Abstract
Background
Nipple-sparing mastectomy (NSM) has become increasingly popular, given its oncologic safety and preserved nipple areolar complex (NAC) aesthetics. Reconstruction has recently shifted from traditional submuscular (SM) to prepectoral (PP) implant placement. It remains unclear how the plane of implant placement might affect NAC perfusion. Our goal was to assess postoperative outcomes following NSM with SM versus PP implant placement.
Methods
A retrospective single-institution review was performed of all patients undergoing NSM and immediate breast reconstruction in either the PP or SM plane from January 2015 to June 2019. Clinicopathologic details and 90-day complication rates were collected. SM and PP group complications were compared using Chi square analysis.
Results
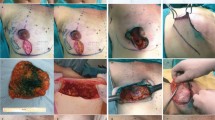
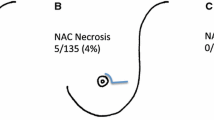
A total of 288 breasts (160 patients) were included, including SM in 79 cases (44 patients) and PP in 209 cases (116 patients). Clinicopathologic features between groups were similar. Overall, the rate of NAC necrosis was 15.1%, with no differences between the SM and PP cohorts (p = 0.79). In cases of NAC necrosis, there was no difference between the SM and PP groups in return to the operating room for debridement (p = 1.0) or explant (p = 0.33).
Conclusions
In our cohort, immediate implant-based reconstruction in the SM and PP planes following NSM was equally safe with respect to postoperative complications and NAC ischemia.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Valero MG, et al. Increase in Utilization of Nipple-Sparing Mastectomy for Breast Cancer: Indications, Complications, and Oncologic Outcomes. Ann Surg Oncol. 2020;27:344–51.
Smith BL, et al. Oncologic safety of nipple-sparing mastectomy in women with breast cancer. J Am Coll Surg. 2017;225:361–5.
Galimberti V, et al. Nipple-sparing and skin-sparing mastectomy: Review of aims, oncological safety and contraindications. Breast. 2017;34(Suppl 1):S82–4 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.breast.2017.06.034.
Moyer HR, Ghazi B, Daniel JR, Gasgarth R, Carlson GW. Nipple-sparing mastectomy: technical aspects and aesthetic outcomes. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2012;68(5):446–50. https://doi.org/10.1097/sap.0b013e3182394bba
Colwell AS, et al. Breast reconstruction following nipple-sparing mastectomy: predictors of complications, reconstruction outcomes, and 5-year trends. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2014;133(3):496–506. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.prs.0000438056.67375.75
Frey JD, Choi M, Salibian AA, Karp NS. Comparison of outcomes with tissue expander, immediate implant, and autologous breast reconstruction in greater than 1000 nipple-sparing mastectomies. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2017;139:1300–10.
Carlson GW, Chu CK, Moyer HR, Duggal C, Losken A. Predictors of nipple ischemia after nipple sparing mastectomy. Breast J. 2014;20:69–73.
Wang CY, et al. Intraoperative assessment of the relationship between nipple circulation and incision site in nipple-sparing mastectomy with implant breast reconstruction using the SPY imaging system. Ann Plast Surg. 2018;80:S59–65.
Manrique OJ, et al. Prepectoral Breast reconstruction in nipple-sparing mastectomy with immediate mastopexy. Ann Plast Surg. 2020;85(1):18–23.
Sbitany H, Piper M, Lentz R. Prepectoral breast reconstruction: a safe alternative to submuscular prosthetic reconstruction following nipple-sparing mastectomy. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2017;140:432–43.
Bhat D, Darrach H, Sacks JM. Prepectoral Breast Reconstruction. Curr. Breast Cancer Rep. 2018;10:48–54. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12609-018-0276-9.
Sobti N, et al. Evaluation of capsular contracture following immediate prepectoral versus subpectoral direct-to-implant breast reconstruction. Sci Rep. 2020;10:1137.
Chatterjee A, et al. Early assessment of post-surgical outcomes with pre-pectoral breast reconstruction: a literature review and meta-analysis. J Surg Oncol. 2018;117:1119–30.
Djohan R, et al. Patient satisfaction following nipple-sparing mastectomy and immediate breast reconstruction: an 8-year outcome study. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2010;125(3):818–29 https://doi.org/10.1097/prs.0b013e3181ccdaa4.
Yueh JH, et al. Nipple-sparing mastectomy: evaluation of patient satisfaction, aesthetic results, and sensation. Ann Plast Surg. 2009;62(5):586–90. https://doi.org/10.1097/sap.0b013e31819fb1ac.
Wei CH, et al. Psychosocial and sexual well-being following nipple-sparing mastectomy and reconstruction. Breast J. 2016;22:10–7.
Romanoff A, et al. A comparison of patient-reported outcomes after nipple-sparing mastectomy and conventional mastectomy with reconstruction. Ann Surg Oncol. 2018;25:2909–16.
Ahn SJ, Woo TY, Lee DW, Lew DH, Song SY. Nipple-areolar complex ischemia and necrosis in nipple-sparing mastectomy. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2018;44(8):1170–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejso.2018.05.006.
Salibian AA, Frey JD, Bekisz JM, Karp NS, Choi M. Ischemic Complications after Nipple-sparing Mastectomy. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2019;7:e2280.
Frey JD, Choi M, Karp NS. The effect of neoadjuvant chemotherapy compared to adjuvant chemotherapy in healing after nipple-sparing mastectomy. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2017;139:10e–9e.
Patel AU, et al. Functional return after implant-based breast reconstruction: a prospective study of objective and patient-reported outcomes. J Plast Reconstr Aesthetic Surg. 2020;73(5):850–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjps.2019.11.038.
Walia GS, et al. Prepectoral versus subpectoral tissue expander placement: a clinical and quality of life outcomes study. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2018;6(4):e1731. https://doi.org/10.1097/gox.0000000000001731.
Salibian AH, Harness JK, Mowlds DS. Staged suprapectoral expander/implant reconstruction without acellular dermal matrix following nipple-sparing mastectomy. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2017;139:30–9.
Salibian AA, Frey JD, Karp NS. Strategies and considerations in selecting between subpectoral and prepectoral breast reconstruction. Gland Surgery. 2019;8(1):11–8. https://doi.org/10.21037/gs.2018.08.01.
Margenthaler JA, et al. Oncologic safety and outcomes in patients undergoing nipple-sparing mastectomy. J Am Coll Surg. 2020;230:535–41.
Young WA, et al. Outcomes of > 1300 nipple-sparing mastectomies with immediate reconstruction: the impact of expanding indications on complications. Ann Surg Oncol. 2019;26:3115–23.
Frey JD, Salibian AA, Levine JP, Karp NS, Choi M. Incision choices in nipple-sparing mastectomy: a comparative analysis of outcomes and evolution of a clinical algorithm. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2081;142:826E–35E.
Acknowledgment
The authors thank Holly R. Zink, MSA, of the Department of Surgery, University of Kansas, Kansas City, for providing medical writing and editorial support for this research. The authors would also like to thank Dr. Amin Amin, Dr. Christa Balanoff, and Dr. Jamie Wagner for providing editorial comments on the abstract.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosures
The authors have no financial interests to declare in relation to the contents of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Braun, S.E., Dreicer, M., Butterworth, J.A. et al. Do Nipple Necrosis Rates Differ in Prepectoral Versus Submuscular Implant-Based Reconstruction After Nipple-Sparing Mastectomy?. Ann Surg Oncol 27, 4760–4766 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-020-08887-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-020-08887-8