Abstract
Background
Angiotensin 2 is a key biologic peptide in the renin–angiotensin system (RAS) that regulates blood pressure and renal hemodynamics. The potential role of the RAS in the promotion of tumor growth, angiogenesis, and metastasis also has been shown in the past few decades. This study investigated the prognostic impact of RAS blockade on patients with renal cell carcinoma (RCC) after surgery.
Methods
The study identified 557 patients with pathologically diagnosed RCC (pT1-4 N0M0) and evaluated the prognostic factors after surgery for patients administered or not administered angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACEs) or angiotensin 2 receptor blockers (ARBs).
Results
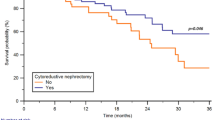
The median follow-up period was 5.1 years. Radical nephrectomy was performed for 349 patients (62.7 %), whereas the remaining 208 patients (37.3 %) underwent partial nephrectomy. A total of 104 patients (18.7 %) were administered RAS inhibitors: ACEs (n = 22) or ARBs (n = 82). Multivariate analysis showed that administration of RAS inhibitors (P = 0.044; HR 2.69), longer tumor length (P < 0.001; HR 1.02), high-grade tumor (P < 0.001; HR 3.55), and positive microvascular invasion (P < 0.003; HR 3.13) were not independent risk factors for a decrease in subsequent disease-specific survival after surgery for RCC. The 5-year disease-specific survival rate was 96.8 % among the patients administered RAS inhibitors and 89.8 % among their counterparts (P = 0.019).
Conclusions
The authors propose renin–angiotensin blockade as a possible potent choice for effective treatment after surgical treatment of RCC.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Motzer RJ, Bander NH, Nanus DM. Renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 1996;335:865–75.
Guinan PD, Vogelzang NJ, Fremgen AM, et al. Renal cell carcinoma: tumor size, stage, and survival. Members of the Cancer Incidence and End Results Committee. J Urol. 1995;153(3 Pt 2):901–3.
Figlin RA. Renal cell carcinoma: management of advanced disease. J Urol. 1999;161:381–6; (discussion 386–7).
Escudier B, Pluzanska A, Koralewski P, et al. Bevacizumab plus interferon alfa-2a for treatment of metastatic renal cell carcinoma: a randomised, double-blind phase III trial. Lancet. 2007;370:2103–11.
Escudier B, Eisen T, Stadler WM, et al. Sorafenib in advanced clear-cell renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2007;356:125–34.
Motzer RJ, Hutson TE, Tomczak P, et al. Sunitinib versus interferon alfa in metastatic renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2007;356:115–24.
Lever AF, Hole DJ, Gillis CR, et al. Do inhibitors of angiotensin-I-converting enzyme protect against risk of cancer? Lancet. 1998;352:179–84.
Egami K, Murohara T, Shimada T, et al. Role of host angiotensin II type 1 receptor in tumor angiogenesis and growth. J Clin Invest. 2003;112:67–75.
Juillerat-Jeanneret L, Celerier J, Chapuis Bernasconi C, et al. Renin and angiotensinogen expression and functions in growth and apoptosis of human glioblastoma. Br J Cancer. 2004;90:1059–68.
Ager EI, Neo J, Christophi C. The renin-angiotensin system and malignancy. Carcinogenesis. 2008;29:1675–84.
George AJ, Thomas WG, Hannan RD. The renin-angiotensin system and cancer: old dog, new tricks. Nat Rev Cancer. 2010;10:745–59.
Miyajima A, Kosaka T, Asano T, Seta K, Kawai T, Hayakawa M. Angiotensin II type I antagonist prevents pulmonary metastasis of murine renal cancer by inhibiting tumor angiogenesis. Cancer Res. 2002;62:4176–9.
Kosugi M, Miyajima A, Kikuchi E, Horiguchi Y, Murai M. Angiotensin II type 1 receptor antagonist candesartan as an angiogenic inhibitor in a xenograft model of bladder cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2006;12:2888–93.
