Abstract
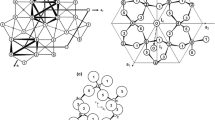
Three sepiolite clays studied showed evidence for the presence of structural hydroxyl groups in three to five different environments depending on the composition of the clay. A 3720 cm−1 i.r. frequency is shown to be characteristic of SiOH at crystal edges which are very abundant in sepiolites. This band has not been seen by most workers because the Nujol, fluorolube or KBr used in sample preparation perturb it sufficiently to obscure it under other OH stretching bands. The 3680 cm−1 band is confirmed as being from the (Mg)3OH and evidence of a very small band near 3640 cm−1 is suggested to arise from limited trioctahedral substitution. The very crystalline Ampandrandava sepiolite shows only the above three bands. The intermediately crystalline Vallecas shows a 3620 cm−1 band in addition which is characteristic of dioctahedral systems and is due to either some vacancy sites or to the presence of attapulgite. This dioctahedral band is greater in the less crystalline Salinelles sepiolite; in addition, it has a smaller 3585 cm−1 band. Mg-Al-vacancy and Mg-Fe‴-vacancy are suggested as the source of the 3620 cm−1 and 3585 cm−1 bands.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cannings, F. R. (1968) An i.r. study of hydroxyl groups on sepiolite: J. Phys. Chem. 72, 1072–1074.
Farmer, V. C. and Russell, J. D. (1964) The i.r. spectra of layer silicates: Spectrochim Acta 20, 1149–1173.
Farmer, V. C, Rüssel, J. D., Ahlrichs, J. L. and Velde, B. (1967) Vibrations du groupe hydroxyle dans les silicates en couches: Bull. Grpe. Fr. Argiles 19, 5–10.
Fernandez Alverez, T. (1972) Activación de la sepiolita con ácido clorhídrico. Bol. Soc. Esp. Ceram. Vidrio 11, 365–374.
Hayashi, H., Otsuka, R. and Imai, N. (1969) I.r. study of sepiolite and palygorskite on heating: Am. Miner. 55, 1613–1624.
McDonald, R. S. (1957) Study of the interaction between hydroxyl groups of Aerosil silica and adsorbed nonpolar molecules by i.r. spectrometry: J. Am. Chem. Soc. 79, 850–854.
McDonald, R. S. (1958) Surface functionality of amorphous silica by infrared spectroscopy: J. Phys. Chem. 62, 1168–1178.
Mendelovici, E. (1973) Infrared study of attapulgite and HCl treated attapulgite: Clays and Clay Minerals 21, 115–119.
Preisinger, A. (1959) X-ray study of the structure of sepio-lite: Clays and Clay Minerals 6, 61–67.
Prost, R. (1973) Spectre infrarouge de l’eau présente dans láttapulgite et la sépiolite: Bull. Grpe. Fr. Argiles 25, 53–56.
Rautureau, M., Tchoubar, C. and Mering, J. (1973) Analyse structurale de la sepiolite a partir de donnees de la diffraction electronique: Proc. Int. Clay Conf., Madrid pp. 115–121.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahlrichs, J.L., Serna, C. & Serratosa, J.M. Structural Hydroxyls in Sepiolites. Clays Clay Miner. 23, 119–124 (1975). https://doi.org/10.1346/CCMN.1975.0230207
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1346/CCMN.1975.0230207