Abstract
Background
It is estimated that 37 % of the U.S. population is obese. It is unknown how obesity influences the operative and survival outcomes of cytoreductive surgery (CRS)/hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy (HIPEC) procedures.
Methods
A retrospective analysis of a prospective database of 1,000 procedures was performed. Type of malignancy, performance status, resection status, hospital and intensive care unit stay, comorbidities, morbidity, mortality, and survival were reviewed.
Results
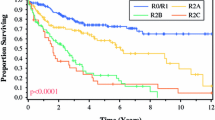
A total of 246 patients with body mass index (BMI) of >30 kg/m2 underwent 272 CRS/HIPEC procedures. Ninety-five (38.6 %) were severely obese (BMI > 35 kg/m2). A total of 135 (49.6 %) procedures were performed for appendiceal and 60 (22.1 %) for colon cancer. Median follow-up was 52 months. Both major and minor morbidity were similar for obese and non-obese patients. The 30-day mortality rates for obese and non-obese patients were 1.5 and 2.5 %, respectively. Median intensive care unit and hospital stay were 1 and 9 days, regardless of BMI. The 30-day readmission rate was similar between obese and non-obese patients (24.8 vs. 19.4 %, p = 0.11). Median survival for low-grade appendiceal cancer (LGA) was 76 months for obese patients and 107 months for non-obese patients (p = 0.32). Survival was worse for severely obese patients (median survival 54 months) versus non-obese patients with LGA (p = 0.04). Survival was similar for obese and non-obese patients with peritoneal surface disease (PSD) from colon cancer or high-grade appendiceal cancer.
Conclusions
Obesity does not influence postoperative morbidity or mortality of patients with PSD, regardless of primary tumor. Severe obesity is associated with decreased long-term survival only in patients with LGA primary disease; however, application of CRS/HIPEC still offers meaningful prolongation of life. Obesity should not be considered a contraindication for CRS/HIPEC procedures.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Olsen CM, Nagle CM, Whiteman DC, Purdie DM, Green AC, Webb PM. Body size and risk of epithelial ovarian and related cancers: a population-based case-control study. Int J Cancer. 2008;123:450–6.
Renehan AG, Roberts DL, Dive C. Obesity and cancer: pathophysiological and biological mechanisms. Arch Physiol Biochem. 2008;114:71–83.
Renehan AG, Tyson M, Egger M, Heller RF, Zwahlen M. Body-mass index and incidence of cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective observational studies. Lancet. 2008;371:569–78.
Ogden CL, Yanovski SZ, Carroll MD, Flegal KM. The epidemiology of obesity. Gastroenterology. 2007;132:2087–102.
Ogden CL, Carroll MD, Kit BK, Flegal KM. Prevalence of obesity in the United States, 2009–2010. NCHS Data Brief. 2012;82:1–8.
Chua TC, Moran BJ, Sugarbaker PH, et al. Early- and long-term outcome data of patients with pseudomyxoma peritonei from appendiceal origin treated by a strategy of cytoreductive surgery and hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy. J Clin Oncol. 2012;30:2449–56.
Elias D, Gilly F, Boutitie F, et al. Peritoneal colorectal carcinomatosis treated with surgery and perioperative intraperitoneal chemotherapy: retrospective analysis of 523 patients from a multicentric French study. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28:63–8.
Goere D, Malka D, Tzanis D, et al. Is there a possibility of a cure in patients with colorectal peritoneal carcinomatosis amenable to complete cytoreductive surgery and intraperitoneal chemotherapy? Ann Surg. 2013;257:1065–71.
Glehen O, Gilly FN, Boutitie F, et al. Toward curative treatment of peritoneal carcinomatosis from nonovarian origin by cytoreductive surgery combined with perioperative intraperitoneal chemotherapy: a multi-institutional study of 1,290 patients. Cancer. 2010;116:5608–18.
Levine EA, Stewart JH, Russell GB, Geisinger KR, Loggie BL, Shen P. Cytoreductive surgery and intraperitoneal hyperthermic chemotherapy for peritoneal surface malignancy: experience with 501 procedures. J Am Coll Surg. 2007;204:943–53.
Obesity: preventing and managing the global epidemic. Report of a WHO consultation. WHO Technical Report Series 894. 2000;894:1–253.
Shen P, Stewart JH, Levine EA. Cytoreductive surgery and hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy for peritoneal surface malignancy: overview and rationale. Curr Probl Cancer. 2009;33:125–41.
Dindo D, Demartines N, Clavien PA. Classification of surgical complications: a new proposal with evaluation in a cohort of 6336 patients and results of a survey. Ann Surg. 2004;240:205–13.
Dindo D, Muller MK, Weber M, Clavien PA. Obesity in general elective surgery. Lancet. 2003;361:2032–5.
Mullen JT, Moorman DW, Davenport DL. The obesity paradox: body mass index and outcomes in patients undergoing nonbariatric general surgery. Ann Surg. 2009;250:166–72.
Campbell PT, Newton CC, Dehal AN, Jacobs EJ, Patel AV, Gapstur SM. Impact of body mass index on survival after colorectal cancer diagnosis: the cancer prevention study-II nutrition cohort. J Clin Oncol. 2012;30:42–52.
Flegal KM, Kit BK, Orpana H, Graubard BI. Association of all-cause mortality with overweight and obesity using standard body mass index categories: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA. 2013;309:71–82.
Disclosure
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Votanopoulos, K.I., Swords, D.S., Swett, K.R. et al. Obesity and Peritoneal Surface Disease: Outcomes after Cytoreductive Surgery with Hyperthermic Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy for Appendiceal and Colon Primary Tumors. Ann Surg Oncol 20, 3899–3904 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-013-3087-2
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-013-3087-2