Abstract
Background
Improved resolution and utilization of screening breast imaging has increased identification of nonpalpable high-risk lesions (HRL) and subsequent excisional breast biopsies (EBBs). Wire localization (WL), used most commonly for EBBs, may have shortcomings, including wire displacement, patient discomfort, limitations with incision planning and scheduling logistics. Radioactive seed localization (RSL) may overcome these drawbacks. The purpose of this study was to compare WL and RSL for EBBs for HRLs.
Methods
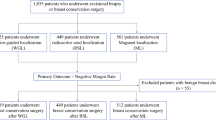
All single-site EBBs for HRL performed by four breast surgeons were retrospectively reviewed over two consecutive 1-year periods. Patients with cancer on percutaneous core biopsy (CB) were excluded. Clinicopathologic information, operative time, targeted lesion retrieval rate, and upstage rate were collected.
Results
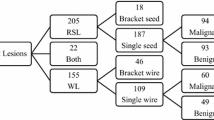
A total of 324 EBBs for HRL were performed: 196 using WL and 128 using RSL. CB pathology was atypical hyperplasia in 56 % of WLs and 62 % of RSLs. The remaining pathologies were radial scar, papilloma, atypical papilloma or lobular carcinoma in situ. Mean age was 54 years. OR time was 27 ± 8 min for WL and 27 ± 7 min for RSL (p = 0.9). Upstage rate was 6 and 5 % for WLs and RSLs, respectively (p = 0.5). Targeted lesions were retrieved in 98 % of WL and 99 % of RSL (p = 0.5). SV was 37.2 ± 32.8 cm3 and 25.7 ± 22.3 cm3 for WL and RSL, respectively (p = 0.001).
Conclusions
RSL is comparable to WL for EBB of HRLs with similar OR times and upstage rates. SV is significantly decreased with RSL and may translate into improved cosmetic outcomes without sacrificing the diagnostic accuracy of the EBB.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Garcia EM, Storm ES, Atkinson L, Kenny E, Mitchell LS. Current breast imaging modalities, advances, and impact on breast care. Obstet Gynecol Clin N Am. 2013;40(3):429–457.
White RR, Halperin TJ, Olson JA Jr, Soo MS, Bentley RC, Seigler HF. Impact of core-needle breast biopsy on the surgical management of mammographic abnormalities. Ann Surg. 2001;233(6):769–777.
Hall FM, Frank HA. Preoperative localization of nonpalpable breast lesions. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1979;132(1):101–105.
Hall FM, Kopans DB, Sadowsky NL, Homer MJ. Development of wire localization for occult breast lesions: Boston remembrances. Radiology. 2013;268(3):622–627.
Homer MJ, Pile-Spellman ER. Needle localization of occult breast lesions with a curved-end retractable wire: technique and pitfalls. Radiology. 1986;161(2):547–548.
Yagan R. Needle localization of occult breast lesions with a curved-end retractable wire: techniques and pitfalls. Radiology. 1987;163(1):284.
Hughes JH, Mason MC, Gray RJ, et al. A multi-site validation trial of radioactive seed localization as an alternative to wire localization. Breast J. 2008;14(2):153–157.
Klein RL, Mook JA, Euhus DM, et al. Evaluation of a hydrogel based breast biopsy marker (HydroMARK(R)) as an alternative to wire and radioactive seed localization for non-palpable breast lesions. J Surg Oncol. 2012;105(6):591–594.
Postma EL, Witkamp AJ, van den Bosch MA, Verkooijen HM, van Hillegersberg R. Localization of nonpalpable breast lesions. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2011;11(8):1295–1302.
Sajid MS, Parampalli U, Haider Z, Bonomi R. Comparison of radioguided occult lesion localization (ROLL) and wire localization for non-palpable breast cancers: a meta-analysis. J Surg Oncol. 2012;105(8):852–858.
Jakub JW, Gray RJ, Degnim AC, Boughey JC, Gardner M, Cox CE. Current status of radioactive seed for localization of non palpable breast lesions. Am J Surg. 2010;199(4):522–528.
Gray RJ, Salud C, Nguyen K, et al. Randomized prospective evaluation of a novel technique for biopsy or lumpectomy of nonpalpable breast lesions: radioactive seed versus wire localization. Ann Surg Oncol. 2001;8(9):711–715.
McGhan LJ, McKeever SC, Pockaj BA, et al. Radioactive seed localization for nonpalpable breast lesions: review of 1,000 consecutive procedures at a single institution. Ann Surg Oncol. 2011;18(11):3096–3101.
Alderliesten T, Loo CE, Pengel KE, Rutgers EJ, Gilhuijs KG, Vrancken Peeters MJ. Radioactive seed localization of breast lesions: an adequate localization method without seed migration. Breast J. 2011;17(6):594–601.
Barentsz MW, van den Bosch MA, Veldhuis WB, et al. Radioactive seed localization for non-palpable breast cancer. Br J Surg. 2013;100(5):582–588.
Gobardhan PD, de Wall LL, van der Laan L, et al. The role of radioactive iodine-125 seed localization in breast-conserving therapy following neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Ann Oncol. 2013;24(3):668–673.
Gray RJ, Giuliano R, Dauway EL, Cox CE, Reintgen DS. Radioguidance for nonpalpable primary lesions and sentinel lymph node(s). Am J Surg. 2001;182(4):404–406.
Lovrics PJ, Goldsmith CH, Hodgson N, et al. A multicentered, randomized, controlled trial comparing radioguided seed localization to standard wire localization for nonpalpable, invasive and in situ breast carcinomas. Ann Surg Oncol. 2011;18(12):3407–3414.
Barnes G, Jr., Matory WE. Needle localization and surgical management of occult breast lesions. J Natl Med Assoc. 1989;81(6):633–636.
Snell MJ, Ostrow LB, DuBois JJ, Boyle LM, Calfee LW. Needle-localized biopsy of occult breast lesions: an update. Mil Med. 1992;157(2):61–64.
United States Nuclear Regulatory Commission. Part 20- standards for protection against radiation. http://www.nrc.gov/reading-rm/doc-collections/cfr/part020/part020-1201.html (1991). Accessed 2 April 2014.
Rao R, Moldrem A, Sarode V, et al. Experience with seed localization for nonpalpable breast lesions in a public health care system. Ann Surg Oncol. 2010; 17(12):3241–3246.
Murphy JO, Moo TA, King TA, et al. Radioactive seed localization compared to wire localization in breast-conserving surgery: initial 6-month experience. Ann Surg Oncol. 2013;20(13):4121–4127.
Gray RJ, Pockaj BA, Karstaedt PJ, Roarke MC. Radioactive seed localization of nonpalpable breast lesions is better than wire localization. Am J Surg. 2004;188(4):377.
Acknowledgment
The authors thank Cindy Steiner, MS, Medical Health Physicists, Radiation Safety Office, University of Pittsburgh and Michael Sheetz, MS, CHP, DABMP, Radiation Safety Officer, Clinical Assistant Professor of Radiology, University of Pittsburgh, for their data on radiation exposure for the surgeons.
Disclosure
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Diego, E.J., Soran, A., McGuire, K.P. et al. Localizing High-Risk Lesions for Excisional Breast Biopsy: A Comparison Between Radioactive Seed Localization and Wire Localization. Ann Surg Oncol 21, 3268–3272 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-014-3912-2
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-014-3912-2