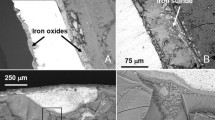
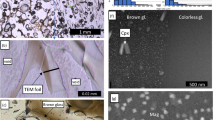
Abstract
Volcanic tuff from the Cabo de Gata region in Almería, southeastern Spain, was altered under hydrothermal conditions at different temperatures (60 to 180°C), reaction times (60 to 360 days), and reacting solutions (deionized water and NaCl and KCl solutions with Na/K ratios from 0.01 to 100, and a total salt concentration of 0.1 to 1 M).
X-ray diffraction (XRD) patterns of the reacted samples revealed a very weak, broad peak at ∼13 Å that migrated to 17 Å upon glycolation. Comparison between simulated (NEWMOD) and experimental XRD patterns indicated that the neoformed phase is a random mixed-layer illite-smectite (I-S) with 75% expandable layers. Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy showed that I-S formation was most extensive for high pH (8–9) solutions, corresponding to dilute solutions and, especially, to deionized water. Analytical electron microscopy (AEM) analyses of isolated I-S particles showed that most of them are smectite-rich I-S regardless of the experimental conditions, in agreement with XRD results. The I-S particles had a wide range of octahedral Mg contents. The pH and Na, K, Ca and Mg concentrations in the final solutions suggested cation (including H+) exchange as a major process in the alteration experiments. Analysis of aqueous activity diagrams (log aK/aHvs. log \({a_{{\rm{Si}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{2}}}}}\)) showed that some solution compositions are consistent and some are inconsistent with I-S formation. These results, combined with complementary electron microscopy analyses (de la Fuente et al., 2000a), are interpreted to be due to direct transformation of the glass into I-S in a process controlled by glass composition.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aja, S.U. (1991) Illite equilibria in solutions: III. A re-interpretation of the data of Sass et al. (1987). Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 55, 3431–3435.
Aja, S.U., Rosenberg, P.E. and Kittrick, J.A. (1991) Illite equilibria in solutions: I. Phase relationships in the system K2O-MgO-Al2O3-SiO2-H2O between 25 and 250°C. Geochimica et Cosmichimica Acta, 55, 1353–1364.
Alt, J. and Jiang, W.-T. (1991) Hydrothermally precipitated mixed-layer illite-smectite in recent massive sulfide deposits from the sea floor. Geology, 19, 570–573.
Amouric, M. and Olives, J. (1991) Illitization of smectite as seen by high-resolution transmission electron microscopy. European Journal of Mineralogy, 3, 831–835.
Bellon, H. (1976) Séries magmatiques néogènes et quaternaires du pourtour de la Méditerrané occidentale, comparées dans leur cadre geochronométrique — implications geodinamiques. PhD thesis, Université de Paris Sud, France, 367 pp.
Bellon, H., Bordet, P. and Montenat, C. (1983) Chronologie du magmatisme néogene des Cordillères Bétiques (Espagne meridionale). Bulletin Societè Geologique de France, 25, 205–217.
Bradley, G.W. and Grim, R.E. (1951) High temperature thermal effects of clay and related materials. American Mineralogist, 36, 182–201.
Brindley, G.W. and Lemaitre, J. (1987) Thermal, oxidation and reduction reactions of clay minerals. Pp. 319–370 in: Chemistry of Clays and Clay Minerals (A.C.D. Newman, editor). Monograph 6, Mineralogical Society, London.
Caballero, E., Reyes, E., Huertas, F., Linares, J. and Pozzuoli, A. (1991) Early-stage smectites from pyroclastic rocks of Almería (Spain). Chemical Geology, 89, 353–358.
Casey, W.H. and Bunker, B. (1990) Leaching of mineral and glass surfaces during dissolution. Pp. 397–426 in: Mineral-Water Interface Geochemistry, (M.F. Hochella, Jr. and A.F. White, editors). Reviews in Mineralogy, 23. Mineralogical Society of America, Washington, D.C.
Cerling, T.E., Brown, F.H. and Bowman, J.R. (1985) Low-temperature alteration of volcanic glass: hydration, Na, K, 18O and Ar mobility. Chemical Geology, 52, 281–293.
Christidis, G., Scott, P. and Marcopoulos, T. (1995) Origin of the bentonite deposits of eastern Milos, Aegean, Greece: geological, mineralogical and geochemical evidence. Clays and Clay Minerals, 43, 63–77.
