Abstract
Introduction
Appendiceal neoplasms are uncommon tumors. Optimal treatment for patients with perforation or high-grade pathology after initial resection is unknown. This study evaluated patients with increased risk for peritoneal dissemination after primary resection, but no evidence of peritoneal disease, who underwent adjuvant hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy (HIPEC).
Methods
This multi-institutional cohort study evaluated 56 patients with high-risk (HR) appendiceal neoplasms with a peritoneal carcinomatosis index of 0 who underwent HIPEC. The patients were divided into two groups: perforated low-grade appendiceal (LGA) carcinoma and HR neoplasms, which included perforated high-grade appendiceal carcinoma, positive margins after initial resection, minimal macroscopic peritoneal disease that was previously resected or completely responded to systemic chemotherapy prior to HIPEC, goblet cell carcinoma, and adenocarcinoma with signet ring cell features. Overall survival (OS) and recurrence-free survival (RFS) were estimated by Kaplan–Meier analysis.
Results
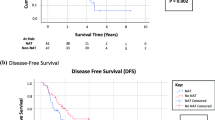
Thirty-eight percent of patients had perforated LGA and 68% had HR features. Five-year OS probability was 82.1% for the entire cohort, and 100% and 70.1% for patients with perforated LGA and HR features, respectively (p = 0.024). Five-year RFS probability was 79.3% for the entire cohort, and 90.0% and 72.4% for patients with perforated LGA and HR features, respectively (p = 0.025). Eight patients recurred after HIPEC and their OS was significantly worse (p < 0.001).
Conclusion
While adjuvant HIPEC is both safe and feasible, there appears to be little benefit over close surveillance when outcomes are compared with historical and prospective studies, especially for perforated LGA carcinoma.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
McCusker ME, Cote TR, Clegg LX, Sobin LH. Primary malignant neoplasms of the appendix: a population-based study from the surveillance, epidemiology and end-results program, 1973–1998. Cancer. 2002;94(12):3307–3312.
Marmor S, Portschy PR, Tuttle TM, Virnig BA. The rise in appendiceal cancer incidence: 2000–2009. J Gastrointest Surg. 2015;19(4):743–750.
Smeenk RM, van Velthuysen ML, Verwaal VJ, Zoetmulder FA. Appendiceal neoplasms and pseudomyxoma peritonei: a population based study. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2008;34(2):196–201.
Madani A, van der Bilt JD, Consten EC, Vriens MR, Borel Rinkes IH. Perforation in appendiceal well-differentiated carcinoid and goblet cell tumors: impact on prognosis? A systematic review. Ann Surg Oncol. 2015;22(3):959–965.
Carr NJ, Cecil TD, Mohamed F, et al. A consensus for classification and pathologic reporting of pseudomyxoma peritonei and associated appendiceal neoplasia: the results of the Peritoneal Surface Oncology Group International (PSOGI) modified Delphi process. Am J Surg Pathol. 2016;40(1):14–26.
Mehta A, Mittal R, Chandrakumaran K, et al. Peritoneal involvement is more common than nodal involvement in patients with high-grade appendix tumors who are undergoing prophylactic cytoreductive surgery and hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy. Dis Colon Rectum. 2017;60(11):1155–1161.
Chua TC, Moran BJ, Sugarbaker PH, et al. Early- and long-term outcome data of patients with pseudomyxoma peritonei from appendiceal origin treated by a strategy of cytoreductive surgery and hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy. J Clin Oncol. 2012;30(20):2449–2456.
Glehen O, Kwiatkowski F, Sugarbaker PH, et al. Cytoreductive surgery combined with perioperative intraperitoneal chemotherapy for the management of peritoneal carcinomatosis from colorectal cancer: a multi-institutional study. J Clin Oncol. 2004;22(16):3284–3292.
Glehen O, Gilly FN, Boutitie F, et al. Toward curative treatment of peritoneal carcinomatosis from nonovarian origin by cytoreductive surgery combined with perioperative intraperitoneal chemotherapy: a multi-institutional study of 1,290 patients. Cancer. 2010;116(24):5608–5618.
