koagulationskonzentration bei pH 10,0 waren −42,7 mV für Kaolinit; −40,7 mV für Illit; −21,2 mV für Montmorillonit; und − 66,9 mV für Palygorskit. [U.W.]
Résumé
La spectroscopie à corrélation de photons (PCS), une technique dynamique, éparpillant la lumière pour mesurer la taille de particules, a été utilisée pour déterminer les allures de coagulation des dispersions aqueuses relativement monodisperses de kaolinite Peerless de Caroline du Sud, d’illite de Silver Hill du Montana, de montmorillonite du Wyoming, et de palygorskite de Floride. Cette technique permet de mesurer l’allure de coagulation de particules d’argile de manière quantitative, tandis que la méthode traditionnelle de turbidité ne donne qu’une mesure qualitative. Les concentrations de coagulation critiques pour KCl au pH = 10,0 étaient: 0,199 M pour la kaolinite, 0,202 M pour l’illite, 0,290 M pour la montmorillonite, et 0,034 M pour la palygorskite. Les constantes effectives d’Hamaker, calculées d’après la théorie Derjaguin-Landau-Verwey-Overbeek, étaient 3,1 × 10−20 J pour la kaolinite, 2,5 × 10−20 J pour l’illite, 2,2 × 10−20 J pour la montmorillonite, et 1,63 × 10−19 J pour la palygorskite. Les potentiels de Stern aux concentrations critiques de coagulation au pH 10,0 étaient: −42,7 mV pour la kaolinite, −40,7 mV pour l’illite, −21,2 mV pour la montmorillonite, et −66,9 mV pour la palygorskite. [D.J.]
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen, T. (1981) Particle Size Measurement: 3rd ed., Chapman and Hall Publ., London, 104 pp.
Barringer, E. A., Novich, B. E. and Ring, T. A. (1983) Colloidal stability of ceramic powders using photon correlation spectroscopy: J. Colloid Interface Sci. (in press).
Bleier, A. and Matijevic, E. (1976) Heterocoagulation. VI. Interactions of a monodispersed chromium hydroxide with polyvinyl chloride latex: J. Colloid Interface Sci. 55 510–535.
Chu, B. (1974) Laser Light Scattering: Academic Press, N.Y., 318 pp.
Cummings, H. Z. and Pusey, P. N. (1977) Dynamics of macromolecular motion: in Photon Correlation Spectroscopy and Velocimetry, H. Z. Cummings and E. R. Pike, eds., Plenum Press, N.Y., 164–199.
Friend, J. P. and Hunter, R. J. (1970) Vermiculite as a model system in the testing of double layer theory: Clays & Clay Minerals 18 275–283.
Honig, E. P., Roberson, G. J., and Wiersema, P. H. (1971) Effect of hydrodynamic interaction on the coagulation rate of hydrophobic colloids: J. Colloid Interface Sci. 36 97–109.
Israelachvilli, J. N. and Adams, G. E. (1978) Measurement of forces between two mica surfaces in aqueous electrolyte solutions in the range 0–100 nm: J. Chem. Soc, Faraday Trans. 774 975–1001.
Koppel, D. E. (1972) Analysis of macromolecular polydis-persity in intensity correlation spectroscopy: the method of cumulants: J. Chem. Phys. 57 4814–4820.
Krupp, H., Schnabel, W., and Walter, G. (1972) The Lif-shitz-Van der Waals constant on the basis of optical data: J. Colloid Interface Sci. 39 421–423.
Lambe, T. W. and Whitman, R. V. (1968) Soil Mechanics: Wiley, N.Y., 29–40.
Lips, A. and Willis, E. (1973) Low angle light scattering technique for the study of coagulation: J. Chem. Soc, Faraday Trans. 169 1226–1236.
Marmur, A. (1979) A kinetic theory approach to primary and secondary minimum coagulations and their combination: J. Colloid Interface Sci. 72 41–48.
Mathews, B. A. and Rhodes, C. T. (1970) Studies of the coagulation kinetics of mixed suspensions: J. Colloid Interface Sci. 32 332–338.
May, A. and Smelley, A. G. (1979) Effects of electrolytes on the electrophoretic mobilities of Florida phosphatic clay wastes: Bur. Mines Rept. Invest. RI 8398 1–13.
Novich, B. (1983) Composition and rheology of Florida phosphatic waste clay slurries: geotechnical implications: M.S. thesis, Dept. of Civil Engineering, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, Mass., 252 pp.
Overbeek, J. Th. G. (1952) Coagulation phenomena: in Colloid Science, Vol. 1 H. R. Kruyt, ed., Elsevier, London, p. 159.
Reerink, H. and Overbeek, J. Th. G. (1954) The rate of coagulation as a measure of the stability of silver iodide sols: Disc. Faraday Soc. 18 74–84.
Sasaki, H., Matejevic, E., and Barouch, E. (1980) Heterocoagulation. VI. Interactions of a monodispersed hydrous aluminum oxide sol with polystyrene latex: J. Colloid Interface Sci. 76 319–329.
Spielman, L. (1970) Viscous interactions in Brownian coagulation: J. Colloid Interface Sci. 33 562–571.
Tabor, D. and Winterton, R. H. S. (1969) The direct measurement of normal and retarded Van der Waals forces: Proc. Roy. Soc. A312 435–450.
Tambour, V. and Seinfeld, J. H. (1980) Solution of the discrete coagulation equation: J. Colloid Interface Sci. 74 260–272.
van Olphen, H. (1957) Surface conductance of various ion forms of bentonite in water and the electrical double layer: J. Amer. Chem. Soc. 61 1276–1280.
van Olphen, H. (1977) Introduction to Clay Colloid Chemistry: 2nd ed., Wiley, N.Y., 318 pp.
van Olphen, H. and Fripiat, J. J. (1979) Data Handbook for Clay Materials and other Non-Metallic Minerals: Pergamon Press, New York, 346 pp.
von Smoluchowski, M. (1917) Versuch einer mathematischen Theorieder Koagulationskinetic kolloider Lösungen: Z. Phys. Chem. 92 129–168.
Weise, G. R. and Healy, T. W. (1975) Coagulation and electrokinetic behavior of TiO2 and H2O colloidal dispersions: J. Colloid Interface Sci. 51 427–433.
Williams, D. J. A. and Williams, K. P. (1978) Electrophoresis and zeta potential of kaolinite: J. Colloid Interface Sci. 65 79–87.
Yates, D.E. (1975) The structure of the oxide/aqueous electrolyte interface: Ph.D. thesis, University of Melbourne, Australia, 272 pp.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Novich, B.E., Ring, T.A. Colloid Stability of Clays Using Photon Correlation Spectroscopy. Clays Clay Miner. 32, 400–406 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1346/CCMN.1984.0320508
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1346/CCMN.1984.0320508