Abstract
Purpose
Modern treatment concepts for bladder/prostate rhabdomyosarcoma (BPRMS) are designed to improve survival, to reduce therapy intensity, and to increase bladder preservation rates. Nevertheless, treatment is not optimal. The purpose of this study was to analyze BPRMS patients treated within the CWS-2002P trial regarding outcome, treatment modalities, complications, and to compare the data with the precursor trial CWS-96.
Methods
Fifty children with localized embryonal BPRMS were analyzed. Eight patients were excluded. Patients received neoadjuvant chemotherapy. At week 9, reassessment using MRI scan was performed. Depending on tumor size, age, and response, local therapy consisting of radiotherapy and/or surgery was initiated. After local therapy, systemic therapy was continued.
Results
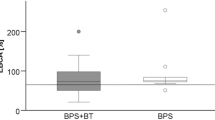
Patients’ median age was 35.6 months. Median follow-up was 59 months. The 5-year OS was 84.5 % and the 5-year ES 79.9 %. Ten patients underwent combined radiochemotherapy and tumor resection (5-year ES: 87.5 %). Six patients were treated solely with radiochemotherapy (5-year ES: 60 %). Twenty-six patients received preoperative chemotherapy followed by tumor resection (ES: 80.8). One patient was treated with chemotherapy only and survived. The bladder preservation rate was 80.9 %.
Conclusions
The outcome within the CWS-2002P trial regarding OS and ES seemed to be better than in the precursor trial CWS-96 due to a reduction of protocol violations, but there was no statistical significant difference possibly due to low numbers. Radiotherapy was used less frequently, and the bladder preservation rate was slightly higher. Novel concepts will be required in the future to improve bladder preservation rates.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
McDowell HP. Update on childhood rhabdomyosarcoma. Arch Dis Child. 2003;88:354–7.
Arndt C, Rodeberg D, Breitfeld PP, et al. Does bladder preservation (as a surgical principle) lead to retaining bladder function in bladder/prostate rhabdomyosarcoma? Results from the Intergroup Rhabdomyosarcoma Study IV. J Urol. 2004;171:2396.
Pappo AS, Shapiro DN, Crist WM, et al. Biology and therapy of pediatric rhabdomyosarcoma. J Clin Oncol. 1995;13:2129–39.
Fryer CJ. Pelvic rhabdomyosarcoma: paying the price of bladder preservation. Lancet. 1995;345:141–2.
Seitz G, Dantonello TM, Int-Veen C, et al. Treatment efficiency, outcome and surgical treatment problems in patients suffering from localized embryonal bladder/prostate rhabdomyosarcoma: a report from the Cooperative Soft Tissue Sarcoma Trial CWS-96. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2011;56(5):718–24.
Jenney M, Oberlin O, Audry G, et al. Conservative approach in localized rhabdomyosarcoma of the bladder and prostate: results from the International Society of Paediatric Oncology (SIOP) studies: malignant mesenchymal tumour (MMT) 84, 89 and 95. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2014;61(2):217–22.
Ferrer FA, Isakoff M, Koyle MA. Bladder/prostate rhabdomyosarcoma: past, present and future. J Urol. 2006;176(4Pt1):1283–91.
Kaplan EL, Meyer P. Nonparametric estimation from incomplete observations. J Am Stat Assoc. 1958;477–81.
Dindo D, Demartines N, Clavien PA. Classification of surgical complications: a new proposal with evaluation in a cohort of 6336 patients and results of a survey. Ann Surg. 2004;240:205–13.
Harel M, Ferrer FA, Shapiro LH, et al. Future directions in risk stratification and therapy of advanced pediatric genitourinary rhabdomyosarcoma. Urol Oncol Sem Orig Invest 2016; 34:103–15.
Rodeberg DA, Anderson JR, Arndt CA, et al. Comparison of outcomes based on treatment algorithms for rhabdomyosarcoma of the bladder/prostate: combined results from the Children´s Oncology Group, German Cooperative Soft Tissue Sarcoma Study, Italian Cooperative Group, and International Society of Pediatric Oncology Malignant Mesenchymal Tumor Committee. Int J Cancer. 2011;128:1232–9.
Raney B, Anderson J, Jenney M, et al. Late effects in 164 patients with rhabdomyosarcoma of the bladder/prostate region: a report from the international workshop. J Urol. 2006;176:2190–4.
Acknowledgment
The authors acknowledge Iris Veit, Simone Feuchtgruber, and Erika Hallmen for their tremendous help acquiring data for this paper. Additionally, they thank all contributing centers, physicians, parents, and patients for contributing the CWS-2002P trial and the German Cancer Aid for the financial support (founded from 2002–2005, Project No. 50-2721).
Disclosure
The authors state no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Guido Seitz and Jörg Fuchs contributed equally to the first authorship.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Seitz, G., Fuchs, J., Sparber-Sauer, M. et al. Improvements in the Treatment of Patients Suffering from Bladder-Prostate Rhabdomyosarcoma: A Report from the CWS-2002P Trial. Ann Surg Oncol 23, 4067–4072 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-016-5391-0
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-016-5391-0