Yan TD, Deraco M, Elias D, et al. A novel tumor-node-metastasis (TNM) staging system of diffuse malignant peritoneal mesothelioma using outcome analysis of a multi-institutional database. Cancer. 2011;117(9):1855–1863.
Tuvin D, Berger Y, Aycart SN, et al. Prophylactic hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy in patients with epithelial appendiceal neoplasms. Int J Hyperth. 2016;32(3):311–315.
Baratti D, Kusamura S, Iusco D, et al. Hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy (HIPEC) at the time of primary curative surgery in patients with colorectal cancer at high risk for metachronous peritoneal metastases. Ann Surg Oncol. 2017;24(1):167–175.
Sammartino P, Sibio S, Biacchi D, et al. Prevention of peritoneal metastases from colon cancer in high-risk patients: preliminary results of surgery plus prophylactic HIPEC. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2012;2012:141585.
Goere D, Glehen O, Quenet F, et al. Results of a randomized phase 3 study evaluating the potential benefit of a second-look surgery plus HIPEC in patients at high risk of developing colorectal peritoneal metastases. J Clin Oncol. 2018;36(15 Suppl):3531.
Klaver CE, Wisselink DD, Punt CJ, et al. Adjuvant HIPEC in patients with colon cancer at high risk of peritoneal metastases: primary outcome of the COLOPEC multicenter randomized trial. J Clin Oncol. 2019;37(4 Suppl):482.
Glehen O, Passot G, Villeneuve L, et al. GASTRICHIP: D2 resection and hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy in locally advanced gastric carcinoma: a randomized and multicenter phase III study. BMC Cancer. 2014;14:183.
Coccolini F, Celotti A, Ceresoli M, et al. Hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy (HIPEC) and neoadjuvant chemotherapy as prophylaxis of peritoneal carcinosis from advanced gastric cancer-effects on overall and disease free survival. J Gastrointest Oncol. 2016;7(4):523–529.
Honore C, Caruso F, Dartigues P, et al. Strategies for preventing pseudomyxoma peritonei after resection of a mucinous neoplasm of the appendix. Anticancer Res. 2015;35(9):4943–4947.
Zih FS, Wong-Chong N, Hummel C, et al. Mucinous tumor of the appendix with limited peritoneal spread: is there a role for expectant observation? Ann Surg Oncol. 2014;21(1):225–231.
McDonald JR, O’Dwyer ST, Rout S, et al. Classification of and cytoreductive surgery for low-grade appendiceal mucinous neoplasms. Br J Surg. 2012;99(7):987–992.
Madsen AH, Ladekarl M, Villadsen GE, et al. Effects of cytoreductive surgery and hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy (HIPEC) in the treatment of goblet cell carcinoma: a prospective cohort study. Ann Surg Oncol. 2018;25(2):422–430.
Votanopoulos KI, Bartlett D, Moran B, et al. PCI is not predictive of survival after complete CRS/HIPEC in peritoneal dissemination from high-grade appendiceal primaries. Ann Surg Oncol. 2018;25(3):674–678.
Levine EA, Votanopoulos KI, Qasem SA, et al. Prognostic molecular subtypes of low-grade cancer of the appendix. J Am Coll Surg. 2016;222(4):493–503.
Levine EA, Votanopoulos KI, Shen P, et al. A multicenter randomized trial to evaluate hematologic toxicities after hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy with oxaliplatin or mitomycin in patients with appendiceal tumors. J Am Coll Surg. 2018;226(4):434–443.
Pai RK, Beck AH, Norton JA, Longacre TA. Appendiceal mucinous neoplasms: clinicopathologic study of 116 cases with analysis of factors predicting recurrence. Am J Surg Pathol. 2009;33(10):1425–1439.
Carr NJ, McCarthy WF, Sobin LH. Epithelial noncarcinoid tumors and tumor-like lesions of the appendix. A clinicopathologic study of 184 patients with a multivariate analysis of prognostic factors. Cancer. 1995;75(3):757–768.