Levey AS, Bosch JP, Lewis JB, Greene T, Rogers N, Roth D. A more accurate method to estimate glomerular filtration rate from serum creatinine: a new prediction equation. Modification of Diet in Renal Disease Study Group. Ann Intern Med. 1999;130:461–70.
Grandi AM, Maresca AM. Blockade of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system: effects on hypertensive target organ damage. Cardiovasc Hematol Agents Med Chem. 2006;4:219–28.
Arrieta O, Guevara P, Escobar E, Garcia-Navarrete R, Pineda B, Sotelo J. Blockage of angiotensin II type I receptor decreases the synthesis of growth factors and induces apoptosis in C6 cultured cells and C6 rat glioma. Br J Cancer. 2005;92:1247–52.
Greco S, Muscella A, Elia MG, et al. Angiotensin II activates extracellular signal regulated kinases via protein kinase C and epidermal growth factor receptor in breast cancer cells. J Cell Physiol. 2003;196:370–7.
Khakoo AY, Sidman RL, Pasqualini R, Arap W. Does the renin-angiotensin system participate in regulation of human vasculogenesis and angiogenesis? Cancer Res. 2008;68:9112–5.
Ronquist G, Rodriguez LA, Ruigomez A, et al. Association between captopril, other antihypertensive drugs, and risk of prostate cancer. Prostate. 2004;58:50–6.
Christian JB, Lapane KL, Hume AL, Eaton CB, Weinstock MA, Trial V. Association of ACE inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers with keratinocyte cancer prevention in the randomized VATTC trial. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2008;100:1223–32.
Uemura H, Ishiguro H, Nakaigawa N, et al. Angiotensin II receptor blocker shows antiproliferative activity in prostate cancer cells: a possibility of tyrosine kinase inhibitor of growth factor. Mol Cancer Ther. 2003;2:1139–47.
Tatokoro M, Fujii Y, Kawakami S, et al. Phase II trial of combination treatment of interferon-alpha, cimetidine, cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor, and renin-angiotensin-system inhibitor (I-CCA therapy) for advanced renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 2011;102:137–43.
Wilop S, von Hobe S, Crysandt M, Esser A, Osieka R, Jost E. Impact of angiotensin I converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin II type 1 receptor blockers on survival in patients with advanced non–small cell lung cancer undergoing first-line platinum-based chemotherapy. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2009;135:1429–35.
Keizman D, Huang P, Eisenberger MA, et al. Angiotensin system inhibitors and outcome of sunitinib treatment in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma: a retrospective examination. Eur J Cancer. 2011;47:1955–61.
Sipahi I, Debanne SM, Rowland DY, Simon DI, Fang JC. Angiotensin-receptor blockade and risk of cancer: meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Lancet Oncol. 2010;11:627–36.
Collaboration ARBT. Effects of telmisartan, irbesartan, valsartan, candesartan, and losartan on cancers in 15 trials enrolling 138,769 individuals. J Hypertens. 2011;29:623–35.
Shirotake S, Miyajima A, Kosaka T, et al. Regulation of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 through angiotensin II type 1 receptor in prostate cancer. Am J Pathol. 2012;180:1008–16.
Shirotake S, Miyajima A, Kosaka T, et al. Angiotensin II type 1 receptor expression and microvessel density in human bladder cancer. Urology. 2011;77:1009, e1019–25.
Yuge K, Miyajima A, Tanaka N, et al. Prognostic value of renin-angiotensin system blockade in non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 2012;19:3987–93.
Tanaka N, Miyajima A, Kikuchi E, et al. Prognonstic impact of renin-angiotensin system blockade in localised upper-tract urothelial carcinoma. Br J Cancer. 2012;106:290–6.
Conflict of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Satoshi Yazawa have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miyajima, A., Yazawa, S., Kosaka, T. et al. Prognostic Impact of Renin–Angiotensin System Blockade on Renal Cell Carcinoma After Surgery. Ann Surg Oncol 22, 3751–3759 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-015-4436-0
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-015-4436-0