Summary
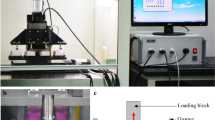
Chondrocytes comprise less than 10% of cartilage tissue but are responsible for sensing and responding to mechanical stimuli imposed on the joint. However, the effect of mechanical signals at the cellular level is not yet fully defined. The purpose of this study was to test the hypothesis that mechanical stimulation in the form of cyclic strain modulates proliferative capacity and integrin expression of chondrocytes from osteoarthritic knee joints. Chondrocytes isolated from articular cartilage during total knee arthroplasty were propagated on flexible silicone membranes. The cells were subjected to cyclic strain for 24 h using a computer-controlled vacuum device, with replicate samples maintained under static conditions. Our results demonstrated increase in proliferative capacity of the cells subjected to cyclic strain compared with cells maintained under static conditions. The flexed cells also exhibited upregulation of the chondrocytic gene markers type II collagen and aggrecan. In addition, cyclic strain resulted in increased expression of the α2 and α5 integrin subunits, as well as an increased expression of vimentin. There was also intracellular reconfiguration of the enzyme protein kinase C. Our findings suggest that these molecules may play a role in the signal transduction pathway, eliciting cellular response to mechanical stimulation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bouchet, B.; Colon, M.; Polotsky, A.; Shikani, A. H.; Hungerford, D. S. Beta-1 integrin expression by human nasal chondrocytes in microcarrier spinner culture. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 52:716–724; 2000.
Buschmann, M. D.; Gluzband, Y. A.; Grodzinsky, A. J.; Hunziker, E. B. Mechanical compression modulates matrix biosynthesis in chondrocyte/agarose culture. J. Cell Sci. 108:1497–1508; 1995.
Camper, L.; Heinegard, D.; Lundgren-Akerlund, E. Integrin Alpha2-Betal is a receptor for the cartilage matrix protein chondroadherin. J. Cell. Biol. 138:1159–1167; 1997.
Damsky, C. H.; Werb, Z. Signal transduction by integrin receptors for extracellular matrix: cooperative processing of extracellular information. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 4:772–781; 1992.
Davisson, T. H.; Wu, F. J.; Jain, D.; Sah, R. L.; Ratcliffe, A. R. Effect of perfusion of the growth of tissue engineered cartilage. Trans. Orthop. Res. Soc. 45:811; 1999.
Durrant, L. A.; Archer, C. W.; Benjamin, M.; Ralphs, J. R. Organization of the chondrocyte cytoskeleton and its response to changing mechanical conditions in organ culture. J. Anat. 194:343–353; 1999.
Frondoza, C.; Sohrabi, A.; Hungerford, D. S. Human chondrocytes proliferate and produce matrix components in microcarrier suspension culture. Biomaterials 17:879–888; 1996.
Giannoni, P.; Siegrist, M.; Hunziker, E. B.; Wong, M. The mechanosensitivity of cartilage oligomeric matrix protein (COMP). Biorheology 40:101–109; 2003.
Gilbert, J. A.; Weinhold, P. S.; Banes, A. J.; Link, G. W.; Jones, G. L. Strain profiles for circular cell culture plates containing flexible surfaces employed to mechanically deform cells in vitro. J. Biomech. 27:1169–1177; 1994.
Hynes, R. O. Integrins: versatility, modulation, and signaling in cell adhesion. Cell 69:11–25; 1992.
Karjalainen, H. M.; Sironen, R. K.; Elo, M. A.; Kaarniranta, K.; Takigawa, M.; Helminen, H. J.; Lammi, M. J. Gene expression profiles in chondrosarcoma cells subjected to cyclic stretching and hydrostatic pressure. A cDNA array study. Biorheology 40:93–100; 2003.
Korver, T. H. V.; van de Stadt, R. J.; Kiljan, E.; Jos van Kampen, G. P.; van der Korst, J. K. Effects of loading on the synthesis of proteoglycans in different layers of anatomically intact articular cartilage in vitro. J. Rheumatol. 19:905–912; 1992.
Langelier, E.; Suetterlin, R.; Hoemann, C. D.; Aebi, U.; Buschmann, M. D. The chondrocyte cytoskeleton in mature articular cartilage: structure and distribution of actin, tubulin, and vimentin filaments. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 48:1307–1320; 2000.
Lapadula, G.; Iannone, F.; Zuccaro, C.;Grattagliano, V.; Covelli, M.; Patella, V.; Lo Bianco, G.; Pipitone, V. Integrin expression on chondrocytes: correlations with the degree of cartilage damage in human osteoarthritis. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 15:247–254; 1997.
Larsson, T.; Aspden, R. M.; Heinegard, D. Effects of mechanical load on cartilage matrix biosynthesis in vitro. Matrix 11:388–394; 1991.
Lee, D. A.; Bader, D. L. Compressive strains at physiological frequencies influence the metabolism of chondrocytes seeded in agarose. J. Orthop. Res. 15:181–188; 1997.
Lee, H. S.; Millward-Sadler, S. J.; Wright, M. O.; Nuki, G.; Al-Jamal, R.; Salter, D. M. Activation of integrin-RACK1/PKCalpha signalling in human articular chondrocyte mechanotransduction. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 10:890–897; 2002.
Lee, H. S.; Millward-Sadler, S. J.; Wright, M. O.; Nuki, G.; Salter, D. M. Integrin and mechanosensitive ion channel-dependent tyrosine phosphorylation of focal adhesion proteins and beta-catenin in human articular chondrocytes after mechanical stimulation. J. Bone Miner. Res. 15:1501–1509; 2000.