Crovisier, J.L., Honnorez, J. and Fritz, B. (1992) Dissolution of subglacial volcanic glasses from Iceland: laboratory study and modelling. Applied Geochemistry, Supplementary Issue, 1, 55–81.
Cuadros, J. and Altaner, S.P. (1998) Characterization of mixed-layer illite-smectite from bentonites using microscopic, chemical, and X-ray methods: Constraints on the smectite-to-illite transformation mechanism. American Mineralogist, 83, 762–774.
Cuadros, J. and Linares, J. (1996) Experimental kinetic study of the smectite-to-illite transformation. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 60, 439–453.
de’ Gennaro, M., Langella, A., Cappelletti, P. and Colella, C. (1999) Hydrothermal conversion of trachytic glass to zeolite. 3. Monocationic model glasses. Clays and Clay Minerals, 47, 348–357.
de la Fuente, S., Cuadros, J., Fiore, S. and Linares, J. (2000a) Electron microscopy study of volcanic tuff alteration to illite-smectite under hydrothermal conditions. Clays and Clay Minerals, 48, 339–350.
de la Fuente, S., Cuadros, J. and Linares, J. (2000b) Quantification of mixed-layer illite-smectite in glass matrices by Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy. Clays and Clay Minerals, 48, 299–303.
Decher, A., Bechtel, A., Echle, W., Friedrich, G. and Hoernes, S. (1996) Stable isotope geochemistry of bentonites from the island of Milos (Greece). Chemical Geology, 129, 101–113.
Di Battistini, G., Toscani, L., Iaccarino, S. and Villa, I.M. (1987) K/Ar ages and the geological setting of calc-alkaline volcanic rocks from Sierra de Gata, SE Spain. Neues Jahrbuch für Mineralogie, Monatshefte, 1987(8), 337–383.
Drits, V.A., Salyn, A.L. and Šucha, V. (1996) Structural transformations of interstratified illite-smectites from Dolná Ves hydrothermal deposits: dynamics and mechanisms. Clays and Clay Minerals, 44, 181–190.
Farmer, V.C. (1974) The Layer Silicates. Pp. 331–363 in: The Infrared Spectra of Minerals (V.C. Farmer, editor). Monograph 4, Mineralogical Society, London.
Fernández Soler, J.M. (1992) El volcanismo calco-alcalino de Cabo de Gata (Almería). PhD thesis, The University of Granada, Spain, 243 pp.
Fiore, S., Huertas, F.J., Tazaki, K., Huertas, F. and Linares, J. (1999) A low temperature experimental alteration of a rhyolitic obsidian. European Journal of Mineralogy, 11, 1–15.
Foster, M. (1960) Interpretation of the composition of trioctahedral micas. US Geological Survey Professional Paper, 354B, 11–43.
Ghiara, M.R., Franco, E., Petti, C., Stanzione, D. and Valentino, G.M. (1993) Hydrothermal interaction between basaltic glass, deionized water and seawater. Chemical Geology, 104, 125–138.
Grauby, O., Petit, S., Decarreau, A. and Baronnet, A. (1993) The beidellite-saponite series: an experimental approach. European Journal of Mineralogy, 5, 623–635.
Harvey, C.C. and Browne, P.R. (1991) Mixed-layer clay geothermometry in the Wairakei geothermal field, New Zealand. Clays and Clay Minerals, 39, 614–621.
Inoue, A., Watanabe, T., Kohoyama, N. and Brusewitz, A.M. (1990) Characterization of illitization of smectite in bentonite beds at Kinnekulle, Sweden. Clays and Clay Minerals, 38, 241–249.
Inoue, A., Utada, M. and Wakita, K. (1992) Smectite-to-illite conversion in natural hydrothermal systems. Applied Clay Science, 7, 131–145.
Kawano, M. and Tomita, K. (1992) Formation of allophane and beidellite during hydrothermal alteration of volcanic glass below 200°C. Clays and Clay Minerals, 40, 666–674.
Kawano, M., Tomita, K. and Kamino, Y. (1993) Formation of clay minerals during low temperature. Experimental alteration of obsidian. Clays and Clay Minerals, 41, 431–441.
Keene, J.B., Clague, D.A. and Nishimori, R.K. (1976) Ex perimental hydrothermal alteration of tholeiitic basalt: resultant mineralogy and textures. Journal of Sedimentary Petrology, 46, 647–653.
