Abstract
Purpose
This study was designed to assess the efficacy and morbidity of the endoscopic endonasal approach for the treatment of sinonasal adenocarcinomas.
Methods
This was a retrospective, multicenter study of nine French tertiary referral centers, including untreated patients. All patients were operated by an endoscopic approach. Tumors were classified according to the UICC 2002. Demographic, therapeutic, histological, morbidity data, and the course of the disease were recorded. Survival rates were obtained using the Kaplan-Meier method.
Results
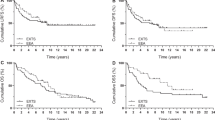
A total of 159 patients were included with a mean age of 69 years. There were 19T1, 62T2 (1M1), 36T3 (1N1), 26T4a, and 16T4b (1N2a-1N2c). The mean duration of hospitalization was 4.4 days. The histologic outcomes showed that the olfactory cleft, the posterior and anterior ethmoid sinus, and the sphenoid, maxillary, and frontal sinuses were invaded in 95, 64, 55, 19, 7, and 3 % of cases, respectively. Histologic margins were positive in 17 % (1T1, 4T2, 3T3, 2T4a, and 8T4b). In total, 130 patients received adjuvant radiotherapy on the primary tumor site (58 Gy), 24 cases were not irradiated, and 5 refused treatment. The mean follow-up was 32.5 ± 24 months. The complication rate was 19 %: 6 epistaxis, 3 meningitis, 6 CSF leaks, 2 dacryocystitis, and 8 septoplasties. The recurrence rate was 17.6 % (28 cases) within 23 ± 21 months. Eleven patients underwent a second surgical procedure. Nine patients died of their disease (3T2, 2T3, 4T4b). The global and disease-specific, recurrence-free survival rate at 3 years was 74 and 84 % respectively.
Conclusions
The endoscopic approach seems to be efficient to remove sinonasal adenocarcinoma with low morbidity.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Choussy O, Ferron C, Vedrine PO, et al. Role of radiotherapy in the treatment of nasoethmoidal adenocarcinoma. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2010;136:143–6.
Choussy O, Ferron C, Vedrine PO, et al. Adenocarcinoma of Ethmoid: a GETTEC retrospective multicenter study of 418 cases. Laryngoscope. 2008;118:437–43.
de Gabory L, Maunoury A, Maurice-Tison S, Abdulkhaleq MH, Darrouzet V, Bebear JP, Stoll D, et al. Long-term single-center results of management of ethmoid adenocarcinoma: 95 patients over 28 years. Ann Surg Oncol. 2010;17:1127–34.
Lund VJ, Chisholm EJ, Takes RP, et al. Evidence for treatment strategies in sinonasal adenocarcinoma. Head Neck. 2012;34:1168–78.
Carta F, Kania R, Sauvaget E, Bresson D, George B, Herman P. Endoscopy skull-base resection for ethmoid adenocarcinoma and olfactory neuroblastoma. Rhinology. 2011;49:74–9.
Hanna E, DeMonte F, Ibrahim S, Roberts D, Levine N, Kupferman M. Endoscopic resection of sinonasal cancers with and without craniotomy: oncologic results. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2009;135:1219–24.
Lund V, Howard DJ, Wei WI. Endoscopic resection of malignant tumors of the nose and sinuses. Am J Rhinol. 2007;21:89–94.
Vergez S, Nadeau SH, Percodani J, Pessey JJ, Serrano E. Endoscopic resection of sinonasal adenocarcinomas. Rev Laryngol Otol Rhinol (Bord). 2009;130:255–9.
Lund VJ, Stammberger H, Nicolai P, et al. European position paper on endoscopic management of tumours of the nose, paranasal sinuses and skull base. Rhinol Suppl. 2010(22):1–143.
Cohen MA, Liang J, Cohen IJ, Grady MS, O’Malley BW Jr, Newman JG. Endoscopic resection of advanced anterior skull base lesions: oncologically safe? ORL J Otorhinolaryngol Relat Spec. 2009;71:123–8.
Van Gerven L, Jorissen M, Nuyts S, Hermans R, Vander Poorten V. Long-term follow-up of 44 patients with adenocarcinoma of the nasal cavity and sinuses primarily treated with endoscopic resection followed by radiotherapy. Head Neck. 2011;33:898–904.
UICC. Paranasal sinus. In: Sobin LH, Wittekind Ch, editors. TNM classification of malignant tumors. 6th ed. New York: Springer; 2002.
French Guidelines for sino-nasal malignant tumors. French expert web of rare ENT cancers. www.orlfrance.org/refcor/RefcorSINUS.pdf. Accessed 2 July 2013.
Nicolai P, Villaret AB, Bottazzoli M, Rossi E, Valsecchi MG. Ethmoid adenocarcinoma from craniofacial to endoscopic resections: a single institution experience over 25 years. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2011;145(2):330–7.
Nicolai P, Battaglia P, Bignami M, et al. Endoscopic surgery for malignant tumors of the sinonasal tract and adjacent skull base: a 10-year experience. Am J Rhinol. 2008;22:308–16.
Goffart Y, Jorissen M, Daele J, et al. Minimally invasive endoscopic management of malignant sinonasal tumours. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Belg. 2000;54(2):221–32.
Jankowski R, Georgel T, Vignaud JM, et al. Endoscopic surgery reveals that woodworkers’ adenocarcinomas originate in the olfactory cleft. Rhinology. 2007;45:308–14.
de Gabory L, Darrouzet V, Stoll D. Morbidity assessment of degloving after sino-nasal tumor treatment: à propos of 170 cases. In Rapport du XXXVIIIeme French Head Neck Surgery Society Congress, Ed. EDK, Paris 2006. p. 179–89.
Vergez S, Martin-Dupont N, Lepage B, De Bonnecaze G, Decotte A, Serrano E. Endoscopic vs. transfacial resection of sinonasal adenocarcinomas. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2012;146:848–53.
Ganly I, Patel SG, Singh B, Kraus DH, Bridger PG, Cantu G, et al. Complications of craniofacial resection for malignant tumors of the skull base: report of an International Collaborative Study. Head Neck. 2005;27:445–51.
Ganly I, Patel SG, Singh B, Kraus DH, Bridger PG, Cantu G, et al. Craniofacial resection for malignant paranasal sinus tumors: Report of an International Collaborative Study. Head Neck. 2005;27:575–84.
Bernard P, Biller H, Lawson W, LeBenger J. Complications following rhinotomy. Review of 148 patients. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1989;98(9):684–92.
Mertz JS, Pearson BW, Kern EB. Lateral rhinotomy. Indications, technique, and review of 226 patients. Arch Otolaryngol. 1983;109(4):235–9.
Acknowledgment
The authors thank Dr. Ray Cooke for linguistic assistance and Dr Antoine Benard for statistic analysis.
Financial support and conflict of interest
The authors have received no financial support and have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vergez, S., du Mayne, M.D., Coste, A. et al. Multicenter Study to Assess Endoscopic Resection of 159 Sinonasal Adenocarcinomas. Ann Surg Oncol 21, 1384–1390 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-013-3385-8
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-013-3385-8