Loeser, R. F. Integrin-mediated attachment of articular chondrocytes to extracellular matrix proteins. Arthritis Rheum. 36:1103; 1993.
Loeser, R. F. Integrins and cell signaling in chondrocytes. Biorheology 39:119–124; 2002.
Loeser, R. F.; Carlson, C. S.; McGee, M. P. Expression of β-1 integrins by cultured articular chondrocytes and in osteoarthritic cartilage. Exp. Cell Res. 217:248–257; 1995.
Loeser, R. F.; Forsyth, C. B.; Samarel, A. M.; Im, H. J. Fibronectin fragment activation of proline-rich tyrosine kinase PYK2 mediates integrin signals regulating collagenase-3 expression by human chondrocytes through a protein kinase C-dependent pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 278:24577–24585; 2003.
Maniotis, A. J.; Chen, C. S.; Ingber, D. E. Demonstration of mechanical connections between integrins, cytoskeletal filaments, and nucleoplasm that stabilize nuclear structure. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. US 94:849–854; 1997.
Millward-Sadler, S. J.; Wright, M. O.; Lee, H.; Caldwell, H.; Nuki, G.; Salter, D. M.: Altered electrophysiological responses to mechanical stimulation and abnormal signaling through alpha 5 beta 1 integrin in chondrocytes from osteoarthritic cartilage. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 4:272–278; 2000.
Oh, C. D.; Chun, J. S. Signaling mechanisms leading to the regulation of differentiation and apoptosis of articular chondrocytes by insulin-like growth factor-1. J. Biol. Chem. 19:36563–36571; 2003.
Ostergaard, K.; Salter, D. M.; Petersen, J.; Bendtzen, K.; Hvolris, J.; Andersen, C. B. Expression of alpha and beta subunits of the integrin superfamily in articular cartilage from macroscopically normal and osteoarthritic human femoral heads. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 57:303–308; 1998.
Parkkinen, J. J.; Lammi, M. J.; Helminen, H. J.; Tammi, M. Local stimulation of proteoglycan synthesis in articular cartilage explants by dynamic compression in vitro. J. Orthop. Res. 10:610–620; 1992
Piperno, M.; Reboul, P.; Hellio Le Graverand, M. P.; Peschard, M. J.; Annefeld, M.; Richard, M.; Vignon, E. Glucosamine sulfate modulates dysregulated activities of human osteoarthritic chondrocytes in vitro. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 8:207–212; 2000.
Salter, D. M.; Hughes, D. E.; Simpson, R.; Gardner, D. L. Integrin expression by human articular chondrocytes. Br. J. Rheumatol. 31:231–234; 1992.
Salter, D. M.; Millward-Sadler, S. J.; Nuki, G.; Wright, M. O. Integrin-inter-leukin-4 mechanotransduction pathways in human chondrocytes. Clin. Orthop. 391:S49-S60; 2001.
Salter, D. M.; Millward-Sadler, S. J.; Nuki, G.; Wright, M. O. Differential responses of chondrocytes from normal and osteoarthritic human articular cartilage to mechanical stimulation. Biorheology 39:97–108; 2002.
Schmitt, D. A.; Hatton, J. P.; Emond, C., et al. The distribution of protein kinase c in human leukocytes is altered in microgravty. FASEB J. 10:1627–1633; 1996.
Shikhman, A. R.; Brinson, D. C.; Lotz, M. K. Distinct pathways regulate facilitated glucose transport in human articular chondrocytes during anabolic and catabolic responses. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab.; 2004, electronic publication ahead of print.
Shyy, J. Y.; Chien, S. Role of integrins in cellular responses to mechanical stress and adhesion. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 9:707–713; 1997.
Steinmeyer, J.; Ackermann, B.; Raiss, R. X. Intermittent cyclic loading of cartilage explants modulates fibronectin metabolism. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 5:331–341; 1997.
Wang, N.; Butler, J. P.; Ingber, D. E. Mechanotransduction across the cell surface and through the cytoskeleton. Science 260:1124–1127; 1993.
Wong, M.; Siegrist, M.; Cao, X. Cyclic compression of articular cartilage explants is associated with progressive consolidation and altered expression pattern of extracellular matrix proteins. Matrix. Biol. 18:391–399; 1999.
Woods, V. L.; Schreck, P. J.; Gesink, D. S.; Pacheco, H. O.; Amiel, D.; Akeson, W. H.; Lotz, M. Integrin expression by human articular chondrocytes. Arthritis Rheum. 37:537–544; 1993.
Wright, M. O.; Nishida, K.; Bavington, C., et al. Hyperpolarisation of cultured human chondrocytes following cyclic pressure-induced strain: evidence of a role for alpha 5 beta 1 integrin as a chondrocyte mechanoreceptor. J Orthop Res. 15:742–747; 1997.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lahiji, K., Polotsky, A., Hungerford, D.S. et al. Cyclic strain stimulates proliferative capacity, α2 and α5 integrin, gene marker expression by human articular chondrocytes propagated on flexible silicone membranes. In Vitro Cell.Dev.Biol.-Animal 40, 138–142 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1290/1543-706X(2004)40<138:CSSPCA>2.0.CO;2
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1290/1543-706X(2004)40<138:CSSPCA>2.0.CO;2