Misdraji J, Yantiss RK, Graeme-Cook FM, Balis UJ, Young RH. Appendiceal mucinous neoplasms: a clinicopathologic analysis of 107 cases. Am J Surg Pathol. 2003;27(8):1089–1103.
Dhage-Ivatury S, Sugarbaker PH. Update on the surgical approach to mucocele of the appendix. J Am Coll Surg. 2006;202(4):680–684.
Yantiss RK, Shia J, Klimstra DS, Hahn HP, Odze RD, Misdraji J. Prognostic significance of localized extra-appendiceal mucin deposition in appendiceal mucinous neoplasms. Am J Surg Pathol. 2009;33(2):248–255.
Roxburgh CS, Fenig YM, Cercek A, et al. Outcomes of low-grade appendiceal mucinous neoplasms with remote acellular mucinous peritoneal deposits. Ann Surg Oncol. 2019;26(1):118–124.
Haslinger M, Francescutti V, Attwood K, et al. A contemporary analysis of morbidity and outcomes in cytoreduction/hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemoperfusion. Cancer Med. 2013;2(3):334–342.
Bao P, Bartlett D. Surgical techniques in visceral resection and peritonectomy procedures. Cancer J. 2009;15(3):204–211.
Levine EA, Stewart JH 4th, Shen P, Russell GB, Loggie BL, Votanopoulos KI. Intraperitoneal chemotherapy for peritoneal surface malignancy: experience with 1,000 patients. J Am Coll Surg. 2014;218(4):573–585.
Bradley RF, Stewart JH 4th, Russell GB, Levine EA, Geisinger KR. Pseudomyxoma peritonei of appendiceal origin: a clinicopathologic analysis of 101 patients uniformly treated at a single institution, with literature review. Am J Surg Pathol. 2006;30(5):551–559.
Radomski M, Pai RK, Shuai Y, et al. Curative surgical resection as a component of multimodality therapy for peritoneal metastases from goblet cell carcinoids. Ann Surg Oncol. 2016;23(13):4338–4343.
Blackham AU, Swett K, Eng C, et al. Perioperative systemic chemotherapy for appendiceal mucinous carcinoma peritonei treated with cytoreductive surgery and hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy. J Surg Oncol. 2014;109(7):740–745.
Bijelic L, Kumar AS, Stuart OA, Sugarbaker PH. Systemic chemotherapy prior to cytoreductive surgery and HIPEC for carcinomatosis from appendix cancer: impact on perioperative outcomes and short-term survival. Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2012;2012:163284.
Dindo D, Demartines N, Clavien PA. Classification of surgical complications: a new proposal with evaluation in a cohort of 6336 patients and results of a survey. Ann Surg. 2004;240(2):205–213.
Yan TD, Black D, Sugarbaker PH, et al. A systematic review and meta-analysis of the randomized controlled trials on adjuvant intraperitoneal chemotherapy for resectable gastric cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 2007;14(10):2702–2713.
Coccolini F, Cotte E, Glehen O, et al. Intraperitoneal chemotherapy in advanced gastric cancer Meta-analysis of randomized trials. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2014;40(1):12–26.
Funding
No specific funding was received for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: LME, PS; Data acquisition: LME, MHC, DLB, LT, GNM, JJS, KCP, KIV, EAL, PS; Data analysis and interpretation: LME, EAL, PS; Drafting of the manuscript: LME, PS; Editing and final approval of the manuscript: LME, MHC, DLB, LT, GNM, JJS, KCP, KIV, EAL, PS.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosure
Laura M. Enomoto, M. Haroon Choudry, David L. Bartlett, Linsay Totin, Gary N. Mann, Joseph J. Skitzki, Kathleen C. Perry, Konstantinos I. Votanopoulos, Edward A. Levine, and Perry Shen have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Enomoto, L.M., Choudry, M.H., Bartlett, D.L. et al. Outcomes After Adjuvant Hyperthermic Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy for High-Risk Primary Appendiceal Neoplasms After Complete Resection. Ann Surg Oncol 27, 107–114 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-019-07634-y
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-019-07634-y