Abstract
Background
Although a high neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) has been reported to be a predictor of poor survival in patients with pancreatic cancers, its prognostic role in patients with advanced pancreatic cancer undergoing chemotherapy remains unclear. This study was performed to determine the prognostic role of NLR in patients with advanced pancreatic cancer undergoing chemotherapy.
Methods
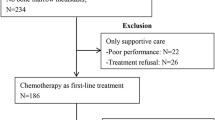
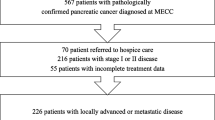
We retrospectively enrolled 403 patients undergoing chemotherapy for advanced pancreatic adenocarcinoma from 2002 to 2013. Univariate and multivariate analyses were performed to identify clinicopathological predictors of overall survival including baseline NLR (NLR before chemotherapy) and postchemotherapy NLR change (NLR change before and after one cycle of chemotherapy), using the Cox proportional hazards model. Clinicopathological characteristics related to baseline NLR and postchemotherapy NLR change were evaluated.
Results
Univariate and multivariate analyses showed that both baseline NLR (NLR ≥ 3.1 vs. NLR < 3.1, hazard ratio [HR] = 1.42; P = 0.001) and postchemotherapy NLR change (NLR ≥ 3.1 and increased vs. NLR < 3.1 and decreased, HR = 2.39; P = 0.000) were independent prognostic factors in overall survival. NLR ≥ 3.1 before chemotherapy and NLR postchemotherapy change were significantly correlated with distant metastasis, serum CA19-9 levels, and serum albumin levels.
Conclusions
Baseline NLR and postchemotherapy NLR change may serve as potential biomarkers for overall survival in patients with advanced pancreatic cancer undergoing chemotherapy.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Li D, Xie K, Wolff R, Abbruzzese JL. Pancreatic cancer. Lancet. 2004;363:1049−57.
Liu L, Xu HX, Wang WQ, et al. Cavin-1 is essential for the tumor-promoting effect of caveolin-1 and enhances its prognostic potency in pancreatic cancer. Oncogene. 2014;33:2728–36.
Luo G, Long J, Zhang B, et al. Stroma and pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: an interaction loop. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012;1826:170–8.
Bardeesy N, DePinho RA. Pancreatic cancer biology and genetics. Nat Rev Cancer. 2002;2:897–909.
Long J, Luo GP, Xiao ZW, et al. Cancer statistics: current diagnosis and treatment of pancreatic cancer in Shanghai, China. Cancer Lett. 2014;346:273–7.
Neoptolemos JP, Stocken DD, Friess H, et al. A randomized trial of chemoradiotherapy and chemotherapy after resection of pancreatic cancer. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:1200–10.
Ferrone CR, Pieretti-Vanmarcke R, Bloom JP, et al. Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: long-term survival does not equal cure. Surgery. 2012;152:S43–9.
Shi S, Yao W, Xu J, Long J, Liu C, Yu X. Combinational therapy: new hope for pancreatic cancer? Cancer Lett. 2012;317:127–35.
Azab B, Bhatt VR, Phookan J, et al. Usefulness of the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in predicting short- and long-term mortality in breast cancer patients. Ann Surg Oncol. 2012;19:217–24.
Bhatti I, Peacock O, Lloyd G, Larvin M, Hall RI. Preoperative hematologic markers as independent predictors of prognosis in resected pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: neutrophil-lymphocyte versus platelet-lymphocyte ratio. Am J Surg. 2010;200:197–203.
Garcea G, Ladwa N, Neal CP, Metcalfe MS, Dennison AR, Berry DP. Preoperative neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) is associated with reduced disease-free survival following curative resection of pancreatic adenocarcinoma. World J Surg. 2011;35:868–72.
Sharaiha RZ, Halazun KJ, Mirza F, et al. Elevated preoperative neutrophil:lymphocyte ratio as a predictor of postoperative disease recurrence in esophageal cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 2011;18:3362–9.
Shimada H, Takiguchi N, Kainuma O, et al. High preoperative neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio predicts poor survival in patients with gastric cancer. Gastric Cancer. 2010;13:170–6.
Stotz M, Gerger A, Eisner F, et al. Increased neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio is a poor prognostic factor in patients with primary operable and inoperable pancreatic cancer. Br J Cancer. 2013;109:416–21.