Kharaka, Y.K., Gunter, W.D., Aggarwal, P.K., Perkins, E.H. and De Braal, J.D. (1988) SOLMINEQ.88: A computer program for geochemical modelling of water-rock interaction. US Geological Survey Water-Resources Investigation Report 88–4227, 420 pp.
Lanson, B. and Champion, D. (1991) The I/S-to-illite reaction in the late stage diagenesis. American Journal of Science, 291, 473–506.
Linares, J. (1985) The process of bentonite formation in Cabo de Gata, Almería, Spain. Mineralogica et Petrographica Acta, 29-A, 17–33.
Mackenzie, R.C. (1970) Simple phyllosilicates based on gibbsite- and brucite-like sheets. Pp. 504–514 in: Differential Thermal Analysis, volume 1 (R.C. Mackenzie, editor). Academic Press, London and New York.
Magonthier, M.C., Petit, J.C. and Dran, J.C. (1992) Rhyolitic glasses as natural analogues of nuclear waste glasses: behaviour of an Icelandic glass upon natural aqueous corrosion. Applied Geochemistry, Supplementary Issue, 1, 83–93.
Nadeau, P.H. and Reynolds, R.C., Jr. (1981) Volcanic components in pelitic sediments. Nature, 294, 72–74.
Papin, A., Sergent, J. and Robert, J. (1997) Intersite OH-F distribution in an Al-rich synthetic phlogopite. European Journal of Mineralogy, 9, 501–508.
Reynolds, R.C., Jr. (1985) NEWMOD: A computer program for the calculation of one-dimensional patterns of mixed-layered clays. R.C. Reynolds, 8 Brook Drive, Hanover, New Hampshire, USA.
Shapiro, L. (1975) Rapid analysis of silicate, carbonate, and phosphate rocks. US Geological Survey Bulletin, 1401, 76 pp.
Shiraki, R. and Iiyama, T. (1990) Na-K ion exchange reaction between rhyolitic glass and (Na, K) Cl aqueous solution under hydrothermal conditions. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 54, 2923–2931.
Šucha, V., Kraus, I., Gerthofferová, H., Peteš, J. and Sereková, M. (1993) Smectite to illite conversion in bentonites and shales of the east Slovak Basin. Clay Minerals, 28, 243–253.
Šucha, V., Elsass, F., Eberl, D.D., Kuchta, L., Madejová, J., Gates, W.P. and Komadel, P. (1998) Hydrothermal synthesis of ammonium illite. American Mineralogist, 83, 58–67.
Tazaki, K., Fyfe, W.S. and van der Gaast, S.J. (1989) Growth of clay minerals in natural and synthetic glasses. Clays and Clay Minerals, 37, 348–354.
Thomassin, J.H., Boutonnat, F., Touray, J.C. and Baillif, P. (1989) Geochemical role of the water/rock ratio during the experimental alteration of a synthetic basaltic glass at 50°C. An XPS and STEM investigation. European Journal of Mineralogy, 1, 261–274.
Tomita, K., Yamane, H. and Kawano, M. (1993) Synthesis of smectite from volcanic glass at low temperature. Clays and Clay Minerals, 41, 655–661.
Velde, B. (1985) Smectites. Pp. 104–169 in: Clay Minerals. A Physico-Chemical Explanation of their Occurrence (C.E. Weaver and L.D. Pollard, editors). Developments in Sedimentology, 40. Elsevier, New York.
Weaver, C.E. and Pollard, L.D. (1973) The Chemistry of Clay Minerals. Developments in Sedimentology, 15. Elsevier, New York, 213 pp.
Yates, D.M. and Rosenberg, P.E. (1996) Formation and stability of end member illite: I. Solution equilibration experiments at 100–250°C and Pv,soln. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 60, 1873–1883.
Zevenbergen, C., Van Reeuwijk, L.P., Bradley, J.P., Bloemen, P. and Comans, R.N.J. (1996) Mechanism and conditions of clay formation during natural weathering of MSWI bottom ash. Clays and Clay Minerals, 44, 546–552.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de la Fuente, S., Cuadros, J. & Linares, J. Early stages of volcanic tuff alteration in hydrothermal experiments: Formation of mixed-layer illite-smectite. Clays Clay Miner. 50, 578–590 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1346/000986002320679468
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1346/000986002320679468