Walsh SR, Cook EJ, Goulder F, Justin TA, Keeling NJ. Neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio as a prognostic factor in colorectal cancer. J Surg Oncol. 2005;91:181–4.
Sugiura T, Uesaka K, Kanemoto H, Mizuno T, Okamura Y. Elevated preoperative neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio as a predictor of survival after gastroenterostomy in patients with advanced pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol. 2013;20:4330–7.
Chua W, Charles KA, Baracos VE, Clarke SJ. Neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio predicts chemotherapy outcomes in patients with advanced colorectal cancer. Br J Cancer. 2011;104:1288–95.
Kao SC, Pavlakis N, Harvie R, et al. High blood neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio is an indicator of poor prognosis in malignant mesothelioma patients undergoing systemic therapy. Clin Cancer Res. 2010;16:5805–13.
Yao Y, Yuan D, Liu H, Gu X, Song Y. Pretreatment neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio is associated with response to therapy and prognosis of advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients treated with first-line platinum-based chemotherapy. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2013;62:471–9.
Lee S, Oh SY, Kim SH, et al. Prognostic significance of neutrophil lymphocyte ratio and platelet lymphocyte ratio in advanced gastric cancer patients treated with FOLFOX chemotherapy. BMC Cancer. 2013;13:350.
Edge SB, Compton CC. The American Joint Committee on Cancer: the 7th edition of the AJCC cancer staging manual and the future of TNM. Ann Surg Oncol. 2010;17:1471–4.
Ino Y, Yamazaki-Itoh R, Shimada K, et al. Immune cell infiltration as an indicator of the immune microenvironment of pancreatic cancer. Br J Cancer. 2013;108:914–23.
Fogar P, Sperti C, Basso D, et al. Decreased total lymphocyte counts in pancreatic cancer: an index of adverse outcome. Pancreas. 2006;32:22–8.
Ji H, Houghton AM, Mariani TJ, et al. K-ras activation generates an inflammatory response in lung tumors. Oncogene. 2006;25:2105–12.
Aliustaoglu M, Bilici A, Seker M, et al. The association of pre-treatment peripheral blood markers with survival in patients with pancreatic cancer. Hepatogastroenterology. 2010;57:640–5.
Luo G, Xiao Z, Long J, et al. CA125 is superior to CA19-9 in predicting the resectability of pancreatic cancer. J Gastrointest Surg. 2013;17:2092–8.
Ferrone CR, Finkelstein DM, Thayer SP, Muzikansky A, Fernandez-delCastillo C, Warshaw AL. Perioperative CA19-9 levels can predict stage and survival in patients with resectable pancreatic adenocarcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24:2897–902.
Sarraf KM, Belcher E, Raevsky E, Nicholson AG, Goldstraw P, Lim E. Neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio and its association with survival after complete resection in non-small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2009;137:425–8.
Farah R, Khamisy-Farah R. Association of neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio with presence and severity of gastritis due to Helicobacter pylori infection. J Clin Lab Anal. 2014;28:219–23.
Kaya H, Ertas F, Islamoglu Y, et al. Association between neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio and severity of coronary artery disease. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2014;20:50–4.
Sefil F, Ulutas KT, Dokuyucu R, et al. Investigation of neutrophil lymphocyte ratio and blood glucose regulation in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Int Med Res. 2014;42:581–8.
Buyukkaya E, Karakas MF, Karakas E, et al. Correlation of neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio with the presence and severity of metabolic syndrome. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2012;20:159–63.
Acknowledgment
This study was supported in part by the Sino-German Center (GZ857), by the Science Foundation of Shanghai (13ZR1407500), by the Shanghai Rising Star Program (12QH1400600, 14QA1400900), by the Fudan University Young Investigator-promoting program (20520133403), and by the National Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 81101807, No. 81001058, No. 81372649, No. 81372653, and No. 81172276).
Disclosure
The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest in this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Guopei Luo, Meng Guo and Zuqiang Liu have contributed equally to the manuscript.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Luo, G., Guo, M., Liu, Z. et al. Blood Neutrophil–Lymphocyte Ratio Predicts Survival in Patients with Advanced Pancreatic Cancer Treated with Chemotherapy. Ann Surg Oncol 22, 670–676 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-014-4021-y
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-014-4021-y